Recombinant Human SPARC Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Ala18-Ile303, with a C-terminal 10-His tag
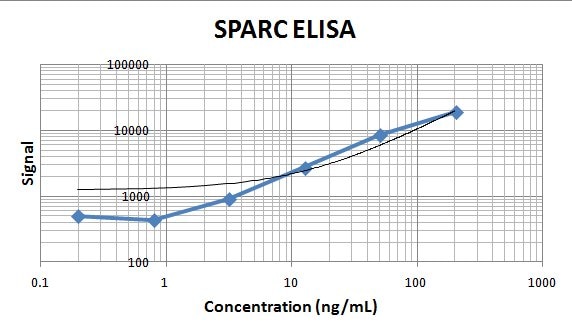
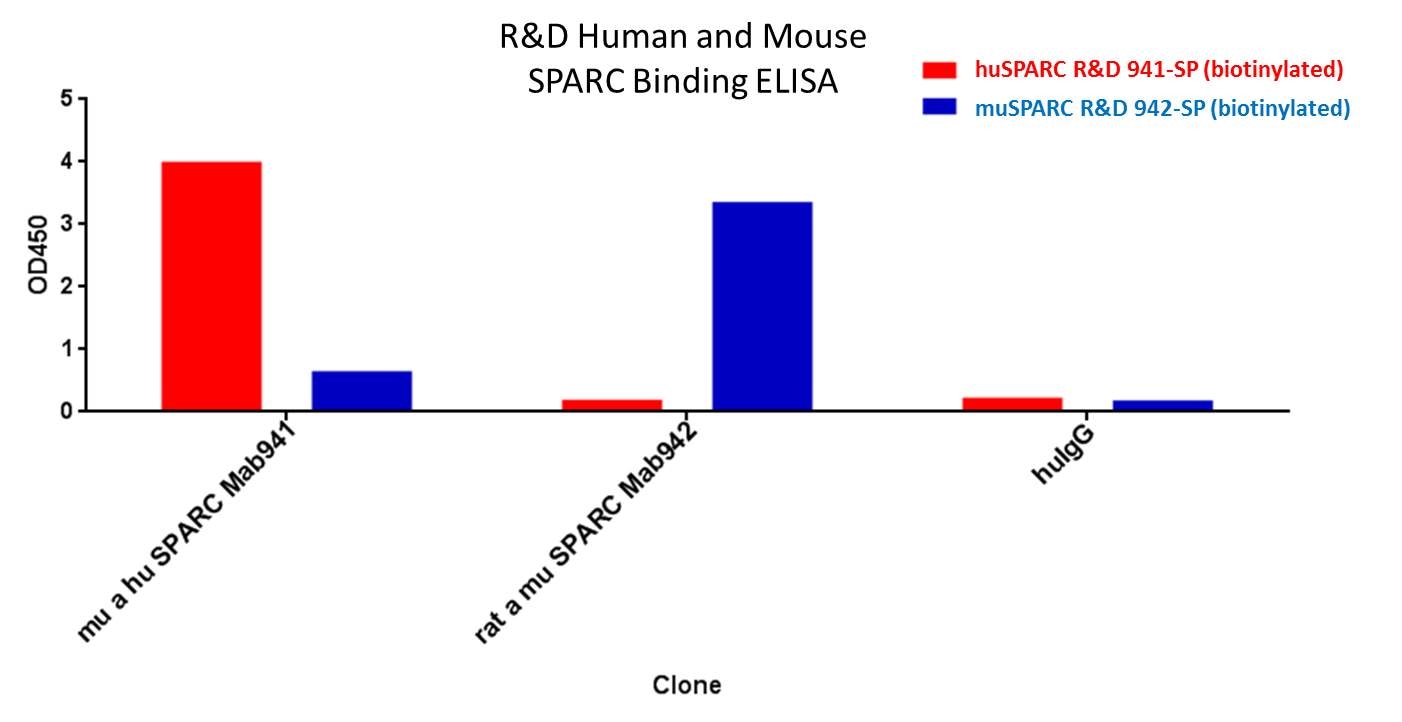
Analysis
Product Datasheets
941-SP
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
941-SP
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: SPARC
SPARC, an acronym for “secreted protein, acidic and rich in cysteine”, is also known as osteonectin or BM-40 (1-5). It is the founding member of a family of secreted matricellular proteins with similar domain structure. The 286 amino acid (aa), 43 kDa protein contains an N-terminal acidic region that binds calcium, a follistatin domain that contains Kazal-like sequences, and a C-terminal extracellular calcium (EC) binding domain with two EF-hand motifs (1-5). Crystal structure modeling shows that residues implicated in cell binding, inhibition of cell spreading, and disassembly of focal adhesions cluster on one face of SPARC, while a collagen binding epitope and an N-glycosylation site are opposite this face (6). SPARC is produced by fibroblasts, capillary endothelial cells, platelets and macrophages, especially in areas of tissue morphogenesis and remodeling (3, 7). SPARC shows context-specific effects, but generally inhibits adhesion, spreading and proliferation, and promotes collagen matrix formation (3-5). For endothelial cells, SPARC disrupts focal adhesions and binds and sequesters PDGF and VEGF (3-5). SPARC is abundantly expressed in bone, where it promotes osteoblast differentiation and inhibits adipogenesis (5, 8). SPARC is potentially cleaved by metalloproteinases, producing an angiogenic peptide that includes the copper-binding sequence KGHK (7). Paradoxically, SPARC is highly expressed in many tumor types undergoing an endothelial to mesenchymal transistion; its expression, however, mainly decreases the likelihood of metastasis and confers sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiation (4, 9-11). Stabilin-1, which is expressed on alternately activated macrophages, is the first SPARC receptor to be identified. It binds the SPARC EC domain and mediates endocytosis for degradation (12). Mature human SPARC shows 92%, 92%, 97%, 99%, 96% and 85% aa identity with mouse, rat, canine, bovine, porcine and chick SPARC, respectively.
- Lankat-Buttgereit, B. et al. (1988) FEBS Lett. 236:352.
- Sweetwyne, M. T. et al. (2004) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 52:723.
- Sage, H. et al. (1989) J. Cell Biol. 109:341.
- Framson, P. E. and E. H. Sage (2004) J. Cell. Biochem. 92:679.
- Alford, A. I. and K. D. Hankenson (2006) Bone 38:749.
- Hohenester, E et al. (1997) EMBO J. 16:3778.
- Sage, E. H. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:37849.
- Delany, A. M. et al. (2003) Endocrinology 144:2588.
- Robert, G. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66:7516.
- Koblinski, J. E. et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65:7370.
- Tai, I. T. et al. (2005) J. Clin. Invest. 115:1492.
- Kzhyshkowska, J. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 176:5825.
Citations for Recombinant Human SPARC Protein, CF
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
7
Citations: Showing 1 - 7
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
SPARC Aggravates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption via Integrin alphaVbeta3/MAPKs/MMP-9 Signaling Pathway after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Authors: T Okada, H Suzuki, ZD Travis, O Altay, J Tang, JH Zhang
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021-11-11;2021(0):9739977.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: In Vivo -
Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine (SPARC) Enhances Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition, and SPARC Expression is Associated with Tumor Grade in Head and Neck Cancer.
Authors: Chih-Hau Chang, Meng-Chi Yen, Ssu-Hui Liao, Yu-Ling Hsu, Chung-Sheng Lai, Kao-Ping Chang, Ya-Ling Hsu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017-07-18;0(0):1422-0067.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
SPARC expression by cerebral microvascular endothelial cells in vitro and its influence on blood-brain barrier properties
J Neuroinflammation, 2016-08-31;13(1):225.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Collagen signaling enhances tumor progression after anti-VEGF therapy in a murine model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Authors: Aguilera K, Rivera L, Hur H, Carbon J, Toombs J, Goldstein C, Dellinger M, Castrillon D, Brekken R
Cancer Res, 2013-12-17;74(4):1032-44.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Protein
Applications: ELISA Developmet -
SPARC expression in CML is associated to imatinib treatment and to inhibition of leukemia cell proliferation.
Authors: Giallongo C, La Cava P, Tibullo D, Barbagallo I, Parrinello N, Cupri A, Stagno F, Consoli C, Chiarenza A, Palumbo G, Di Raimondo F
BMC Cancer, 2013-02-05;13(0):60.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
SMOC1 is a tenascin-C interacting protein over-expressed in brain tumors.
Authors: Brellier F, Ruggiero S, Zwolanek D, Martina E, Hess D, Brown-Luedi M, Hartmann U, Koch M, Merlo A, Lino M, Chiquet-Ehrismann R
Matrix Biol., 2011-02-21;30(3):225-33.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Recombinant Protein
Applications: Surface Plasmon Resonance -
Dynamic interaction networks in a hierarchically organized tissue.
Authors: Kirouac DC, Ito C, Csaszar E, Roch A, Yu M, Sykes EA, Bader GD, Zandstra PW
Mol. Syst. Biol., 2010-10-05;6(0):417.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human SPARC Protein, CF
Average Rating: 4.5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Recombinant Human SPARC Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: