Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Protein, CF
Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
| Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP-1 (Gln24-Lys265) Accession # NP_001035118.1 | IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
Analysis
Gln24, blocked, deduced from Lys25 upon deblocking
Product Datasheets
10406-EP
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
10406-EP
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
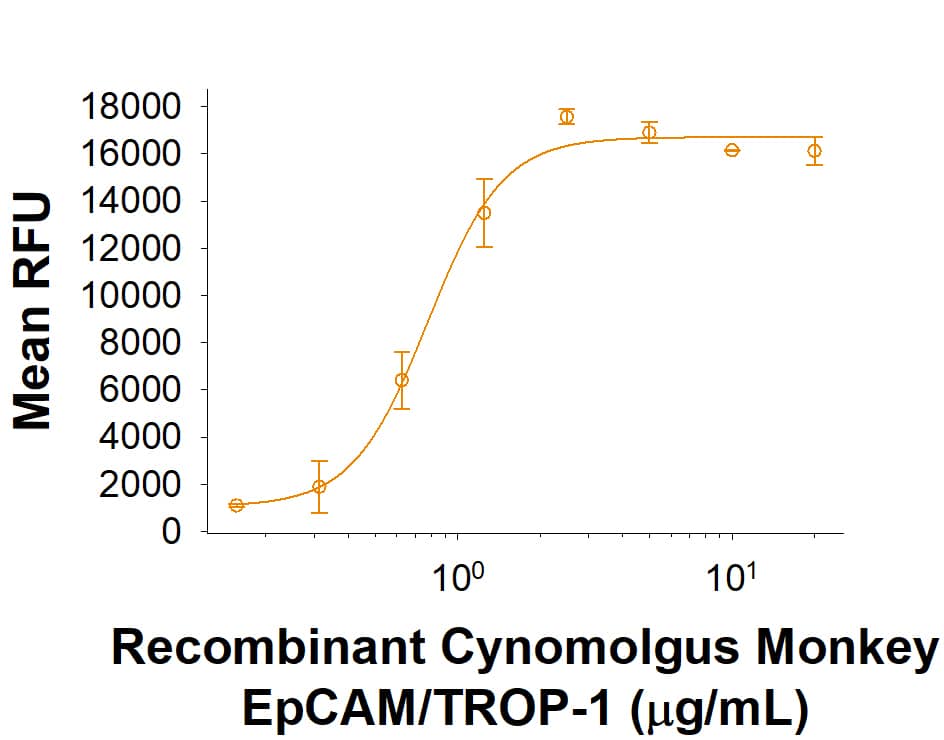
Immobilized Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP-1 His-tag protein (Catalog # 10406-EP) supports the adhesion of L Cells mouse fibroblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.3-1.8 μg/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
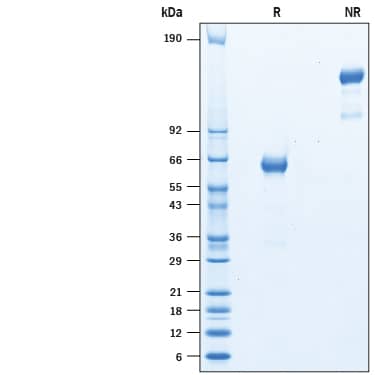
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP-1 His-tag (Catalog # 10406-EP) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 60-66 kDa and 120-150 kDa, respectively.
Background: EpCAM/TROP1
Epithelial Cellular Adhesion Molecule (EpCAM), also known as KS1/4, gp40, GA733-2, 17-1A, and TROP-1, is a 40 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein. Based on its similarity with human EpCAM, Cynomolgus EpCAM is predicted to consist of a 242 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain with two epidermal growth factor like (EGF like) repeats within the cysteine rich N-terminal region, a 23 aa transmembrane domain, and a 26 aa cytoplasmic domain. Cynomolgus and human EpCAM share 93% aa sequence identity (1). During embryonic development, EpCAM is detected in fetal lung, kidney, liver, pancreas, skin, and germ cells. In adults, human EpCAM is expressed on basolateral cell membranes of all simple, pseudo-stratified, and transitional epithelia but not on normal squamous stratified epithelia, mesenchymal tissue, muscular tissue, neuro-endocrine tissue, or lymphoid tissue (2). It is additionally expressed on undifferentiated embryonic stem cells, thymocytes, and dendritic cells (3-5). It is up-regulated on actively proliferating epithelial tissues, during adult liver regeneration, and on many epithelial cell-derived carcinomas (2, 6). EpCAM functions as a homophilic cell adhesion molecule (7). It associates into tetramers and forms complexes in cis with Claudin-7, CD44v6, TSPAN8, CD9, Integrin alpha 3, and Annexin A1 (8-11) that can interfere with cell adhesion (12, 13). Proteolytic cleavage of EpCAM releases multiple fragments from the ECD as well as a cytoplasmic fragment that can regulate gene transcription (14-16).
- Strnad, J. et al. (1989) Cancer Res. 49:314.
- Schnell, U. et al. (2013) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1828:1989.
- Ng, V.Y. et al. (2010) Stem Cells 28:29.
- Nelson, A.J. et al. (1996) Eur. J. Immunol. 26:401.
- Borkowski, T.A. et al. (1996) Eur. J. Immunol. 26:110.
- de Boer, C.J. et al. (1999) J. Pathol. 188:201.
- Litvinov, S.V. et al. (1994) J. Cell Biol. 125:437.
- Balzar, M. et al. (2001) Mol. Cell. Biol. 21:2570.
- Nubel, T. et al. (2009) Mol. Cancer Res. 7:285.
- Kuhn, S. et al. (2007) Mol. Cancer Res. 5:553.
- Schmidt, D.S. et al. (2004) Exp. Cell Res. 297:329.
- Litvinov, S.V. et al. (1997) J. Cell Biol. 139:1337.
- Gaiser, M.R. et al. (2012) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109:E889.
- Schnell, U. et al. (2013) Biosci. Rep. 33:e00030.
- Schon, M.P. et al. (1993) Int. J. Cancer 55:988.
- Maetzel, D. et al. (2009) Nat. Cell Biol. 11:162.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EpCAM/TROP1 Fc Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image


