Rat TNF-alpha Antibody Summary
Accession # P16599
Applications
Rat TNF-alpha Sandwich Immunoassay
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
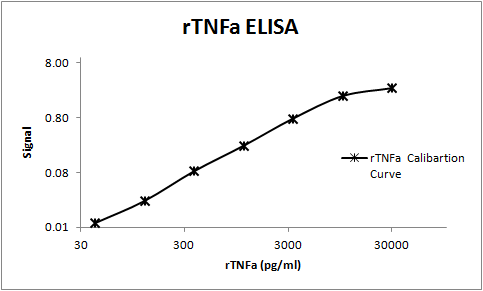
 View Larger
View Larger
Cytotoxicity Induced by TNF‑ alpha and Neutralization by Rat TNF‑ alpha Antibody. Recombinant Rat TNF‑a (Catalog # 510-RT) induces cytotoxicity in the the L‑929 mouse fibroblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line), as measured by crystal violet staining. Cytotoxicity elicited by Recombinant Rat TNF‑a (0.025 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Rat TNF‑a Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB510). The ND50 is typically 10-40 µg/mL in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D (1 µg/mL).
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Rat TNF-alpha by Block/Neutralize IL-10 receptors expressed on hippocampal neurons.(A) Expression of IL-10 receptor mRNAs in hippocampal neurons. The expression of the IL-10 receptor was identified using RT-PCR. The mRNAs of IL-10 receptor alpha and beta were expressed in the hippocampal neurons. IL-10 receptor alpha was expressed mainly in hippocampal neurons of DIV 7. (1, cultured hippocampal neurons at DIV 7; 2, cultured hippocampal neurons at DIV 15; 3, mixed glial culture at DIV 7; 4, mixed glial culture at DIV 15; 5, microglia) Quantification (DIV 15 neuron/ DIV 7 neuron): IL-10 receptor alpha, 0.61; IL-10 receptor beta, 1.06. (B) Expression of IL-10 receptor proteins in cultured hippocampal neurons. Similar to the expression of mRNA, the IL-10 receptor alpha protein was expressed mainly in neurons of DIV 7. Anti-IL-10 receptor alpha antibodies (0.5 μg/ml, Santa Cruz, sc-985) were used for western blotting [27]. Quantification (DIV 15 neuron/ DIV 7 neurons): IL-10 receptor alpha, 0.73.(C) Expression of IL-10 receptor proteins in the developing rat brains. The IL-10 receptor alpha proteins were expressed mainly in the developing brains of embryonic and early postnatal days (E18~P3). Quantification of IL-10 receptor alpha : E18, 0.30; P1, 0.27; P3, 1.0; P7, 0.22; P14, 0.20; P3W, 0.17; P6W, 0.15 (E, embryonic days; P, postnatal days).(D) Images of IL-10 receptor expressions in cultured hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal neurons of DIV 6 were stained with antibodies of IL-10 receptor alpha (5 μg/ml, Santa Cruz, sc-985) (red) and MAP2 (the neuronal marker, green) after treatment with 4% formaldehyde and then -20 °C methanol. Hippocampal neurons expressed IL-10 receptor proteins comparable to spinal neurons or cortical neurons.(E) The induction of synaptic formation by microglia was antagonized by the neutralizing antibody of IL-10 receptor alpha. When anti-mouse IL-10 receptor alpha antibody was applied to the co-culture of mouse microglia and mouse hippocampal neurons, the density of dendritic spines was significantly decreased compared with the control (without anti-IL-10 receptor antibody). Means±SEM. n=30 dendrites for no microglia without anti-IL-10 receptor antibody, 29 for the application of microglia only, 29 for no microglia with anti-IL-10 receptor antibody only, 29 for microglia with anti-IL-10 receptor antibody. ***p<0.001 by the Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test after application of one-way ANOVA, F=17.35, p<0.0001.(F) The induction of synaptic formation via microglia was not antagonized by the blocking antibody of TNF alpha. When anti-rat TNF alpha antibody was applied to the co-culture of rat microglia and rat hippocampal neurons, the density of dendritic spine was not decreased compared with control (without anti-TNF alpha antibody). Means±SEM. n=27 dendrites for no microglia without anti-TNF alpha antibody, 28 for the application of microglia only, 29 for no microglia with anti-TNF alpha receptor antibody only, 27 for microglia with anti-TNF alpha antibody. **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 by the Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test after application of one-way ANOVA, F=9.104, p<0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24278397), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: TNF-alpha
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-alpha ) also known as Cachectin, is the prototypic ligand of the TNF superfamily. It is a pleiotropic molecule that plays a central role in inflammation, apoptosis, and immune system development. TNF-alpha is produced by a wide variety of immune and epithelial cell types (1, 2). Rat TNF-alpha consisits of a 35 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 179 aa extracellular domain (ECD) (3). Within the ECD, rat TNF-alpha shares 94% aa sequence identity with mouse and 69-76% with bovine, canine, cotton rat, equine, feline, human, porcine, and rhesus macaque TNF-alpha. The 26 kDa type 2 transmembrane protein is assembled intracellularly to form a noncovalently linked homotrimer (4). Ligation of this complex induces reverse signaling that promotes lymphocyte co-stimulation but diminishes monocyte responsiveness (5). Cleavage of membrane bound TNF-alpha by TACE/ADAM17 releases a 55 kDa soluble trimeric form of TNF-alpha (6, 7). TNF-alpha trimers bind the ubiquitous TNF RI and the hematopoietic cell-restricted TNF RII, both of which are also expressed as homotrimers (1, 8). TNF-alpha regulates lymphoid tissue development through control of apoptosis (2). It also promotes inflammatory responses by inducing the activation of vascular endothelial cells and macrophages (2). TNF-alpha is a key cytokine in the development of several inflammatory disorders (9). It contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes through its effects on insulin resistance and fatty acid metabolism (10, 11).
- Idriss, H.T. and J.H. Naismith (2000) Microsc. Res. Tech. 50:184.
- Hehlgans, T. and K. Pfeffer (2005) Immunology 115:1.
- Estler, H.C. et al. (1992) Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 373:271.
- Tang, P. et al. (1996) Biochemistry 35:8216.
- Eissner G. et al. (2004) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:353.
- Black, R.A. et al. (1997) Nature 385:729.
- Moss, M.L. et al. (1997) Nature 385:733.
- Loetscher, H. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:18324.
- Clark, I.A. (2007) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 18:335.
- Romanatto, T. et al. (2007) Peptides 28:1050.
- Hector, J. et al. (2007) Horm. Metab. Res. 39:250.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Rat TNF-alpha Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
19
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Hydrogen Gas Inhalation Attenuates Endothelial Glycocalyx Damage and Stabilizes Hemodynamics in a Rat Hemorrhagic Shock Model
Authors: Tomoyoshi Tamura, Motoaki Sano, Tadashi Matsuoka, Joe Yoshizawa, Ryo Yamamoto, Yoshinori Katsumata et al.
Shock
-
Renal denervation reduces atrial remodeling in hypertensive rats with metabolic syndrome
Authors: Simina-Ramona Selejan, Dominik Linz, Muriel Mauz, Mathias Hohl, Anh Khoa Dennis Huynh, Thimoteus Speer et al.
Basic Research in Cardiology
-
Spinal cord injury and its underlying mechanism in rats with temporal lobe epilepsy
Authors: Jinjie Liu, Zanhua Liu, Guoliang Liu, Kai Gao, Hengjie Zhou, Yongbo Zhao et al.
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine
-
Gabexate mesilate ameliorates the neuropathic pain in a rat model by inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide pathway via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B
Authors: Seon Hee Oh, Hyun Young Lee, Young Joon Ki, Sang Hun Kim, Kyung Joon Lim, Ki Tae Jung
The Korean Journal of Pain
-
Effects of early life stress on cocaine conditioning and AMPA receptor composition are sex-specific and driven by TNF
Authors: Prabarna Ganguly, Jennifer A. Honeycutt, June R. Rowe, Camila Demaestri, Heather C. Brenhouse
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity
-
Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 Exacerbate Neurotoxicity of Prothrombin Kringle-2 in Cortex In Vivo via Oxidative Stress
Authors: JY Jeong, YC Chung, BK Jin
Int J Mol Sci, 2019-04-19;20(8):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Ulva lactuca polysaccharides prevent Wistar rat breast carcinogenesis through the augmentation of apoptosis, enhancement of antioxidant defense system, and suppression of inflammation
Authors: GF Abd-Ellate, OM Ahmed, ES Abdel-Rehe, AZ Abdel-Hami
Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press), 2017-02-27;9(0):67-83.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Serum
Applications: ELISA Development (Capture) -
Systemic administration of an anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody protects against endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats
Authors: Qingman Ge, Shaocheng Wang, Yuezhong Zheng
Indian Journal of Ophthalmology
-
Transport patterns of anti-TNF-? in burn wounds: Therapeutic implications of hyaluronic acid conjugation
Authors: Newell R Washburn
Biomaterials, 2016-11-04;114(0):10-22.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Complex Sample Type, In Vivo
Applications: Binding Assay, IHC, In Vivo -
Beneficial Effect of Moderate Exercise in Kidney of Rat after Chronic Consumption of Cola Drinks
Authors: G Cao, J González, A Müller, G Ottaviano, G Ambrosio, JE Toblli, J Milei
PLoS ONE, 2016-03-31;11(3):e0152461.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Urban traffic-derived nanoparticulate matter reduces neurite outgrowth via TNFalpha in vitro.
Authors: Cheng H, Davis D, Hasheminassab S, Sioutas C, Morgan T, Finch C
J Neuroinflammation, 2016-01-26;13(1):19.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Neuronal synapse formation induced by microglia and interleukin 10.
Authors: Lim S, Park E, You B, Jung Y, Park A, Park S, Lee J
PLoS ONE, 2013-11-22;8(11):e81218.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Dose-dependent changes in neuroinflammatory and arachidonic acid cascade markers with synaptic marker loss in rat lipopolysaccharide infusion model of neuroinflammation.
BMC Neurosci, 2012-05-23;13(0):50.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Rat pneumonia and soft-tissue infection models for the study of Acinetobacter baumannii biology.
Authors: Russo TA, Beanan JM, Olson R, MacDonald U, Luke NR, Gill SR, Campagnari AA
Infect. Immun., 2008-06-09;76(8):3577-86.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: BALF
Applications: ELISA Development -
In vivo modulation of LPS-induced alterations in brain and peripheral cytokines and HPA axis activity by cannabinoids.
Authors: Roche M, Diamond M, Finn DP
J. Neuroimmunol., 2006-09-29;181(1):57-67.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Plasma
Applications: ELISA Development -
Oxidative mitochondrial DNA damage and deletion in hepatocytes of rejecting liver allografts in rats: role of TNF-alpha.
Authors: Nagakawa Y, Williams GM, Zheng Q, Tsuchida A, Aoki T, Montgomery RA, Klein AS, Sun Z
Hepatology, 2005-07-01;42(1):208-15.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Melatonin attenuated inflammatory reaction by inhibiting the activation of p38 and NF??B in taurocholate?induced acute pancreatitis
Authors: Y Chen, Q Zhao, Q Chen, Y Zhang, B Shao, Y Jin, J Wu
Mol Med Rep, 2018-02-16;0(0):.
-
Intravenous injection of post‑hemorrhagic shock mesenteric lymph induces multiple organ injury in rats
Authors: Yifeng Zhao, Limin Zhang, Rui Han, Yonghua Si, Zigang Zhao
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Rat TNF-alpha Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Rat TNF-alpha Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: