N-2 MAX Media Supplement (100X)
N-2 MAX Media Supplement (100X) Summary
For culturing neurons, neural progenitors, and stem cells.
Key Benefits
- Optimized for neural and stem cell cultures
- Recombinant Human Insulin ensures low experimental variability
- Consistent, chemically-defined, and serum-free formulation
- Ideal for NPC derivation, maintenance, and differentiation
- Enhances performance of stem cell differentiation protocols
Why Culture Neurons under Fully Defined Conditions?
Serum-free, defined media are routinely used as an alternative to standard serum-containing media in order to reduce unwanted experimental variability.
Uncontrolled variables commonly associated with serum-supplemented media, such as indeterminate levels of vitamins, hormones, and growth factors are eliminated, and the potential for contamination by infectious agents is reduced when cells are cultured under defined conditions. In addition, serum-free media offers researchers the ability to specifically design the culture media for a particular experimental question.
The N-2 MAX Media Supplement:
- Contains high quality factors to support reproducible and efficient NPC expansion.
- Is fully defined to reduce unwanted experimental variability.
- Has been developed and optimized using neural progenitor cells.
Contents
Supplied as a 100X concentrate in water, this media supplement contains the following high quality factors to support neural cell culture:
| Component | Amount (mg/mL) |
| Recombinant Human Insulin | 2,500 µg/mL |
| Human Transferrin | 10,000 µg/mL |
| Putrescine | 1,611 µg/mL |
| Selenite | 0.52 µg/mL |
| Progesterone | 0.63 µg/mL |
Supplied in a volume sufficient to supplement 500 mL of media at the recommended concentration.
Stability and Storage
Store in the dark at < -20 °C in a manual defrost freezer. Do not use past the expiration date.
Precautions
This product contains human transferrin. This transferrin was purified from donor plasma and tested at the donor level using an FDA licensed method and found to be non-reactive for anti-HIV-1/2 and Hepatitis B surface antigen.
Limitations
- FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES.
- The safety and efficacy of this product in diagnostic or other clinical uses has not been established.
- This reagent should not be used beyond the expiration date indicated on the label.
Specifications
Product Datasheets
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
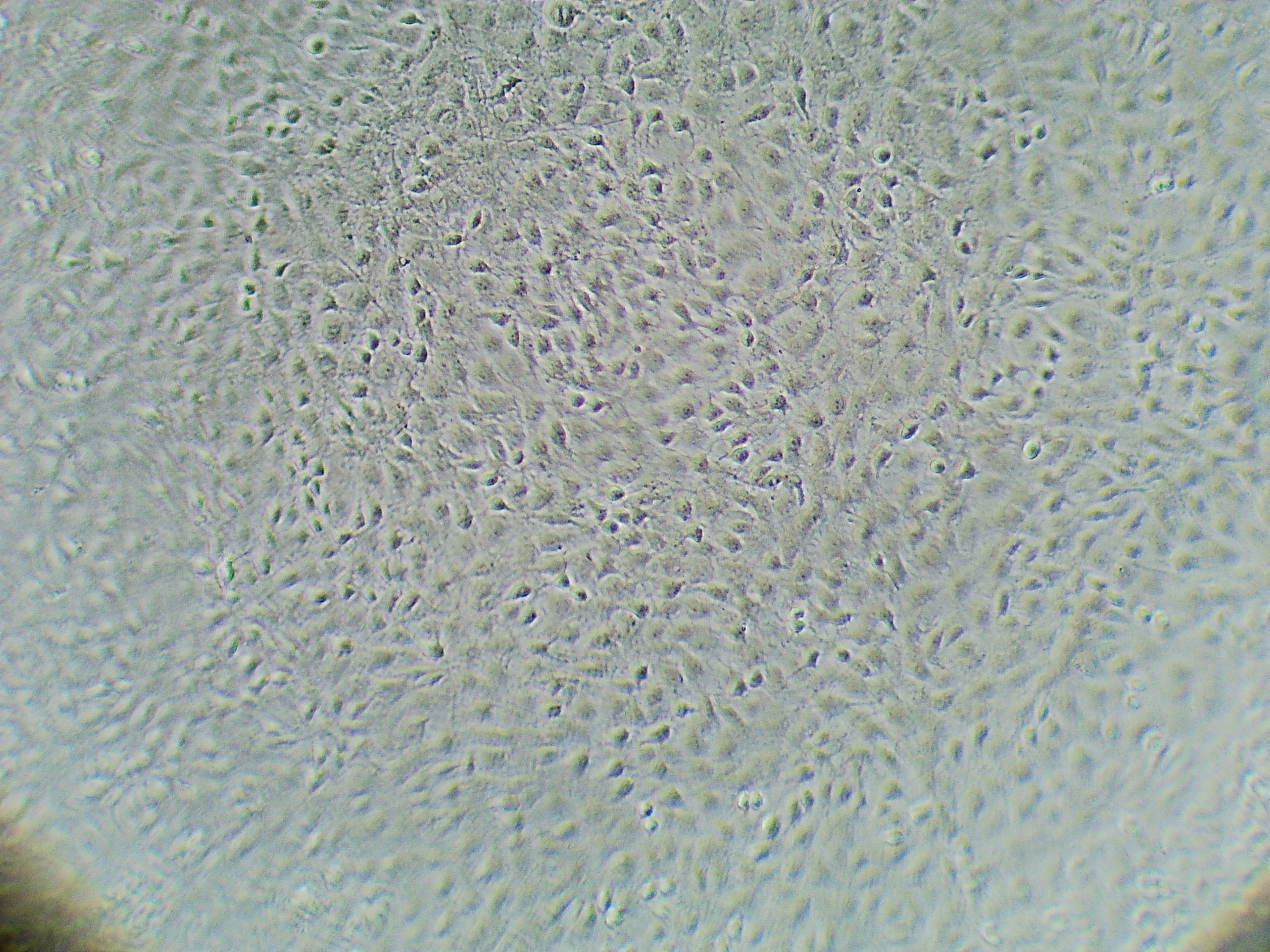
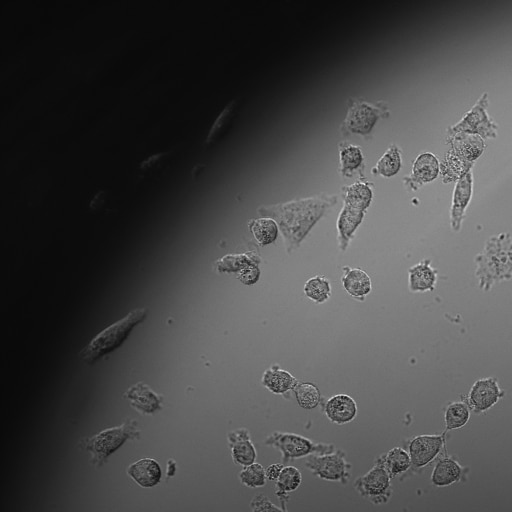
Neural Progenitor Cells Expanded with N-2 MAX Media Supplement Express Nestin and SOX2. Neural Progenitor Cells Expanded with N-2 MAX Media Supplement Express Nestin and SOX2.Rat Cortical Stem Cells (Catalog # NSC001) were cultured for 7 days in media supplemented with 1X N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR009) and 20 ng/mL of Recombinant Human FGF basic (Catalog # 233-FB). The cells were stained with a PE-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human Nestin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC1259P; red histogram), a PE-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse SOX2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC2018P; green histogram), or a PE-conjugated Mouse IgG2AIsotype Control (Catalog # IC003P; open histogram). Under these conditions, cells were shown to express high levels of Nestin and SOX2, two established markers of neural multipotency.
 View Larger
View Larger
Lot Consistency of N-2 MAX Media Supplement. Rat cortical stem cells (RCSC) were cultured over multiple passages using N-2 MAX and evaluated via flow cytometry for the maintenance of stem cell markers, SOX2 and Nestin. Quantification of flow cytometry data demonstrates a high purity of (A) SOX2 or (B) Nestin positive RCSCs across multiple lots of N-2 MAX Supplement. C) Average SOX2 and Nestin-positive RCSCs, demonstrate the consistent lot-to-lot performance of N-2 MAX.
 View Larger
View Larger
Verification of Neural Progenitor Cell Multipotency Following Expansion with N-2 MAX Media Supplement. Verification of Neural Progenitor Cell Multipotency Following Expansion with N-2 MAX Media Supplement.Rat Cortical Stem Cells (Catalog # NSC001) were grown and differentiated for 7 daysin vitroin media supplemented with N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR009). Markers of lineage differentiation were detected using a Mouse Anti-Neuron-specific beta-III Tubulin Monoclonal (clone TuJ-1) Antibody (Catalog # MAB1195), followed by a NorthernLights™(NL)557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (Catalog # NL007; red), a Sheep Anti-Human GFAP Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2594), followed by a NL557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Sheep Secondary Antibody (Catalog # NL010; red), and a Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat/Chicken Oligodendrocyte Marker O4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1326), followed by a NL 557-conjugated Goat Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (Catalog # NL019; red). The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
N-2 MAX Media Supplement is Comparable to GMP N-2 MAX. Rat Cortical Stem Cells (Catalog # NSC001) were cultured for 14 days in media supplemented with 20 ng/mL Recombinant Human FBF basic (Catalog # 233-FB) and either N-2 MAX Media Supplement or GMP N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR016). Cells were harvested and stained with PE-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human Nestin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC1259) or PE-conjugated Anti-Human/Mouse SOX2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC2018). Under these conditions, similar yields of Nestin and SOX2 positive cells were observed.
Assay Procedure
Refer to the product datasheet for complete product details.
Briefly, completed N-2 MAX-supplemented neural cell medium is prepared using the following procedure:
- Dilute the media supplement in basal media
- Store completed media
- Use within 2 weeks
Reagents provided in the N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR009):
- Recombinant Human Insulin (2,500 µg/mL)
- Human Transferrin (10,000 µg/mL)
- Putrescine (1,611 µg/mL)
- Selenite (0.52 µg/mL)
- Progesterone (0.63 µg/mL)
Reagents
- DMEM/F-12 (Invitrogen®, Catalog # 12500-062) or a basal media (e.g., Neurobasal Media from Invitrogen, Catalog # 21103-029)
- Glucose
- Glutamine
- NaHCO3
- Penicillin-Streptomycin (100X)
- Deionized or distilled water
Materials
- Serological pipettes
- Pipettes and pipette tips
- 2 µm filter unit
Equipment
- 2 °C to 8 °C refrigerator
Option 1: Mix the following components with deionized or distilled water to make 500 mL of medium.
| Component | Amount (mg/mL) |
| DMEM/F-12 | 6 g |
| Glucose | 0.775 g |
| Glutamine | 0.0365 g |
| NaHCO3 | 0.854 g |
| N-2 MAX Media Supplement | 5 mL |
Adjust the pH to 7.2. Filter the solution (2 µm filter unit), and add 5 mL of 100X sterile Penicillin-Streptomycin solution. The medium may be stored in the dark at 2 °C to 8 °C for up to 2 weeks.
Option 2: Dilute 100-fold with a basal media (e.g., Neurobasal Media from Invitrogen, Catalog # 21103-029) before use. The medium may be stored in the dark at 2 °C to 8 °C for up to 2 weeks.
Invitrogen is a registered trademark of Invitrogen Corp.
Citations for N-2 MAX Media Supplement (100X)
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
32
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Oxygen-induced stress reveals context-specific gene regulatory effects in human brain organoids
Authors: Umans, BD;Gilad, Y;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology 2024-09-03
-
Multi-Omics Profiles of Small Intestine Organoids in Reaction to Breast Milk and Different Infant Formula Preparations
Authors: Wang, X;Yang, S;Zheng, C;Huang, C;Yao, H;Guo, Z;Wu, Y;Wang, Z;Wu, Z;Ge, R;Cheng, W;Yan, Y;Jiang, S;Sun, J;Li, X;Xie, Q;Wang, H;
Nutrients 2024-09-02
-
Cooperative insulation of regulatory domains by CTCF-dependent physical insulation and promoter competition
Authors: Ealo, T;Sanchez-Gaya, V;Respuela, P;Muñoz-San Martín, M;Martin-Batista, E;Haro, E;Rada-Iglesias, A;
Nature communications 2024-08-23
-
Directed differentiation of functional corticospinal-like neurons from endogenous SOX6+/NG2+ cortical progenitors
Authors: Ozkan, A;Padmanabhan, HK;Shipman, SL;Azim, E;Kumar, P;Sadegh, C;Basak, AN;Macklis, JD;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology 2024-04-23
-
Accessible luminal interface of bovine rectal organoids generated from cryopreserved biopsy tissues
Authors: Kawasaki, M;Ambrosini, YM;
PloS one 2024-03-21
-
Interaction between estrogen receptor-? and PNPLA3 p.I148M variant drives fatty liver disease susceptibility in women
Authors: Cherubini, A;Ostadreza, M;Jamialahmadi, O;Pelusi, S;Rrapaj, E;Casirati, E;Passignani, G;Norouziesfahani, M;Sinopoli, E;Baselli, G;Meda, C;Dongiovanni, P;Dondossola, D;Youngson, N;Tourna, A;Chokshi, S;Bugianesi, E;EPIDEMIC Study Investigators, ;Della Torre, S;Prati, D;Romeo, S;Valenti, L;
Nature medicine 2023-09-25
-
OLR1 Is a Pan-Cancer Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Predictor Associated with EMT and Cuproptosis in HNSCC
Authors: Wu, L;Liu, Y;Deng, W;Wu, T;Bu, L;Chen, L;
International journal of molecular sciences 2023-08-17
-
Transcriptional metabolic reprogramming implements meiotic fate decision in mouse testicular germ cells
Authors: Zhang, X;Liu, Y;Sosa, F;Gunewardena, S;Crawford, PA;Zielen, AC;Orwig, KE;Wang, N;
Cell reports 2023-07-04
-
Targeting BRD3 eradicates nuclear TYRO3-induced colorectal cancer metastasis
Authors: PL Hsu, CW Chien, YA Tang, BW Lin, SC Lin, YS Lin, SY Chen, HS Sun, SJ Tsai
Science Advances, 2023-04-12;9(15):eade3422. 2023-04-12
-
VEGFA-modified DPSCs combined with LC-YE-PLGA NGCs promote facial nerve injury repair in rats
Authors: W Xu, X Xu, L Yao, B Xue, H Xi, X Cao, G Piao, S Lin, X Wang
Heliyon, 2023-03-28;9(4):e14626. 2023-03-28
-
Establishment of a novel in vitro co-culture system of enteric neurons and Caco-2 cells for evaluating the effect of enteric nervous system on transepithelial transport of drugs
Authors: M Maruyama, M Yoshikata, M Sakaguchi, S Wakushima, K Higaki
International journal of pharmaceutics, 2023-01-16;633(0):122617. 2023-01-16
-
Diagnostic testing of chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) by RT-QuIC using multiple tissues
Authors: KR Burgener, SS Lichtenber, A Lomax, DJ Storm, DP Walsh, JA Pedersen
PLoS ONE, 2022-11-16;17(11):e0274531. 2022-11-16
-
Midkine expression by stem-like tumor cells drives persistence to mTOR inhibition and an immune-suppressive microenvironment
Authors: Y Tang, DJ Kwiatkowsk, EP Henske
Nature Communications, 2022-08-26;13(1):5018. 2022-08-26
-
Oligodendrocyte differentiation alters tRNA modifications and codon optimality-mediated mRNA decay
Authors: S Martin, KC Allan, O Pinkard, T Sweet, PJ Tesar, J Coller
Nature Communications, 2022-08-25;13(1):5003. 2022-08-25
-
Effect of Progranulin on Proliferation and Differentiation of Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells after Oxygen/Glucose Deprivation
Authors: I Horinokita, H Hayashi, T Nagatomo, Y Fushiki, Y Iwatani, N Takagi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022-02-09;23(4):. 2022-02-09
-
3D in vitro morphogenesis of human intestinal epithelium in a gut-on-a-chip or a hybrid chip with a cell culture insert
Authors: W Shin, HJ Kim
Nature Protocols, 2022-02-02;0(0):. 2022-02-02
-
Extensive transcriptional and chromatin changes underlie astrocyte maturation in vivo and in culture
Authors: M Lattke, R Goldstone, JK Ellis, S Boeing, J Jurado-Arj, N Marichal, JI MacRae, B Berninger, F Guillemot
Nature Communications, 2021-07-15;12(1):4335. 2021-07-15
-
Aromatic-Turmerone Analogs Protect Dopaminergic Neurons in Midbrain Slice Cultures through Their Neuroprotective Activities
Authors: Y Hori, R Tsutsumi, K Nasu, A Boateng, Y Ashikari, M Sugiura, M Nakajima, Y Kurauchi, A Hisatsune, H Katsuki, T Seki
Cells, 2021-05-03;10(5):. 2021-05-03
-
Self-complementarity in adeno-associated virus enhances transduction and gene expression in mouse cochlear tissues
Authors: G Casey, C Askew, MA Brimble, RJ Samulski, AM Davidoff, C Li, BJ Walters
PLoS ONE, 2020-11-23;15(11):e0242599. 2020-11-23
-
Non-canonical Targets of HIF1a Impair Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Function
Authors: KC Allan, LR Hu, MA Scavuzzo, AR Morton, AS Gevorgyan, EF Cohn, BLL Clayton, IR Bederman, S Hung, CF Bartels, M Madhavan, PJ Tesar
Cell Stem Cell, 2020-10-21;0(0):. 2020-10-21
-
Gut microbiota maturation during early human life induces enterocyte proliferation via microbial metabolites
Authors: MW Dougherty, O Kudin, M Mühlbauer, J Neu, RZ Gharaibeh, C Jobin
BMC Microbiol., 2020-07-11;20(1):205. 2020-07-11
-
Controlling properties of human neural progenitor cells using 2D and 3D conductive polymer scaffolds
Authors: S Song, D Amores, C Chen, K McConnell, B Oh, A Poon, PM George
Sci Rep, 2019-12-20;9(1):19565. 2019-12-20
-
Oligodendrocyte Intrinsic miR-27a Controls Myelination and Remyelination
Authors: A Tripathi, C Volsko, JP Garcia, E Agirre, KC Allan, PJ Tesar, BD Trapp, G Castelo-Br, FJ Sim, R Dutta
Cell Rep, 2019-10-22;29(4):904-919.e9. 2019-10-22
-
Developmental Xist induction is mediated by enhanced splicing
Authors: C Stork, Z Li, L Lin, S Zheng
Nucleic Acids Res., 2019-02-20;0(0):. 2019-02-20
-
Neutrophils Promote Amphiregulin Production in Intestinal Epithelial Cells through TGF-? and Contribute to Intestinal Homeostasis
Authors: F Chen, W Yang, X Huang, AT Cao, AJ Bilotta, Y Xiao, M Sun, L Chen, C Ma, X Liu, CG Liu, S Yao, SM Dann, Z Liu, Y Cong
J. Immunol., 2018-08-31;0(0):. 2018-08-31
-
Accumulation of 8,9-unsaturated sterols drives oligodendrocyte formation and remyelination
Authors: Z Hubler, D Allimuthu, I Bederman, MS Elitt, M Madhavan, KC Allan, HE Shick, E Garrison, M T Karl, DC Factor, ZS Nevin, JL Sax, MA Thompson, Y Fedorov, J Jin, WK Wilson, M Giera, F Bracher, RH Miller, PJ Tesar, DJ Adams
Nature, 2018-07-25;0(0):. 2018-07-25
-
Isolation and characterization of string-forming female germline stem cells from ovaries of neonatal mice
Authors: J Liu, D Shang, Y Xiao, P Zhong, H Cheng, R Zhou
J. Biol. Chem., 2017-08-21;0(0):. 2017-08-21
-
Modeling the Mutational and Phenotypic Landscapes of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease with Human iPSC-Derived Oligodendrocytes
Authors: ZS Nevin, DC Factor, RT Karl, P Douvaras, J Laukka, MS Windrem, SA Goldman, V Fossati, GM Hobson, PJ Tesar
Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2017-03-30;100(4):617-634. 2017-03-30
-
Isolation, expansion and neural differentiation of stem cells from human plucked hair: a further step towards autologous nerve recovery
Authors: Margriet A Huisman
Cytotechnology, 2015-12-24;68(5):1849-58. 2015-12-24
-
Isolation, characterization and propagation of mitotically active germ cells from adult mouse and human ovaries.
Authors: Woods D, Tilly J
Nat Protoc, 2013-04-18;8(5):966-88. 2013-04-18
-
Transcription factor-mediated reprogramming of fibroblasts to expandable, myelinogenic oligodendrocyte progenitor cells.
Authors: Najm, Fadi J, Lager, Angela M, Zaremba, Anita, Wyatt, Krysta, Caprariello, Andrew V, Factor, Daniel C, Karl, Robert T, Maeda, Tadao, Miller, Robert H, Tesar, Paul J
Nat Biotechnol, 2013-04-14;31(5):426-33. 2013-04-14
-
The helicase HAGE expressed by malignant melanoma-initiating cells is required for tumor cell proliferation in vivo.
Authors: Linley AJ, Mathieu MG, Miles AK
J. Biol. Chem., 2012-03-05;287(17):13633-43. 2012-03-05
FAQs
-
What is the difference between N-2 Plus Media Supplement (Catalog # AR003) and N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR009)?
The N-2 Plus Media Supplement (Catalog # AR003) contains Bovine Insulin whereas N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR009) contains Recombinant Human Insulin. All other media components and concentrations in N-2 Plus and N-2 MAX are the same. These two products perform comparably in side-by-side testing. Due to a limited supply of bovine insulin, the products are priced differently.
-
Does N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR009) contain any components that are calcium salts?
- No.
-
Does N-2 MAX Media Supplement (Catalog # AR009) contain any proteins that are produced using Baculovirus?
- No.
-
an the N-2 MAX Media Supplement be stored frozen as 1 mL aliquots?
Yes. The N-2 MAX Media Supplement may be stored frozen as 1 mL aliquots. The frozen aliquots should not undergo multiple freeze-thaws before use.
-
Does the N-2 MAX Media Supplement contain any animal-derived components other than Human Transferrin?
No. The N-2 MAX Media Supplement does not contain any animal-derived components other than Human Transferrin. GMP N-2 MAX Media Supplement is an animal-free supplement (Catalog # AR016).
-
How many freeze/thaw cycles can N-2 MAX Media Supplement (100X), Catalog # AR009, undergo?
The N-2 MAX Media Supplement should be able to undergo one freeze/thaw cycyle as long as the product is used witin the expiration date.
-
How do you recommend thawing this media supplement prior to use?
We recommend thawing the product overnight at 2-8 °C, or on the benchtop at room temperature with gently mixing and monitoring until it has fully thawed, prior to use or preparing any single-use aliquots.
Reviews for N-2 MAX Media Supplement (100X)
Average Rating: 4.8 (Based on 13 Reviews)
Have you used N-2 MAX Media Supplement (100X)?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: