Mouse NKp46/NCR1 Biotinylated Antibody Summary
Glu22-Asn255
Accession # Q8C567
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
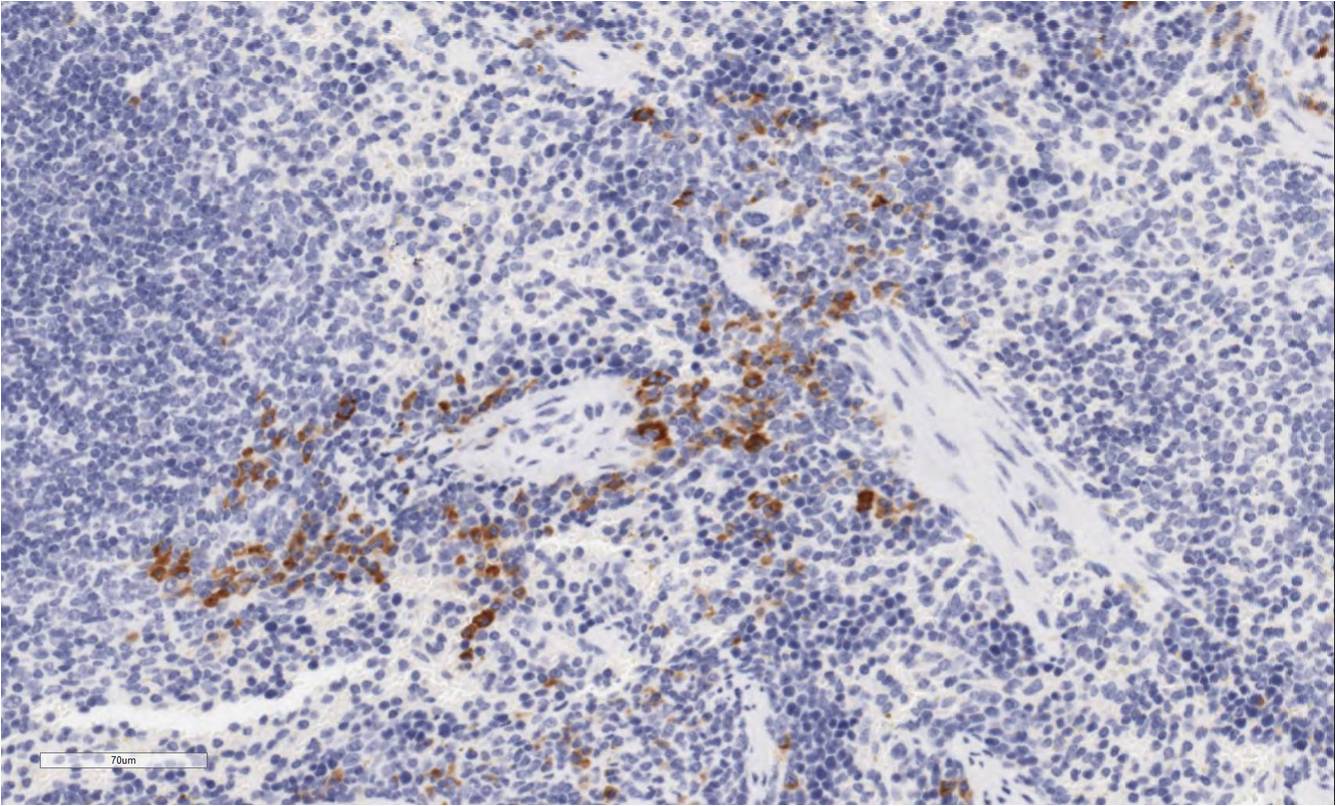
Detection of Mouse NKp46/NCR1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Paternal MHC expression on trophoblast.(a) Expression of paternal H-2Dd on gd9.5 trophoblast from B6 females impregnated by either B6 (top), D8 (middle) or BALB/c (bottom) males. BALB/c mice endogenously express H-2Dd. (b) H-2Dd and cytokeratin staining on control spleen cells. Scale bar=25 μm. (c) Representative sections of the distribution of NKp46+ DBA−(brown) and NKp46+ DBA+ (pink) uNK in the region of trophoblast invasion in the central decidua at gd9.5. Dashed lines demarcate the approximate boundary between invasive ectoplacental cone trophoblast and maternal decidua basalis. Scale bar=250 μm. DBA, Dolichos biflorus agglutinin. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms4359), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse NKp46/NCR1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Paternal H-2Dd expression on trophoblast results in impaired arterial remodelling.(a) Immunohistochemical staining for NKp46 and DBA reveals abundant uNK around decidual vessels, independent of paternal MHC. Scale bar=100 μm. DBA, Dolichos biflorus agglutinin. (b) H&E staining of uterine arteries illustrating the strategy used to measure vessel size (yellow dashed ring) and relative thickness (surface area ratio between areas surrounded by yellow and black ring, red arrows). Scale bar=25 μm. (c–e) Stereological and immunohistochemical analysis of arterial size (c) and relative thickness (d) in the decidua of B6 females mated with either B6 or D8 males. Pooled data from 4 litters per cross, n=13–15 implantation sites. P-values from unpaired Student’s t-tests. Means±s.e.m. (e) Representative staining for smooth muscle actin showing that the characteristic loss of actin in the media of spiral arteries is reduced in matings with D8 males (black arrows). Scale bars=100 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms4359), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: NKp46/NCR1
NKp46, along with NKp30 and NKp44, are activating receptors that have been collectively termed the natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCR) (1). These receptors are expressed almost exclusively by NK cells and play a major role in triggering some of the key lytic activities of NK cells. In human systems, the CD56dimCD16+ subpopulation that makes up the majority of NK cells in the peripheral blood and spleen expresses NKp46 in both resting and activated states (2). The main NK cell population of the lymph node (CD56brightCD16-) expresses low levels of NKp46 in resting cells, but expression is upregulated by IL-2. Mouse NKp46, also known as MAR-1 (3), is a type I transmembrane protein with two extracellular Ig-like domains. It has a positive charge in its transmembrane domain that permits association with the ITAM-bearing signal adapter proteins, CD3 zeta and Fc epsilon RI gamma (4). Studies with neutralizing antibodies indicate that the three NCR are primarily responsible for triggering the NK-mediated lysis of many human tumor cell lines. Blocking any of the NCRs individually resulted in partial inhibition of tumor cell lysis, but nearly complete inhibition of lysis was observed if all three receptors were blocked simultaneously (5). NKp46 has also been implicated in recognition of virus-infected cells through its capacity to bind to viral hemagglutinins (6 - 8).
- Moretta, L. and A. Moretta (2004) EMBO J. 23:255.
- Ferlazzo, G. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 172:1455.
- Biassoni, R. et al. (1999) Eur. J. Immunol. 29:1014.
- Westgaard, I. et al. (2004) J. Leukoc. Biol. PMID 15356098.
- Pende, D. et al. (1999) J. Exp. Med. 190:1505.
- Arnon, T. et al. (2004) Blood 103:664.
- Arnon, T. et al. (2001) Eur. J. Immunol. 31:2680.
- Mandelboim, O. et al. (2001) Nature 409:1055.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse NKp46/NCR1 Biotinylated Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
6
Citations: Showing 1 - 6
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Monocyte behaviour and tissue transglutaminase expression during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in transgenic CX3CR1(gfp/gfp) mice
Authors: Anne-Marie van Dam
Amino Acids, 2016-11-09;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Adoptive transfer of EBV specific CD8+ T cell clones can transiently control EBV infection in humanized mice.
Authors: Antsiferova O, Muller A, Ramer P, Chijioke O, Chatterjee B, Raykova A, Planas R, Sospedra M, Shumilov A, Tsai M, Delecluse H, Munz C
PLoS Pathog, 2014-08-28;10(8):e1004333.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
MHC-dependent inhibition of uterine NK cells impedes fetal growth and decidual vascular remodelling.
Authors: Kieckbusch, Jens, Gaynor, Louise M, Moffett, Ashley, Colucci, Francesc
Nat Commun, 2014-02-28;5(0):3359.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Notch, Id2, and ROR gamma-t sequentially orchestrate the fetal development of lymphoid tissue inducer cells.
Authors: Cherrier M, Sawa S, Eberl G
J. Exp. Med., 2012-03-19;209(4):729-40.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
AHR drives the development of gut ILC22 cells and postnatal lymphoid tissues via pathways dependent on and independent of Notch.
Authors: Lee JS, Cella M, McDonald KG
Nat. Immunol., 2011-11-20;13(2):144-51.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
RORgammat+ innate lymphoid cells regulate intestinal homeostasis by integrating negative signals from the symbiotic microbiota.
Authors: Sawa S, Lochner M, Satoh-Takayama N, Dulauroy S, Berard M, Kleinschek M, Cua D, Di Santo JP, Eberl G
Nat. Immunol., 2011-02-20;12(4):320-6.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse NKp46/NCR1 Biotinylated Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Mouse NKp46/NCR1 Biotinylated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: