Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 Antibody Summary
Phe16-Asp155
Accession # NP_034327
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
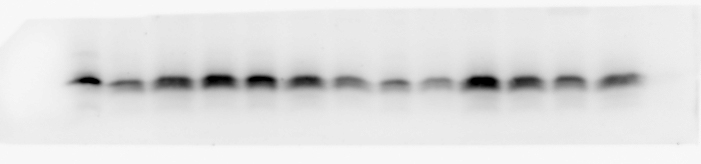
Detection of Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of mouse heart tissue and mouse kidney tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Sheep Anti-Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4686) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). A specific band was detected for FGF acidic/FGF1 at approximately 18 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Cell Proliferation Induced by FGF acidic/FGF1 and Neutralization by Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 Antibody. Recombinant Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 (Catalog # 4686-FA) induces proliferation in the NR6R-3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 (1 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Sheep Anti-Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 Antigen Affinity-purified Poly-clonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4686). The ND50 is typically 0.1-0.6 µg/mL.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: FGF acidic/FGF1
FGF acidic, also known as FGF1, ECGF, and HBGF-1, is a 17 kDa nonglycosylated member of the FGF family of mitogenic peptides. FGF acidic, which is produced by multiple cell types, stimulates the proliferation of all cells of mesodermal origin and many cells of neuroectodermal, ectodermal, and endodermal origin. It plays a number of roles in development, regeneration, and angiogenesis (1-3). Mouse FGF acidic shares 52% amino acid (aa) sequence identity with FGF basic and 15%-35% with other mouse FGFs. It shares 91%, 96%, 94%, and 100% aa sequence identity with bovine, human, porcine, and rat FGF acidic, respectively, and exhibits considerable species crossreactivity. During its nonclassical secretion, FGF acidic associates with S100A13, copper ions, and the C2A domain of synaptotagmin 1 (4). The secreted FGF acidic is stored in complex with extracellular heparan sulfate (5). The ability of heparan sulfate to bind FGF acidic is determined by its pattern of sulfation, and alterations in this pattern during embryogenesis thereby regulating FGF acidic bioactivity (6). The association of FGF acidic with heparan sulfate is a prerequisite for its subsequent interaction with FGF receptors (7, 8). Ligation triggers receptor dimerization, transphosphorylation, and internalization of receptor/FGF complexes (9). Internalized FGF acidic can translocate to the cytosol with the assistance of Hsp90 and then migrate to the nucleus by means of its two nuclear localization signals (10-12). The phosphorylation of FGF acidic by nuclear PKC delta triggers its active export to the cytosol where it is dephosphorylated and degraded (13, 14). Intracellular FGF acidic functions as a survival factor by inhibiting p53 activity and proapoptotic signaling (15).
- Madiai, F. et al. (1996) Gene 179:231.
- Galzie, Z. et al. (1997) Biochem. Cell Biol. 75:669.
- Presta, M. et al. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:159.
- Rajalingam, D. et al. (2007) Biochemistry 46:9225.
- Guerrini, M. et al. (2007) Curr. Pharm. Des. 13:2045.
- Allen, B.L. and A.C. Rapraeger (2003) J. Cell Biol. 163:637.
- Robinson, C.J. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:42274.
- Mohammadi, M. et al. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:107.
- Wiedlocha, A. and V. Sorensen (2004) Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 286:45.
- Wesche, J. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:11405.
- Imamura, T. et al. (1990) Science 249:1567.
- Wesche, J. et al. (2005) Biochemistry 44:6071.
- Wiedlocha, A. et al. (2005) Mol. Biol. Cell 16:794.
- Nilsen, T. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:26245.
- Bouleau, S. et al. (2005) Oncogene 24:7839.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
3
Citations: Showing 1 - 3
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
FGF1 Signaling Modulates Biliary Injury and Liver Fibrosis in the Mdr2-/- Mouse Model of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Authors: O'Brien A, Zhou T, White T et al.
Hepatology communications
-
Sensory nerve niche regulates mesenchymal stem cell homeostasis via FGF/mTOR/autophagy axis
Authors: F Pei, L Ma, J Jing, J Feng, Y Yuan, T Guo, X Han, TV Ho, J Lei, J He, M Zhang, JF Chen, Y Chai
Nature Communications, 2023-01-20;14(1):344.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Lack of miR-378 attenuates muscular dystrophy in mdx mice
Authors: P Podkalicka, O Mucha, I Bronisz-Bu, M Kozakowska, K Pietraszek, A Cetnarowsk, U G?owniak-K, K Bukowska-S, M Cie?la, M Kulecka, J Ostrowski, M Miku?a, A Potulska-C, A Kostera-Pr, A Józkowicz, A ?oboda, J Dulak
JCI Insight, 2020-06-04;5(11):.
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Mouse FGF acidic/FGF1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: