Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Biotinylated Antibody Summary
Glu27-Gly581
Accession # Q8K100
Applications
Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Sandwich Immunoassay
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
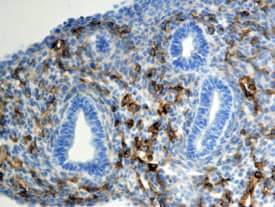 View Larger
View Larger
Endoglin/CD105 in Mouse Lung. Endoglin/CD105 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse lung using 15 µg/mL Goat Anti-Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Biotinylated Antigen Affinity-purified Poly-clonal Antibody (Catalog # BAF1320) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
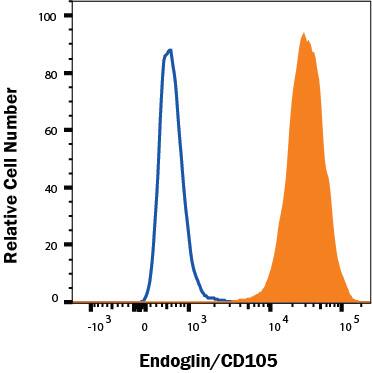 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Endoglin/CD105 in MS-1 Mouse Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. MS-1 mouse cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Biotinylated Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # BAF1320, filled histogram) or control antibody (BAF108, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Streptavidin (F0040). Staining was performed using our Staining Membrane-associated Proteins protocol.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Endoglin/CD105
Endoglin (CD105) is a 90 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein of the zona pellucida (ZP) family of proteins (1-3). Endoglin and betaglycan/T beta RIII are type III receptors for TGF beta superfamily ligands, sharing 71% amino acid (aa) identity within the transmembrane (TM) and cytoplasmic domains. Endoglin is highly expressed on proliferating vascular endothelial cells, chondrocytes, and syncytiotrophoblasts of term placenta, with lower amounts on hematopoietic, mesenchymal and neural crest stem cells, activated monocytes, and lymphoid and myeloid leukemic cells (2-5). Mouse Endoglin cDNA encodes 653 aa including a 26 aa signal sequence, a 555 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with an orphan domain and a two-part ZP domain, a TM domain, and a 47 aa cytoplasmic domain (1-3). A mouse isoform with a 35 aa cytoplasmic domain (S-endoglin) can oppose effects of long (L) Endoglin (6, 7). The mouse Endoglin ECD shares 69%, 84%, 62%, 63%, and 66% aa identity with human, rat, bovine, porcine, and canine Endoglin, respectively. Endoglin homodimers interact with TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 3 (but not TGF-beta 2) but only after binding T beta RII (8). Similarly, they interact with activin-A and BMP-7 via activin type IIA or B receptors, and with BMP-2 via BMPR-1A/ALK-3 or BMPR-1B/ALK-6 (9). BMP-9, however, is reported to bind Endoglin directly (10). Endoglin modifies ligand-induced signaling in multiple ways. For example, expression of Endoglin can inhibit TGF-beta 1 signals but enhance BMP7 signals in the same myoblast cell line (11). In endothelial cells, Endoglin inhibits T beta RI/ALK5, but enhances ALK1-mediated activation (12). Deletion of mouse Endoglin causes lethal vascular and cardiovascular defects, and human Endoglin haploinsufficiency can a cause the vascular disorder, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type I (13, 14). These abnormalities confirm the essential function of Endoglin in differentiation of smooth muscle, angiogenesis, and neovascularization (2-4, 12-14). In preeclampsia of pregnancy, high levels of proteolytically generated soluble Endoglin and VEGF R1 (sFlt-1), along with low placental growth factor (PlGF), are pathogenic due to antiangiogenic activity (15).
- Ge, A.Z. and E.C. Butcher (1994) Gene 138:201.
- ten Dijke, P. et al. (2008) Angiogenesis 11:79.
- Bernabeu, C. et al. (2007) J. Cell. Biochem. 102:1375.
- Mancini, M.L. et al. (2007) Dev. Biol. 308:520.
- Moody, J.L. et al. (2007) Stem Cells 25:2809.
- Velasco, S. et al. (2008) J. Cell Sci. 121:913.
- Perez-Gomez, E. et al. (2005) Oncogene 24:4450.
- Cheifetz, S, et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267:19027.
- Barbara, N.P. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:584.
- Scharpfenecker, M. et al. (2007) J. Cell Sci. 120:964.
- Scherner, O. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:13934.
- Pece-Barbara, N. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:27800.
- Arthur, H.M. et al. (2000) Dev. Biol. 217:42.
- Lebrin, F. and C.L. Mummery (2008) Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 18:25.
- Venkatesha, S. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:642.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Biotinylated Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
7
Citations: Showing 1 - 7
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Decellularized Pancreatic Tail as Matrix for Pancreatic Islet Transplantation into the Greater Omentum in Rats
Authors: Z Berkova, K Zacharovov, A Patikova, I Leontovyc, Z Hladikova, D Cerveny, E Tihlarikov, V Nedela, P Girman, D Jirak, F Saudek
Journal of functional biomaterials, 2022-09-30;13(4):.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Whole Cell
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Targeting Endoglin Expressing Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment Does Not Inhibit Tumor Growth in a Pancreatic Cancer Mouse Model
Authors: MJA Schoonderw, SK Hakuno, M Sassen, EB Kuhlemaije, M Paauwe, M Slingerlan, MF Fransen, LJAC Hawinkels
OncoTargets and Therapy, 2021-10-29;14(0):5205-5220.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Reducing Endoglin Activity Limits Calcineurin and TRPC‐6 Expression and Improves Survival in a Mouse Model of Right Ventricular Pressure Overload
Authors: Navin K Kapur, Xiaoying Qiao, Vikram Paruchuri, Emily E Mackey, Gerard H Daly, Kishan Ughreja et al.
Journal of the American Heart Association
-
Long-Term Retinal PEDF Overexpression Prevents Neovascularization in a Murine Adult Model of Retinopathy.
Authors: Haurigot V, Villacampa P, Ribera A, Bosch A, Ramos D, Ruberte J, Bosch F
PLoS ONE, 2012-07-20;7(7):e41511.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Reduced Endoglin Activity Limits Cardiac Fibrosis and Improves Survival in Heart Failure
Authors: Navin K. Kapur, Szuhuei Wilson, Adil A. Yunis, Xiaoying Qiao, Emily Mackey, Vikram Paruchuri et al.
Circulation
-
ENDOGLIN/CD105 is expressed in KIT positive cells in the gut and in gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Authors: Petra Gromova, Brian P. Rubin, An Thys, Pierre Cullus, Christophe Erneux, Jean-Marie Vanderwinden
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine
-
Endoglin expression in the endothelium is regulated by Fli-1, Erg, and Elf-1 acting on the promoter and a -8-kb enhancer.
Authors: Pimanda JE, Chan WY, Donaldson IJ, Bowen M, Green AR, Gottgens B
Blood, 2006-02-16;107(12):4737-45.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Biotinylated Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Biotinylated Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Biotinylated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image



