Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antibody Summary
Glu27-Gly581
Accession # Q8K100
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
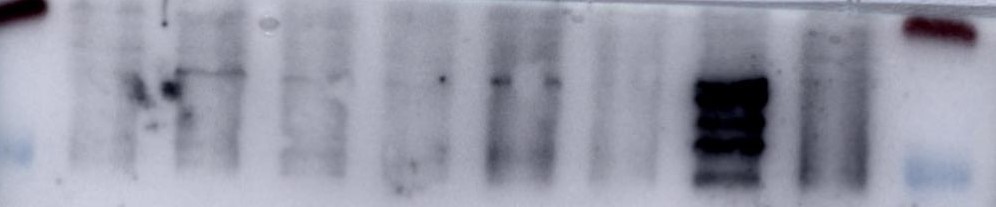
Detection of Mouse Endoglin/CD105 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of bEnd.3 mouse endothelioma cell line and MS-1 mouse pancreatic islet endothelial cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1320) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for Endoglin/CD105 at approximately 90-95 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Endoglin/CD105 in MS-1 Mouse Cell Line. Endoglin/CD105 was detected in immersion fixed MS-1 mouse pancreatic islet endothelial cell line using Goat Anti-Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1320) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (yellow; Catalog # NL001) and counter-stained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
Endoglin/CD105 in Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Endoglin/CD105 was detected in immersion fixed rat mesenchymal stem cells using Goat Anti-Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1320) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
Endoglin/CD105 in Mouse Embryo. Endoglin/CD105 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (E13-15) using Goat Anti-Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1320) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Endoglin/CD105 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of bEnd.3 mouse endothelioma cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for Endoglin/CD105 at approximately 121 kDa (as indicated) using 5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1320) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Porcine Endoglin/CD105 by Immunohistochemistry Chronic intermittent hypoxia modifies the BM vascular structure. a’–e’ Representative images of femur bone marrow stained with vWF, CD105, VE-cadherin, SMA, and CD11b counterstained with hematoxylin. a”, c”, d” BM from CIH exposed rats (n = 6) has more VE-cadherin+ vessels and SMA coverage but less vWF+ sinusoids (400×, Leica DM2500). e’, e” Representative images of CD11b immunohistochemistry in femur BM show an increase in BM monocyte count in CIH exposed animals. (400×, Leica DM2500) a’, a”’, b’, b” No changes in the total number of vessels or in megakaryocyte count were observed, as accounted by CD105 and vWF staining, respectively. Results are represented as the mean ± SD of bone marrow sections from six male Wistar rats (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). f Representative images of femur bone marrow fluorescently immunostained for VE-cadherin show an increase in total VE-cadherin vessels and in VE-cadherin vessel coverage. Scale bar, 50 μm (insets magnified 2.5×). Images were acquired with a Zeiss LSM 510 META microscope. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26856724), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Endoglin/CD105 by Immunohistochemistry Increased tumor necrosis and reduced tumor vascularization after GET of therapeutic plasmids in vivo.Histologically stained and analyzed sections after treatments of TS/A tumors: intratumoral injection of endotoxin-free water alone (control group; CTRL) or in combination with the application of electric pulses (EP group), injection of plasmid pET-antiCD105 (TS group), pU6-antiCD105 (CON group) or pU6-SCR (SCR group) alone or combined with the application of electric pulses (GET of TS plasmid; GET of CON plasmid; GET of SCR plasmid). Triple GET of CON or TS plasmid increased necrosis (HE) and reduced the number of blood vessels (CD105) in TS/A tumors. The percentage of necrosis (upper graph) was statistically significantly increased (*p<0.05) in both of the therapeutic groups (GET of CON and TS plasmid) vs. all the pertinent control groups, with no difference between therapies, also seen in histological sections. The reduced number of blood vessels (CD105) was observed in histological sections of both therapeutic groups that were (lower graph) non-statistically significant to each other after analysis, although the reduction was statistically significant (*p<0.05) vs. all the pertinent control groups. The results represent one experiment, n = 3–4 mice for each experimental group and at least 5 analyzed fields of view for each mouse. The data represent AM ± SEM. N.S. represents statistically non-significant difference between the therapeutic groups. Scale bar = 100 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124913), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse Endoglin/CD105 by Immunohistochemistry Increased tumor necrosis and reduced tumor vascularization after GET of therapeutic plasmids in vivo.Histologically stained and analyzed sections after treatments of TS/A tumors: intratumoral injection of endotoxin-free water alone (control group; CTRL) or in combination with the application of electric pulses (EP group), injection of plasmid pET-antiCD105 (TS group), pU6-antiCD105 (CON group) or pU6-SCR (SCR group) alone or combined with the application of electric pulses (GET of TS plasmid; GET of CON plasmid; GET of SCR plasmid). Triple GET of CON or TS plasmid increased necrosis (HE) and reduced the number of blood vessels (CD105) in TS/A tumors. The percentage of necrosis (upper graph) was statistically significantly increased (*p<0.05) in both of the therapeutic groups (GET of CON and TS plasmid) vs. all the pertinent control groups, with no difference between therapies, also seen in histological sections. The reduced number of blood vessels (CD105) was observed in histological sections of both therapeutic groups that were (lower graph) non-statistically significant to each other after analysis, although the reduction was statistically significant (*p<0.05) vs. all the pertinent control groups. The results represent one experiment, n = 3–4 mice for each experimental group and at least 5 analyzed fields of view for each mouse. The data represent AM ± SEM. N.S. represents statistically non-significant difference between the therapeutic groups. Scale bar = 100 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124913), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Endoglin/CD105
Endoglin (CD105) is a 90 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein of the zona pellucida (ZP) family of proteins (1-3). Endoglin and betaglycan/T beta RIII are type III receptors for TGF beta superfamily ligands, sharing 71% amino acid (aa) identity within the transmembrane (TM) and cytoplasmic domains. Endoglin is highly expressed on proliferating vascular endothelial cells, chondrocytes, and syncytiotrophoblasts of term placenta, with lower amounts on hematopoietic, mesenchymal and neural crest stem cells, activated monocytes, and lymphoid and myeloid leukemic cells (2-5). Mouse Endoglin cDNA encodes 653 aa including a 26 aa signal sequence, a 555 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with an orphan domain and a two-part ZP domain, a TM domain, and a 47 aa cytoplasmic domain (1-3). A mouse isoform with a 35 aa cytoplasmic domain (S-endoglin) can oppose effects of long (L) Endoglin (6, 7). The mouse Endoglin ECD shares 69%, 84%, 62%, 63%, and 66% aa identity with human, rat, bovine, porcine, and canine Endoglin, respectively. Endoglin homodimers interact with TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 3 (but not TGF-beta 2) but only after binding T beta RII (8). Similarly, they interact with activin-A and BMP-7 via activin type IIA or B receptors, and with BMP-2 via BMPR-1A/ALK-3 or BMPR-1B/ALK-6 (9). BMP-9, however, is reported to bind Endoglin directly (10). Endoglin modifies ligand-induced signaling in multiple ways. For example, expression of Endoglin can inhibit TGF-beta 1 signals but enhance BMP7 signals in the same myoblast cell line (11). In endothelial cells, Endoglin inhibits T beta RI/ALK5, but enhances ALK1-mediated activation (12). Deletion of mouse Endoglin causes lethal vascular and cardiovascular defects, and human Endoglin haploinsufficiency can a cause the vascular disorder, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type I (13, 14). These abnormalities confirm the essential function of Endoglin in differentiation of smooth muscle, angiogenesis, and neovascularization (2-4, 12-14). In preeclampsia of pregnancy, high levels of proteolytically generated soluble Endoglin and VEGF R1 (sFlt-1), along with low placental growth factor (PlGF), are pathogenic due to antiangiogenic activity (15).
- Ge, A.Z. and E.C. Butcher (1994) Gene 138:201.
- ten Dijke, P. et al. (2008) Angiogenesis 11:79.
- Bernabeu, C. et al. (2007) J. Cell. Biochem. 102:1375.
- Mancini, M.L. et al. (2007) Dev. Biol. 308:520.
- Moody, J.L. et al. (2007) Stem Cells 25:2809.
- Velasco, S. et al. (2008) J. Cell Sci. 121:913.
- Perez-Gomez, E. et al. (2005) Oncogene 24:4450.
- Cheifetz, S, et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267:19027.
- Barbara, N.P. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:584.
- Scharpfenecker, M. et al. (2007) J. Cell Sci. 120:964.
- Scherner, O. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:13934.
- Pece-Barbara, N. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:27800.
- Arthur, H.M. et al. (2000) Dev. Biol. 217:42.
- Lebrin, F. and C.L. Mummery (2008) Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 18:25.
- Venkatesha, S. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:642.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
44
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Smooth Muscle Cell Reprogramming in Aortic Aneurysms
Authors: Chen PY, Qin L, Li G et al.
Cell Stem Cell
-
Increasing Endoglin Deletion in Endothelial Cells Exacerbates the Severity of Brain Arteriovenous Malformation in Mouse
Authors: Shabani, Z;Do Prado, LB;Zhang, R;Zhu, W;Shaligram, SS;Yadav, A;Wang, C;Su, H;
Biomedicines
Species: Transgenic Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates, Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot -
Cell cycle-dependent centrosome clustering precedes proplatelet formation
Authors: Becker, IC;Wilkie, AR;Nikols, E;Carminita, E;Roweth, HG;Tilburg, J;Sciaudone, AR;Noetzli, LJ;Fatima, F;Couldwell, G;Ray, A;Mogilner, A;Machlus, KR;Italiano, JE;
Science advances
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Q-VAT: Quantitative Vascular Analysis Tool
Authors: Bram Callewaert, Willy Gsell, Uwe Himmelreich, Elizabeth A. V. Jones
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine
-
Carbonic anhydrases reduce the acidity of the tumor microenvironment, promote immune infiltration, decelerate tumor growth, and improve survival in ErbB2/HER2-enriched breast cancer
Authors: Soojung Lee, Nicolai J. Toft, Trine V. Axelsen, Maria Sofia Espejo, Tina M. Pedersen, Marco Mele et al.
Breast Cancer Research
-
Trans-differentiation of trophoblast stem cells: implications in placental biology
Authors: Madhurima Paul, Shreeta Chakraborty, Safirul Islam, Rupasri Ain
Life Science Alliance
-
The adult heart requires baseline expression of the transcription factor Hand2 to withstand right ventricular pressure overload
Authors: Raquel F Videira, Anne Marie C Koop, Lara Ottaviani, Ella M Poels, Jordy M M Kocken, Cristobal Dos Remedios et al.
Cardiovascular Research
-
The low affinity A2B adenosine receptor enhances migratory and invasive capacity in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo of glioblastoma stem-like cells
Authors: José I. Erices, Ignacio Niechi, Atenea Uribe-Ojeda, María de los Ángeles Toro, Noemí García-Romero, Josefa Carrión-Navarro et al.
Frontiers in Oncology
-
Mitochondrial respiration supports autophagy to provide stress resistance during quiescence
Authors: S Magalhaes-, J Blecha, R Naraine, J Mikesova, P Abaffy, A Pecinova, M Milosevic, R Bohuslavov, J Prochazka, S Khan, E Novotna, R Sindelka, R Machan, M Dewerchin, E Vlcak, J Kalucka, S Stemberkov, A Benda, J Goveia, T Mracek, C Barinka, P Carmeliet, J Neuzil, K Rohlenova, J Rohlena
Autophagy, 2022-03-08;0(0):1-18.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Analysis of Placental Arteriovenous Formation Reveals New Insights Into Embryos With Congenital Heart Defects
Authors: Jacinta I. Kalisch-Smith, Emily C. Morris, Mary A. A. Strevens, Andia N. Redpath, Kostantinos Klaourakis, Dorota Szumska et al.
Frontiers in Genetics
-
SCA-1/Ly6A Mesodermal Skeletal Progenitor Subpopulations Reveal Differential Commitment of Early Limb Bud Cells
Authors: Jessica Cristina Marín-Llera, Carlos Ignacio Lorda-Diez, Juan Mario Hurle, Jesús Chimal-Monroy
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
-
The transcription factor Rreb1 regulates epithelial architecture, invasiveness, and vasculogenesis in early mouse embryos
Authors: Sophie M Morgani, Jie Su, Jennifer Nichols, Joan Massagué, Anna-Katerina Hadjantonakis
eLife
-
The spatiotemporal expression patterns of MSC-associated markers contribute to the identification of progenitor subpopulations in developing limbs
Authors: Argelia S. García-Cervera, Jesús Chimal-Monroy, Jessica C. Marín-llera
The International Journal of Developmental Biology
-
Bevacizumab dose adjustment to improve clinical outcomes of glioblastoma
Authors: N García-Rom, I Palacín-Al, R Madurga, J Carrión-Na, S Esteban-Ru, B Jiménez, A Collazo, F Pérez-Rodr, A Ortiz de M, C Fernández-, S García-Duq, J Diamantopo, C Belda-Inie, R Prat-Acín, P Sánchez-Gó, E Calvo, A Ayuso-Saci
BMC Med, 2020-06-22;18(1):142.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
PS1 FAD mutants decrease ephrinB2-regulated angiogenic functions, ischemia-induced brain neovascularization and neuronal survival
Authors: Y Yoon, G Voloudakis, N Doran, E Zhang, C Dimovasili, L Chen, Z Shao, S Darmanis, C Tang, J Tang, VX Wang, PR Hof, NK Robakis, A Georgakopo
Mol. Psychiatry, 2020-06-15;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
C-KIT Expression Distinguishes Fetal from Postnatal Skeletal Progenitors
Authors: DD He, XT Tang, W Dong, G Cui, G Peng, X Yin, Y Chen, N Jing, BO Zhou
Stem Cell Reports, 2020-03-26;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
A Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Organoid Model and Biobank Recapitulates Inter- and Intra-tumoral Heterogeneity
Authors: Fadi Jacob, Ryan D. Salinas, Daniel Y. Zhang, Phuong T.T. Nguyen, Jordan G. Schnoll, Samuel Zheng Hao Wong et al.
Cell
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Renal Endothelium Heterogeneity and Metabolic Adaptation to Water Deprivation
Authors: Sébastien J. Dumas, Elda Meta, Mila Borri, Jermaine Goveia, Katerina Rohlenova, Nadine V. Conchinha et al.
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
-
Endoglin Trafficking/Exosomal Targeting in Liver Cells Depends on N-Glycosylation
Authors: Steffen Meurer, Almut Elisabeth Wimmer, Eddy van de van de Leur, Ralf Weiskirchen
Cells
-
Correlation of two distinct metastasis-associated proteins, MTA1 and S100A4, in angiogenesis for promoting tumor growth
Authors: M Ishikawa, M Osaki, M Yamagishi, K Onuma, H Ito, F Okada, H Endo
Oncogene, 2019-02-11;0(0):.
Species: Xenograft
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Role of glutamine synthetase in angiogenesis beyond glutamine synthesis
Authors: G Eelen, C Dubois, AR Cantelmo, J Goveia, U Brüning, M DeRan, G Jarugumill, J van Rijsse, G Saladino, F Comitani, A Zecchin, S Rocha, R Chen, H Huang, S Vandekeere, J Kalucka, C Lange, F Morales-Ro, B Cruys, L Treps, L Ramer, S Vinckier, K Brepoels, S Wyns, J Souffreau, L Schoonjans, WH Lamers, Y Wu, J Haustraete, J Hofkens, S Liekens, R Cubbon, B Ghesquière, M Dewerchin, FL Gervasio, X Li, JD van Buul, X Wu, P Carmeliet
Nature, 2018-08-29;561(7721):63-69.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, IHC-Fr -
BMP9 (Bone Morphogenetic Protein-9)/Alk1 (Activin-Like Kinase Receptor Type I) Signaling Prevents Hyperglycemia-Induced Vascular Permeability
Authors: Naoufal Akla, Claire Viallard, Natalija Popovic, Cindy Lora Gil, Przemyslaw Sapieha, Bruno Larrivée
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
-
Blockade of myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion with all-trans retinoic acid increases the efficacy of anti-angiogenic therapy
Authors: R Bauer, F Udonta, M Wroblewski, I Ben-Batall, IM Santos, F Taverna, M Kuhlencord, V Gensch, S Päsler, S Vinckier, JM Brandner, K Pantel, C Bokemeyer, T Vogl, J Roth, P Carmeliet, S Loges
Cancer Res., 2018-04-19;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Multicolor quantitative confocal imaging cytometry
Authors: DL Coutu, KD Kokkaliari, L Kunz, T Schroeder
Nat. Methods, 2017-11-13;15(1):39-46.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Mast cells decrease efficacy of anti-angiogenic therapy by secreting matrix-degrading granzyme B
Authors: M Wroblewski, R Bauer, M Cubas Córd, F Udonta, I Ben-Batall, K Legler, C Hauser, J Egberts, M Janning, J Velthaus, C Schulze, K Pantel, C Bokemeyer, S Loges
Nat Commun, 2017-08-16;8(1):269.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Pharmacologic or Genetic Targeting of Glutamine Synthetase Skews Macrophages toward an M1-like Phenotype and Inhibits Tumor Metastasis
Authors: EM Palmieri, A Menga, R Martín-Pér, A Quinto, C Riera-Domi, G De Tullio, DC Hooper, WH Lamers, B Ghesquière, DW McVicar, A Guarini, M Mazzone, A Castegna
Cell Rep, 2017-08-15;20(7):1654-1666.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Endothelial follistatin‐like‐1 regulates the postnatal development of the pulmonary vasculature by modulating BMP/Smad signaling
Authors: Navessa P. Tania, Harm Maarsingh, I. Sophie T. Bos, Andrea Mattiotti, Stuti Prakash, Wim Timens et al.
Pulmonary Circulation
-
DNA sequences within glioma-derived extracellular vesicles can cross the intact blood-brain barrier and be detected in peripheral blood of patients
Authors: N García-Rom, J Carrión-Na, S Esteban-Ru, E Lázaro-Ibá, M Peris-Celd, MM Alonso, J Guzmán-De-, C Fernández-, AO de Mendivi, S García-Duq, C Escobedo-L, R Prat-Acín, C Belda-Inie, A Ayuso-Saci
Oncotarget, 2017-01-03;8(1):1416-1428.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
PI3 kinase inhibition improves vascular malformations in mouse models of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia
Nat Commun, 2016-11-29;7(0):13650.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Electrotransfer of Plasmid DNA Encoding an Anti-Mouse Endoglin (CD105) shRNA to B16 Melanoma Tumors with Low and High Metastatic Potential Results in Pronounced Anti-Tumor Effects
Authors: Tanja Dolinsek, Gregor Sersa, Lara Prosen, Masa Bosnjak, Monika Stimac, Urska Razborsek et al.
Cancers (Basel)
-
Endothelial Msx1 transduces hemodynamic changes into an arteriogenic remodeling response
Authors: Ine Vandersmissen, Sander Craps, Maarten Depypere, Giulia Coppiello, Nick van Gastel, Frederik Maes et al.
Journal of Cell Biology
-
Pretreatment with VEGF(R)-inhibitors reduces interstitial fluid pressure, increases intraperitoneal chemotherapy drug penetration, and impedes tumor growth in a mouse colorectal carcinomatosis model
Authors: Félix Gremonprez, Benedicte Descamps, Andrei Izmer, Christian Vanhove, Frank Vanhaecke, Olivier De Wever et al.
Oncotarget
-
Gene Electrotransfer of Plasmid with Tissue Specific Promoter Encoding shRNA against Endoglin Exerts Antitumor Efficacy against Murine TS/A Tumors by Vascular Targeted Effects.
Authors: Stimac M, Dolinsek T, Lampreht U, Cemazar M, Sersa G
PLoS ONE, 2015-04-24;10(4):e0124913.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Arteriogenic expansion of extratumoral macrovessels – impact of vascular ageing
Authors: B. MEEHAN, A. DOMBROVSKY, N. MAGNUS, J. RAK
Neoplasma
-
Combined VEGF and CXCR4 antagonism targets the GBM stem cell population and synergistically improves survival in an intracranial mouse model of glioblastoma
Authors: Amy Barone, Rajarshi Sengupta, Nicole M. Warrington, Erin Smith, Patrick Y. Wen, Rolf A. Brekken et al.
Oncotarget
-
Ageing-related responses to antiangiogenic effects of sunitinib in atherosclerosis-prone mice
Authors: Brian Meehan, Delphine Garnier, Alexander Dombrovsky, Karrie Lau, Esterina D’Asti, Nathalie Magnus et al.
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development
-
LF-15 & T7, synthetic peptides derived from tumstatin, attenuate aspects of airway remodelling in a murine model of chronic OVA-induced allergic airway disease.
Authors: Grafton K, Moir L, Black J, Hansbro N, Hansbro P, Burgess J, Oliver B
PLoS ONE, 2014-01-15;9(1):e85655.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
In vivo adeno-associated viral vector-mediated genetic engineering of white and brown adipose tissue in adult mice.
Authors: Jimenez V, Munoz S, Casana E, Mallol C, Elias I, Jambrina C, Ribera A, Ferre T, Franckhauser S, Bosch F
Diabetes, 2013-09-16;62(12):4012-22.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Multiple delivery of siRNA against endoglin into murine mammary adenocarcinoma prevents angiogenesis and delays tumor growth.
Authors: Dolinsek T, Markelc B, Sersa G, Coer A, Stimac M, Lavrencak J, Brozic A, Kranjc S, Cemazar M
PLoS ONE, 2013-03-05;8(3):e58723.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
Focal adhesion kinase regulates the localization and retention of pro-B cells in bone marrow microenvironments.
Authors: Park S, Wolfram P, Canty K, Harley B, Nombela-Arrieta C, Pivarnik G, Manis J, Beggs H, Silberstein L
J Immunol, 2012-12-21;190(3):1094-102.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
99mTc-Labeled Tricarbonyl His-CNA35 as an Imaging Agent for the Detection of Tumor Vasculature
Authors: Gilles Mees, Rudi Dierckx, Koen Mertens, Simon Vermeire, Magali Van Steenkiste, Chris Reutelingsperger et al.
Journal of Nuclear Medicine
-
Kinetics of angiogenic changes in a new mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma
Authors: Femke Heindryckx, Koen Mertens, Nicolas Charette, Bert Vandeghinste, Christophe Casteleyn, Christophe Van Steenkiste et al.
Molecular Cancer
-
Direct transcriptional regulation of neuropilin-2 by COUP-TFII modulates multiple steps in murine lymphatic vessel development.
Authors: Lin FJ, Chen X, Qin J, Hong YK, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY
J. Clin. Invest., 2010-04-01;120(5):1694-707.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Decreased blood vessel density and endothelial cell subset dynamics during ageing of the endocrine system
Authors: Chen J, Lippo L, Labella R et al.
Onco Targets Ther
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 2 Reviews)
Have you used Mouse Endoglin/CD105 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: