Human VEGF-C Antibody Summary
Applications
This antibody functions as an ELISA detection antibody when paired with Mouse Anti-Human VEGF‑C Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB752).
This product is intended for assay development on various assay platforms requiring antibody pairs. We recommend the Human VEGF-C DuoSet ELISA Kit (Catalog # DY752B) for convenient development of a sandwich ELISA or the Human VEGF-C Quantikine ELISA Kit (Catalog # DVEC00) for a complete optimized ELISA.
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
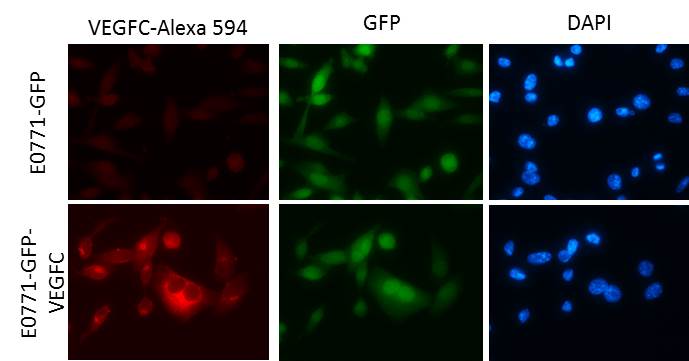
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human VEGF‑C by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human VEGF-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF752) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF017). Specific bands were detected for VEGF-C at approximately 52 kDa, 34 kDa, and 13 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
VEGF-C in Human Colon Cancer Tissue. VEGF-C was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue using Goat Anti-Human VEGF-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF752) at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to stromal cells surrounding crypts in the colon mucosa (cross section across crypts). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
VEGF-C in Human Colon Cancer Tissue. VEGF-C was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue using Goat Anti-Human VEGF-C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF752) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to epithelial cells in crypts of the colon mucusa (longitudinal section of crypts). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Human VEGF‑C ELISA Standard Curve. Recombinant Human VEGF‑C protein was serially diluted 2-fold and captured by Mouse Anti-Human VEGF‑C Monoclonal Antibody (MAB752) coated on a Clear Polystyrene Microplate (DY990). Goat Anti-Human VEGF‑C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF752) was biotinylated and incubated with the protein captured on the plate. Detection of the standard curve was achieved by incubating Streptavidin-HRP (DY998) followed by Substrate Solution (DY999) and stopping the enzymatic reaction with Stop Solution (DY994).
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: VEGF-C
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) and VEGF-D constitute a VEGF sub-family that share the conserved VEGF homology domain (VHD) with other VEGF family members but are distinguished by their preferential formation of non-covalent homodimers. Both VEGF-C and -D have long N- and C-terminal propeptide extensions. The VEGF-C propeptide undergoes stepwise proteolytic processing to generate ligands with increasing affinity for VEGF-R3. However, only the fully processed VEGF-C containing just the VHD can bind VEGF-R2. None of the VEGF-C forms have appreciable affinity for VEGF-R1. VEGF-C is expressed in multiple adult human tissues, most prominently in lymph nodes, heart, placenta, ovary, and small intestine. Traces of VEGF-C are also detected in brain, liver, thymus, skeletal muscles, spleen, prostate, testis and colon. Unlike other VEGF family members, VEGF-C expression is not regulated by hypoxia. VEGF-C is a lymphangiogenic growth factor and the VEGF-C/VEGF-R3 signaling pathway has been shown to be crucial for lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-C and VEGF-R3 are usually co-expressed at sites with lymphatic vessel sprouting, in the embryo, and in various pathological conditions. VEGF-C stimulates lymphangiogenesis in the avian chorioallantoic membrane model. Over-expression of VEGF-C in breast cancer cells has been shown to increase intratumoral lymphangiogenesis, resulting in enhanced metastasis to regional lymph nodes and to the lungs. Mouse tumors expressing elevated levels of VEGF-C have increased lymphatic metastasis and increased lymphatic surface area in the tumor margin. VEGF-C is also associated with lymph node metastasis of colorectal carcinoma. Besides lymphangiogenesis, VEGF-C can have potent effects on physiological angiogenesis through its interaction with VEGF R2. The protein can stimulate migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo and has been shown to stimulate angiogenesis in the mouse cornea and in rabbit hind limb ischaemia.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human VEGF-C Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
28
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
The gain-of-function GLI1 transcription factor TGLI1 enhances expression of VEGF-C and TEM7 to promote glioblastoma angiogenesis.
Authors: Carpenter RL, Paw I, Zhu H et al.
Oncotarget
-
RASSF8 downregulation promotes lymphangiogenesis and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Authors: Lan Zhang, Jian-Hua Wang, Rong-Xin Liang, Shu-Ting Huang, Jing Xu, Lin-Jing Yuan et al.
Oncotarget
-
Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor-C by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the conjunctiva and pterygium
Authors: Yoko Dong, Satoru Kase, Zhenyu Dong, Junichi Fukuhara, Yoshiaki Tagawa, Erdal Tan Ishizuka et al.
International Journal of Molecular Medicine
-
Insufficiency of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor‐1 confers lymphatic invasion of tongue carcinoma cells
Authors: Aya Izumi, Koji Yamamoto, Makiko Kawaguchi, Fumiki Yamashita, Tsuyoshi Fukushima, Takumi Kiwaki et al.
Cancer Science
-
KLK3/PSA and cathepsin D activate VEGF-C and VEGF-D
Authors: SK Jha, K Rauniyar, E Chronowska, K Mattonet, EW Maina, H Koistinen, UH Stenman, K Alitalo, M Jeltsch
Elife, 2019-05-17;8(0):.
-
Effect of CCR7, CXCR4 and VEGF-C on the lymph node metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Authors: JINGHUI GUO, WENHUI LOU, YUAN JI, SHUNCAI ZHANG
Oncology Letters
-
Association Between c-Met and Lymphangiogenic Factors in Patients With Colorectal Cancer
Authors: Han Jo Kim, Moo-Jun Baek, Dong Hyun Kang, Sang-Cheol Lee, Sang Byung Bae, Kyu Taek Lee et al.
Annals of Coloproctology
-
SARS-CoV-2 viral protein Nsp2 stimulates translation under normal and hypoxic conditions
Authors: Nadejda Korneeva, Md Imtiaz Khalil, Ishita Ghosh, Ruping Fan, Thomas Arnold, Arrigo De Benedetti
Virology Journal
-
VEGFR-3 signaling restrains the neuron-macrophage crosstalk during neurotropic viral infection
Authors: Qi, L;Li, X;Zhang, F;Zhu, X;Zhao, Q;Yang, D;Hao, S;Li, T;Li, X;Tian, T;Feng, J;Sun, X;Wang, X;Gao, S;Wang, H;Ye, J;Cao, S;He, Y;Wang, H;Wei, B;
Cell reports
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
ADAMTS2 and ADAMTS14 substitute ADAMTS3 in adults for proVEGFC activation and lymphatic homeostasis
Authors: L Dupont, L Joannes, F Morfoisse, S Blacher, C Monseur, CF Deroanne, A Noël, AC Colige
JCI Insight, 2022-04-22;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Nucleoside-modified VEGFC mRNA induces organ-specific lymphatic growth and reverses experimental lymphedema
Authors: D Sz?ke, G Kovács, É Kemecsei, L Bálint, K Szoták-Ajt, P Aradi, A Styevkóné, BL Mui, YK Tam, TD Madden, K Karikó, RP Kataru, MJ Hope, D Weissman, BJ Mehrara, N Pardi, Z Jakus
Nature Communications, 2021-06-08;12(1):3460.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Tumor-associated macrophage, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis markers predict prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients
Authors: I Hwang, JW Kim, K Ylaya, EJ Chung, H Kitano, C Perry, J Hanaoka, J Fukuoka, JY Chung, SM Hewitt
J Transl Med, 2020-11-23;18(1):443.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Specific fibroblast subpopulations and neuronal structures provide local sources of Vegfc-processing components during zebrafish lymphangiogenesis
Authors: G Wang, L Muhl, Y Padberg, L Dupont, J Peterson-M, M Stehling, F le Noble, A Colige, C Betsholtz, S Schulte-Me, A van Impel
Nat Commun, 2020-06-01;11(1):2724.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: Western Blot -
VEGF-C-driven lymphatic drainage enables immunosurveillance of brain tumours
Authors: E Song, T Mao, H Dong, LSB Boisserand, S Antila, M Bosenberg, K Alitalo, JL Thomas, A Iwasaki
Nature, 2020-01-15;577(7792):689-694.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysate
-
Transcription Factor Prospero Homeobox 1 (PROX1) as a Potential Angiogenic Regulator of Follicular Thyroid Cancer Dissemination
Authors: M Rudzi?ska, M Mikula, KD Arczewska, E Gajda, S Sabali?ska, T St?pie?, J Ostrowski, B Czarnocka
Int J Mol Sci, 2019-11-10;20(22):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
The interplay of matrix metalloproteinase-8, transforming growth factor-?1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-C cooperatively contributes to the aggressiveness of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma
Authors: P Åström, K Juurikka, ES Hadler-Ols, G Svineng, NK Cervigne, RD Coletta, J Risteli, JH Kauppila, S Skarp, S Kuttner, A Oteiza, M Sutinen, T Salo
Br. J. Cancer, 2017-08-03;117(7):1007-1016.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
Efficient activation of the lymphangiogenic growth factor VEGF-C requires the C-terminal domain of VEGF-C and the N-terminal domain of CCBE1
Authors: SK Jha, K Rauniyar, T Karpanen, VM Leppänen, P Brouillard, M Vikkula, K Alitalo, M Jeltsch
Sci Rep, 2017-07-07;7(1):4916.
Species: Primate - Chlorocebus aethiops (African Green Monkey)
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Synaptonemal complex protein 3 is associated with lymphangiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with lymph node metastasis
Authors: H Kitano, JY Chung, KH Noh, YH Lee, TW Kim, SH Lee, SH Eo, HJ Cho, CH Choi, S Inoue, J Hanaoka, J Fukuoka, SM Hewitt
J Transl Med, 2017-06-17;15(1):138.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
A phase Ib/II translational study of sunitinib with neoadjuvant radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma.
Authors: Lewin J, Khamly K, Young R, Mitchell C, Hicks R, Toner G, Ngan S, Chander S, Powell G, Herschtal A, Te Marvelde L, Desai J, Choong P, Stacker S, Achen M, Ferris N, Fox S, Slavin J, Thomas D
Br J Cancer, 2014-10-16;111(12):2254-61.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Lysophosphatidic Acid Enhances Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C Expression in Human Prostate Cancer PC-3 Cells.
Authors: Lin CE, Chen SU, Lin CC
PLoS ONE, 2012-07-20;7(7):e41096.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Dilated thin-walled blood and lymphatic vessels in human endometrium: a potential role for VEGF-D in progestin-induced break-through bleeding.
Authors: Donoghue JF, McGavigan CJ, Lederman FL
PLoS ONE, 2012-02-17;7(2):e30916.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Autocrine loop between vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and VEGF receptor-3 positively regulates tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in oral squamoid cancer cells.
Authors: Matsuura M, Onimaru M, Yonemitsu Y, Suzuki H, Nakano T, Ishibashi H, Shirasuna K, Sueishi K
Am. J. Pathol., 2009-09-24;175(4):1709-21.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Lymphatic reprogramming of microvascular endothelial cells by CEA-related cell adhesion molecule-1 via interaction with VEGFR-3 and Prox1.
Authors: Kilic N, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Neshat-Vahid S, Irmak S, Obst-Pernberg K, Wurmbach JH, Loges S, Kilic E, Weil J, Lauke H, Tilki D, Singer BB, Ergun S
Blood, 2007-08-30;110(13):4223-33.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
VEGF-C is a trophic factor for neural progenitors in the vertebrate embryonic brain.
Authors: Le Bras B, Barallobre MJ, Homman-Ludiye J, Ny A, Wyns S, Tammela T, Haiko P, Karkkainen MJ, Yuan L, Muriel MP, Chatzopoulou E, Breant C, Zalc B, Carmeliet P, Alitalo K, Eichmann A, Thomas JL
Nat. Neurosci., 2006-02-05;9(3):340-8.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Cyclooxygenase-2 induces EP1- and HER-2/Neu-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor-C up-regulation: a novel mechanism of lymphangiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma.
Authors: Su JL, Shih JY, Yen ML, Jeng YM, Chang CC, Hsieh CY, Wei LH, Yang PC, Kuo ML
Cancer Res., 2004-01-15;64(2):554-64.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C in human pterygium
Authors: Junichi Fukuhara, Satoru Kase, Tsutomu Ohashi, Ryo Ando, Zhenyu Dong, Kousuke Noda et al.
Histochemistry and Cell Biology
-
Discovery of pan-VEGF inhibitory peptides directed to the extracellular ligand-binding domains of the VEGF receptors
Authors: Jussara S. Michaloski, Alexandre R. Redondo, Leila S. Magalhães, Caio C. Cambui, Ricardo J. Giordano
Science Advances
-
Autophagy Control by the VEGF-C/NRP-2 Axis in Cancer and Its Implication for Treatment Resistance
Authors: Marissa J. Stanton, Samikshan Dutta, Heyu Zhang, Navatha Shree Polavaram, Alexey A. Leontovich, Pia Hönscheid et al.
Cancer Research
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human VEGF-C Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human VEGF-C Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: