Human/Mouse Glucokinase/GCK Antibody Summary
Val16-Gln465
Accession # P35557
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
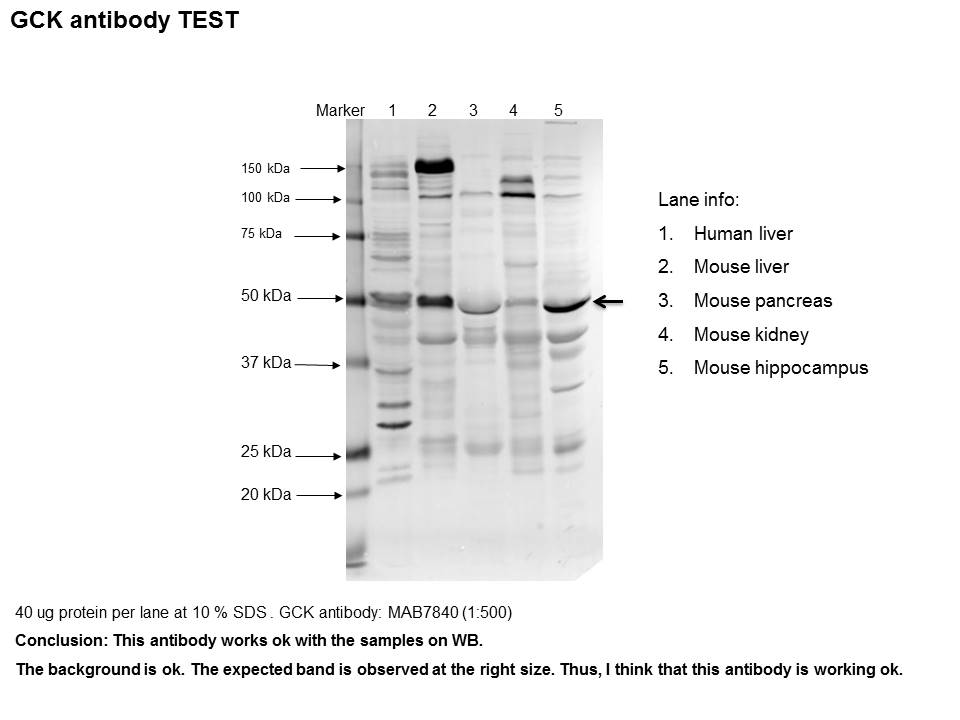
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human and Mouse Glucokinase/GCK by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of Huh-7 human hepatoma cell line, Hepa 1-6 mouse hepatoma cell line, and HT-2 mouse T cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human Glucokinase/GCK Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB7840) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for Glucokinase/GCK at approximately 52 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Glucokinase/GCK
Hexokinases phosphorylate hexose to form hexose 6‑phosphate, the first step for hexose metabolism. There are four mammalian hexokinases (I, II, III and IV) and hexokinase IV is commonly known as glucose kinase (GCK). Unlike hexokinase I, II and III, which have high affinity for glucose and are strongly inhibited by the product, glucose‑6‑phosphate (1), GCK has much lower affinity for glucose and is not inhibited by the product (2, 3). Consequently, GCK has a Km for glucose of approximately 7 mM (4), which is 100 times higher than that of hexokinase I, II, and III. This unique enzymatic property of GCK allows it to respond to blood glucose levels and contribute to the maintenance of blood glucose levels within the normal physiological range of 4 mM to 6 mM. In the pancreatic islets, GCK serves as a glucose sensor to control insulin release in the beta cells, and to control glucagon release in the alpha cells (5). In hepatocytes, GCK responds to changes of ambient glucose levels by increasing or reducing glycogen synthesis. Mutations in GCK have been associated with non‑insulin‑dependent diabetes mellitus (6, 7), maturity‑onset diabetes of the young type 2 (8), and hyperinsulinemia of infancy (9). The enzyme activity was measured using a phosphatase coupled kinase assay (4).
- Aleshin, A.E. et al.(1998) Structure 6:39.
- Takeda, J. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:15200.
- Lange, A.J. et al. (1991) Biochem. J. 277:159.
- Wu, Z.L. (2011) PLoS ONE 6(8):e23172.
- Xu, L.Z. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:9939.
- Gidh-Jain, M. et al. (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90:1932.
- Stoffel, M. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89:7698.
- Hattersley, A.T. et al. (1992) Lancet 339:1307.
- Gloyn, A.L. et al. (2003) Diabetes 52:2433.
Product Datasheets
Citation for Human/Mouse Glucokinase/GCK Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
1 Citation: Showing 1 - 1
-
High Fructose Drives the Serine Synthesis Pathway in Acute Myeloid Leukemic Cells
Authors: Sangmoo Jeong, Angela Maria Savino, Rachel Chirayil, Ersilia Barin, Yuanming Cheng, Sun-Mi Park et al.
Cell Metabolism
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human/Mouse Glucokinase/GCK Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human/Mouse Glucokinase/GCK Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: