Human HGFR/c-MET APC-conjugated Antibody Summary
Glu25-Thr932
Accession # P08581
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
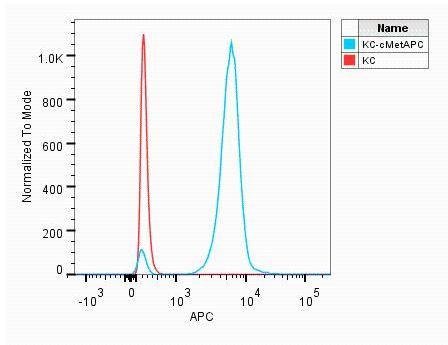
Detection of HGF R/c‑MET in MDA‑MB‑231 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human HGF R/c-MET APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB3582A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC002A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human HGFR/c-MET by Flow Cytometry Influence of selected cytokines on MSC proliferation; receptor expression profiles and concentration. (A) MSC were seeded in 5% pHPL, tPRP and FBS, respectively, and stimulated with for 3 days with 50 ng/ml HGF, 10 ng/ml IGF-1 or 25 ng/ml bFGF. Cell counts were acquired with the CellTiter-Glo assay and then normalized to the unstimulated control to derive relative cell count values. (B)% positivity of IGF, FGF and HGF receptor expression of BM- and LA-MSC (donors 1–3, respectively) in pHPL, tPRP and FBS assessed by flow cytometry. (C – E): IGF, FGF and HGF concentrations were determined by ELISA in pHPL and tPRP supplemented medium (medium, 6 different batches); medium stored for 24 h (control medium) and conditioned by MSC (CM) (each n = 3). Symbols indicate statistically significant diffences between: * stimulation; + supplements; # MSC sources; (one symbol p < 0.05; two symbols p < 0.01). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://bmcmolcellbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2121-14-48), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: HGFR/c-MET
HGF R, also known as Met (from N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induced), is a glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a central role in epithelial morphogenesis and cancer development. HGF R is synthesized as a single chain precursor which undergoes cotranslational proteolytic cleavage. This generates a mature HGF R that is a disulfide-linked dimer composed of a 50 kDa extracellular alpha chain and a 145 kDa transmembrane beta chain (1, 2). The extracellular domain (ECD) contains a seven bladed beta -propeller sema domain, a cysteine-rich PSI/MRS, and four Ig-like E-set domains, while the cytoplasmic region includes the tyrosine kinase domain (3, 4). Proteolysis and alternate splicing generate additional forms of human HGF R which either lack of the kinase domain, consist of secreted extracellular domains, or are deficient in proteolytic separation of the alpha and beta chains (5-7). The sema domain, which is formed by both the alpha and beta chains of HGF R, mediates both ligand binding and receptor dimerization (3, 8). Ligand-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in the cytoplasmic region activates the kinase domain and provides docking sites for multiple SH2-containing molecules (9, 10). HGF stimulation induces HGF R downregulation via internalization and proteasome-dependent degradation (11). In the absence of ligand, HGF R forms non-covalent complexes with a variety of membrane proteins including CD44v6, CD151, EGF R, Fas, Integrin alpha 6/ beta 4, Plexins B1, 2, 3, and MSP R/Ron (12-19). Ligation of one complex component triggers activation of the other, followed by cooperative signaling effects (12-19). Formation of some of these heteromeric complexes is a requirement for epithelial cell morphogenesis and tumor cell invasion (12, 16, 17). Paracrine induction of epithelial cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis results from the stimulation of HGF R on undifferentiated epithelium by HGF released from neighboring mesenchymal cells (20). Genetic polymorphisms, chromosomal translocation, over-expression, and additional splicing and proteolytic cleavage of HGF R have been described in a wide range of cancers (1). Within the ECD, human HGF R shares 86-88% amino acid sequence identity with canine, mouse, and rat HGF R.
- Birchmeier, C. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:915.
- Corso, S. et al. (2005) Trends Mol. Med. 11:284.
- Gherardi, E. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:12039.
- Park, M. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:6379.
- Crepaldi, T. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1750.
- Prat, M. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:5954.
- Rodrigues, G.A. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:2962.
- Kong-Beltran, M. et al. (2004) Cancer Cell 6:75.
- Naldini, L. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:1793.
- Ponzetto, C. et al. (1994) Cell 77:261.
- Jeffers, M. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:799.
- Orian-Rousseau, V. et al. (2002) Genes Dev. 16:3074.
- Klosek, S.K. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336:408.
- Jo, M. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:8806.
- Wang, X. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell 9:411.
- Trusolino, L. et al. (2001) Cell 107:643.
- Giordano, S. et al. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4:720.
- Conrotto, P. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:5131.
- Follenzi, A. et al. (2000) Oncogene 19:3041.
- Sonnenberg, E. et al. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 123:223.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human HGFR/c-MET APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
10
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
A Human Skeletal Muscle Atlas Identifies the Trajectories of Stem and Progenitor Cells across Development and from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
Authors: H Xi, J Langerman, S Sabri, P Chien, CS Young, S Younesi, M Hicks, K Gonzalez, W Fujiwara, J Marzi, S Liebscher, M Spencer, B Van Handel, D Evseenko, K Schenke-La, K Plath, AD Pyle
Cell Stem Cell, 2020-05-11;0(0):.
-
Targeting HGF/c-Met Axis Decreases Circulating Regulatory T Cells Accumulation in Gastric Cancer Patients
Authors: J Palle, L Hirsch, A Lapeyre-Pr, D Malka, M Bourhis, S Pernot, E Marcheteau, T Voron, F Castan, A Lacotte, N Benhamouda, C Tanchot, E François, F Ghiringhel, C de la Fouc, A Zaanan, E Tartour, J Taieb, M Terme
Cancers, 2021-11-05;13(21):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
CX3CL1 Overexpression Prevents the Formation of Lung Metastases in Trastuzumab-Treated MDA-MB-453-Based Humanized Tumor Mice (HTM)
Authors: AK Wege, TF Dreyer, A Teoman, O Ortmann, G Brockhoff, H Bronger
Cancers, 2021-05-18;13(10):.
Species: Xenograft
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Biologically driven cut-off definition of lymphocyte ratios in metastatic breast cancer and association with exosomal subpopulations and prognosis
Authors: L Gerratana, D Basile, B Toffoletto, M Bulfoni, S Zago, A Magini, M Lera, G Pelizzari, P Parisse, L Casalis, MG Vitale, V Fanotto, M Bonotto, F Caponnetto, M Bartoletti, C Lisanti, AM Minisini, C Emiliani, C Di Loreto, G Fasola, F Curcio, AP Beltrami, D Cesselli, F Puglisi
Sci Rep, 2020-04-24;10(1):7010.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Induction of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Down-regulation through Antibody-mediated Receptor Clustering
Authors: W Li, A Dick, F Lu, H Zhang, H Sun
Sci Rep, 2019-02-13;9(1):1988.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Reviving oncogenic addiction to MET bypassed by BRAF (G469A) mutation
Authors: AR Virzì, A Gentile, S Benvenuti, PM Comoglio
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2018-09-17;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Premyogenic progenitors derived from human pluripotent stem cells expand in floating culture and differentiate into transplantable myogenic progenitors
Authors: F Sakai-Take, A Narita, S Masuda, T Wakamatsu, N Watanabe, T Nishiyama, K Nogami, M Blanc, S Takeda, Y Miyagoe-Su
Sci Rep, 2018-04-26;8(1):6555.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
GAA Deficiency in Pompe Disease Is Alleviated by Exon Inclusion in iPSC-Derived Skeletal Muscle Cells
Authors: E van der Wa, AJ Bergsma, TJM van Gestel, SLM In 't Groe, H Zaehres, MJ Araúzo-Bra, HR Schöler, AT van der Pl, WWMP Pijnappel
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2017-03-14;7(0):101-115.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Functional and differential proteomic analyses to identify platelet derived factors affecting ex vivo expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells.
Authors: Kinzebach S, Dietz L, Kluter H, Thierse H, Bieback K
BMC Cell Biol, 2013-10-30;14(0):48.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay.
Authors: Baccelli I, Schneeweiss A, Riethdorf S, Stenzinger A, Schillert A, Vogel V, Klein C, Saini M, Bauerle T, Wallwiener M, Holland-Letz T, Hofner T, Sprick M, Scharpff M, Marme F, Sinn H, Pantel K, Weichert W, Trumpp A
Nat Biotechnol, 2013-04-21;31(6):539-44.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human HGFR/c-MET APC-conjugated Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human HGFR/c-MET APC-conjugated Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: