Human/Hamster ACE-2 Antibody Summary
Gln18-Ser740 (predicted)
Accession # Q9BYF1
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human ACE‑2 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of NS0 mouse myeloma cell line and human kidney tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human ACE-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB933) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF007). A specific band was detected for ACE-2 at approximately 110 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
ACE‑2 in Human Kidney. ACE-2 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using Mouse Anti-Human ACE-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB933) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS002) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surface of epithelial cells in convoluted tubules. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
ACE‑2 in Hamster Lung. ACE‑2 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of hamster lung using Mouse Anti-Human ACE‑2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB933) at 10 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to respiratory bronchioles. Staining was performed our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human ACE-2 by Immunohistochemistry In microvasculature, ACE2 is putatively expressed in pericytes. (A) Representative image of human pancreatic Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) section stained for ACE2 in case #301118. In panel-a, a representative image of a pancreatic section showing two adjacent lobules (blue and red dotted lines) with different staining for ACE2 in endothelial cells/pericytes. A specific segmentation of the two lobules with high (blue) (zoom-in, panel-b) and low or null expression of ACE2 (red) (zoom-in, panel-c) is shown, suggesting lobularity of ACE2 expression in exocrine endothelial cells/pericytes of human pancreas. Scale bar in panel-a: 100 µm. Scale bar in panels-b and -c: 30 µm. (B) Double immunofluorescence staining of ACE2 (green) and CD31 (red) in FFPE pancreas sections from Body01A of Case #110118 (panels-a to -d) and of Body01B of Case #141117 (panels-e to -i). Digital zoom-in overlay images are shown in panels-d, -h and -i. Scale bar in panels-d and -g: 100 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33281748), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human ACE-2 by Immunohistochemistry ACE2 staining pattern in human pancreas. Immunohistochemistry for ACE2 in human pancreatic tissue sections (case #110118) using R&D MAB933 antibody. ACE2 is markedly expressed in microvasculature associated cells (A, B) in some rare ductal cells (C, D) and in a subset of endocrine cells within pancreatic islets (E, F). Scale bars in (A, C, E) 150 µm. Scale bars in (B, D, F) 70 µm. Zoom-in images are reported in (B, D, F). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33281748), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human ACE-2 by Immunohistochemistry In microvasculature, ACE2 is putatively expressed in pericytes. (A) Representative image of human pancreatic Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) section stained for ACE2 in case #301118. In panel-a, a representative image of a pancreatic section showing two adjacent lobules (blue and red dotted lines) with different staining for ACE2 in endothelial cells/pericytes. A specific segmentation of the two lobules with high (blue) (zoom-in, panel-b) and low or null expression of ACE2 (red) (zoom-in, panel-c) is shown, suggesting lobularity of ACE2 expression in exocrine endothelial cells/pericytes of human pancreas. Scale bar in panel-a: 100 µm. Scale bar in panels-b and -c: 30 µm. (B) Double immunofluorescence staining of ACE2 (green) and CD31 (red) in FFPE pancreas sections from Body01A of Case #110118 (panels-a to -d) and of Body01B of Case #141117 (panels-e to -i). Digital zoom-in overlay images are shown in panels-d, -h and -i. Scale bar in panels-d and -g: 100 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33281748), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human ACE-2 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence In microvasculature, ACE2 is putatively expressed in pericytes. (A) Representative image of human pancreatic Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) section stained for ACE2 in case #301118. In panel-a, a representative image of a pancreatic section showing two adjacent lobules (blue and red dotted lines) with different staining for ACE2 in endothelial cells/pericytes. A specific segmentation of the two lobules with high (blue) (zoom-in, panel-b) and low or null expression of ACE2 (red) (zoom-in, panel-c) is shown, suggesting lobularity of ACE2 expression in exocrine endothelial cells/pericytes of human pancreas. Scale bar in panel-a: 100 µm. Scale bar in panels-b and -c: 30 µm. (B) Double immunofluorescence staining of ACE2 (green) and CD31 (red) in FFPE pancreas sections from Body01A of Case #110118 (panels-a to -d) and of Body01B of Case #141117 (panels-e to -i). Digital zoom-in overlay images are shown in panels-d, -h and -i. Scale bar in panels-d and -g: 100 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33281748), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
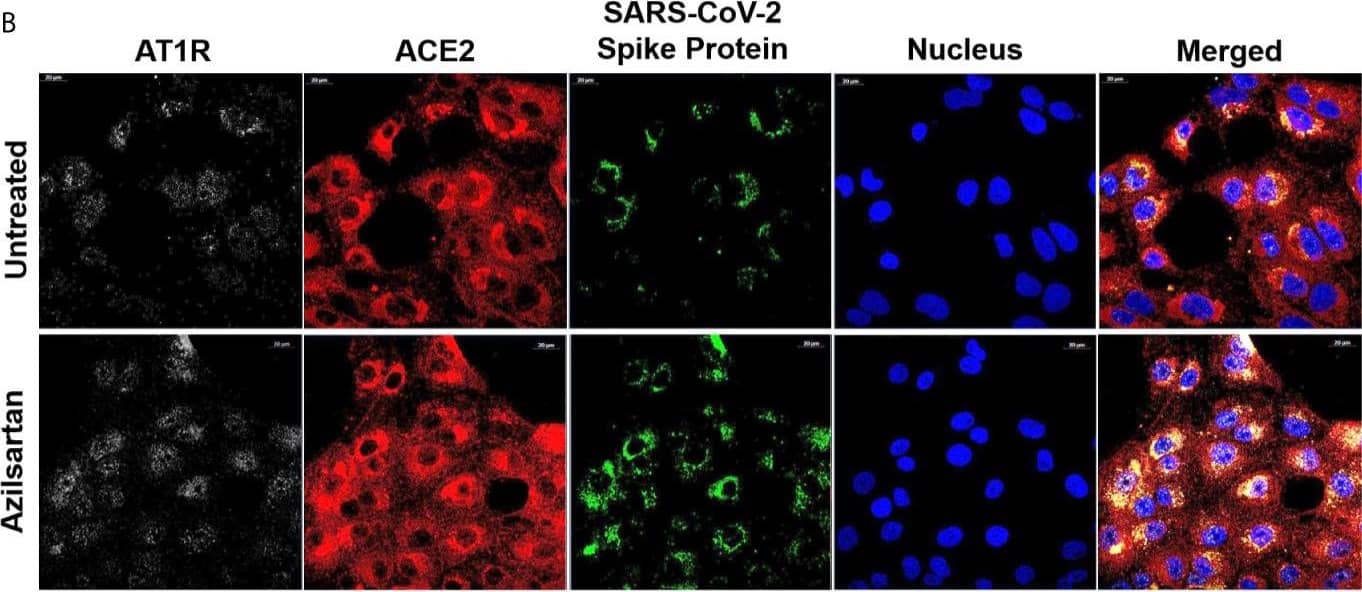
Detection of Chlorocebus sabaeus ACE-2 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Modulation of cell surface-expressed ATR1 and ACE2 molecules in Vero E6 cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 (24 h.p.i) and treated with Azilsartan (15 µM) for 72 hours by immunofluorescence microscopy. (A) Schematic flow of the analysis: Vero E6 cells were treated with various ARBs (the MTT assay previously defined non-cytotoxic concentrations: Azilosartan 15µM; Eprosartan 30µM; Irbesartan 60µM; Losartan 7µM; Olmesartan 15µM; Telmisartan 7µM; Valsartan 7µM) for 72 hours and were subsequently infected for analysis of ACE2 and ATR1 on treated and infected cells, 24 hours post-infection (h.p.i.). (B) The panel presents SARS-CoV-2 infected cells after incubation with Azilsartan (15 µM) and evaluation of fluorescence corresponding to the ATR1, ACE2, viral spike protein, and the nucleus of the cells. The merge of the images is displayed at the right of the panel. Images were acquired using a confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM 800) with a 63X/1.4 oil objective. (C) Quantitative representation of Mean Fluorescence corresponding to ATR1 and ACE2 molecules expression on VERO E6 cells treated or not treated with Azilsartan and SARS-CoV-2 in the cells. ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34178717), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: ACE-2
Angiogensin I Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE-2), also called ACEH (ACE homolog), is a type I transmembrane zinc protease that cleaves angiotensins I and II to produce vasodilatory and anti-proliferative peptides. The balance between ACE-1 and ACE-2 activity is critical for maintaining cardiovascular, renal, and pulmonary function (1). ACE-2 also functions as the cellular uptake receptor for the SARS coronoavirus. Within the extracellular domain, human ACE-2 shares 83% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat ACE-2. Human ACE-2 has about 40% amino acid identity to the N- and C-terminal domains of human somatic ACE. The predicted human ACE-2 protein sequence consists of 805 amino acids, including a N-terminal signal peptide, a single catalytic domain, a C-terminal membrane anchor, and a short cytoplasmic tail. ACE-2 mRNA is found at high levels in testis, kidney and heart and at moderate levels in colon, small intestine and ovary. Classical ACE inhibitors such as captopril and lisinopril do not inhibit ACE-2 activity. Novel peptide inhibitors of ACE-2 do not inhibit ACE activity (2). Genetic data from Drosophila, mice and rats show that ACE-2 is an essential regulator of heart function in vivo (3). ACE-2 isoforms of 75 kDa and 120 kDa are differentially expressed between lung and kidney, respectively, and a shed soluble form is generated by TACE/ADAM17 mediated cleavage.
- Tipnis, S.R. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:33238.
- Crackower, M.A. et al. (2002) Nature 417:822.
- Huang, L. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:15532.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human/Hamster ACE-2 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
59
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Pulmonary stromal expansion and intra-alveolar coagulation are primary causes of COVID-19 death
Authors: L Szekely, B Bozoky, M Bendek, M Ostad, P Lavignasse, L Haag, J Wu, X Jing, S Gupta, E Saccon, A Sönnerborg, Y Cao, M Björnstedt, A Szakos
Heliyon, 2021-05-24;7(5):e07134.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 binding receptors and miscellaneous targets as well as mucosal surface area of the human lacrimal drainage system
Authors: Rau, AL;Schicht, M;Zahn, I;Ali, MJ;Coroneo, MT;Paulsen, F;
The ocular surface
Species: Human
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
SARS-CoV-2 virus associated angiotensin converting enzyme 2 expression modulation in colorectal cancer: Insights from mRNA and protein analysis COVID-19 associated (ACE2) expression in colorectal cancer
Authors: Alotaibi, MA;Al-Hazani, TMI;Alwaili, MA;Jalal, AS;Alshaya, DS;Safhi, FA;Alamoudi, MO;Alarifi, S;Saeed Al-Qahtani, W;
Microbial pathogenesis
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Human Taste Cells Express ACE2: a Portal for SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Authors: Máire E Doyle, Ashley Appleton, Qing-Rong Liu, Qin Yao, Caio Henrique Mazucanti, Josephine M Egan
bioRxiv
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelialitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Evidence for VE-Cadherin Cleavage by ACE2
Authors: Bouillet, L;Deroux, A;Benmarce, M;Guérin, C;Bouvet, L;Garnier, O;Martin, DK;Vilgrain, I;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Serum
Applications: Western Blot -
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor (LDLR) Is Involved in Internalization of Lentiviral Particles Pseudotyped with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in Ocular Cells
Authors: Uppal S, Postnikova O, Villasmil R et al.
International journal of molecular sciences
-
Neuronal progenitors of the dentate gyrus express the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor during migration in the developing human hippocampus
Authors: José Manuel Hernandez-Lopez, Cristina Hernandez-Medina, Cristina Medina-Corvalan, Mónica Rodenas, Almagro Francisca, Claudia Perez-Garcia et al.
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
-
Rapid Generation of Pulmonary Organoids from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells by Co-Culturing Endodermal and Mesodermal Progenitors for Pulmonary Disease Modelling
Authors: Mitchell, A;Yu, C;Zhao, X;Pearmain, L;Shah, R;Hanley, KP;Felton, T;Wang, T;
Biomedicines
Species: Human
Sample Types: Organoids
Applications: IHC -
Association between tissue stress reaction and ACE2/TMPRSS2 expression in endometria of reproductive aged women before and during Covid-19 pandemic
Authors: Ogawa, K;Khan, KN;Koshiba, A;Fujishita, A;Horiguchi, G;Teramukai, S;Itoh, K;Guo, SW;Mori, T;
BMC women's health
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Age-dependent regulation of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry genes and cell death programs correlates with COVID-19 disease severity
Authors: Zintis Inde, Clarence Yapp, Gaurav N. Joshi, Johan Spetz, Cameron Fraser, Brian Deskin et al.
bioRxiv
-
Mouse models susceptible to HCoV-229E and HCoV-NL63 and cross protection from challenge with SARS-CoV-2
Authors: Donglan Liu, Chunke Chen, Dingbin Chen, Airu Zhu, Fang Li, Zhen Zhuang et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
-
Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme type 2 expression is increased in pancreatic islets of type 2 diabetic donors
Authors: Fignani, D;Pedace, E;Licata, G;Grieco, G;Aiello, E;Luca, C;Marselli, L;Marchetti, P;Sebastiani, G;Dotta, F;
medRxiv
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC/IF -
Ocular tropism of SARS-CoV-2 in animal models with retinal inflammation via neuronal invasion following intranasal inoculation
Authors: GU Jeong, HJ Kwon, WH Ng, X Liu, HW Moon, GY Yoon, HJ Shin, IC Lee, ZL Ling, AG Spiteri, NJC King, A Taylor, JS Chae, C Kim, DG Ahn, KD Kim, YB Ryu, SJ Kim, S Mahalingam, YC Kwon
Nature Communications, 2022-12-12;13(1):7675.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC/IF -
Human Type II Taste Cells Express Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Are Infected by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Authors: Máire E. Doyle, Ashley Appleton, Qing-Rong Liu, Qin Yao, Caio H. Mazucanti, Josephine M. Egan
The American Journal of Pathology
-
Goblet Cell Hyperplasia Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Authors: Jaspreet Osan, Sattya N. Talukdar, Friederike Feldmann, Beth Ann DeMontigny, Kailey Jerome, Kristina L. Bailey et al.
Microbiology Spectrum
-
Expression of SARS-CoV-2-Related Surface Proteins in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients and the Influence of Standard of Care Therapy
Authors: Christophe Deben, Maxim Le Compte, Vasiliki Siozopoulou, Hilde Lambrechts, Christophe Hermans, Ho Wa Lau et al.
Cancers (Basel)
-
GDF15 and ACE2 stratify COVID-19 patients according to severity while ACE2 mutations increase infection susceptibility
Authors: Margalida Torrens-Mas, Catalina M. Perelló-Reus, Neus Trias-Ferrer, Lesly Ibargüen-González, Catalina Crespí, Aina Maria Galmes-Panades et al.
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
-
Intronic regulation of SARS-CoV-2 receptor (ACE2) expression mediated by immune signaling and oxidative stress pathways
Authors: Daniel Richard, Pushpanathan Muthuirulan, Jennifer Aguiar, Andrew C. Doxey, Arinjay Banerjee, Karen Mossman et al.
iScience
-
Atypical Unilateral SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in a Single Lung Re-Transplanted Patient: A Case Report
Authors: M Furstenber, F Gallais, S Freudenber, R Kessler, MP Chenard, B Renaud-Pic
Transplantation Proceedings, 2022-05-30;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Control of CDH1/E-Cadherin Gene Expression and Release of a Soluble Form of E-Cadherin in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Caco-2 Intestinal Cells: Physiopathological Consequences for the Intestinal Forms of COVID-19
Authors: Ikram Omar Osman, Clémence Garrec, Gabriel Augusto Pires de Souza, Ana Zarubica, Djamal Brahim Belhaouari, Jean-Pierre Baudoin et al.
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
-
COVID‐19 and vertical transmission: assessing the expression of ACE2/TMPRSS2 in the human fetus and placenta to assess the risk of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection
Authors: M A Beesley, J R Davidson, F Panariello, S Shibuya, D Scaglioni, B C Jones et al.
BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology
-
OM-85 Broncho-Vaxom�, a Bacterial Lysate, Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Binding Proteins on Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells
Authors: L Fang, L Zhou, M Tamm, M Roth
Biomedicines, 2021-10-26;9(11):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Viral S protein histochemistry reveals few potential SARS-CoV-2 entry sites in human ocular tissues
Authors: Gottfried Martin, Julian Wolf, Thabo Lapp, Hansjürgen T. Agostini, Günther Schlunck, Claudia Auw-Hädrich et al.
Scientific Reports
-
ZMPSTE24 Regulates SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein–enhanced Expression of Endothelial PAI-1
Authors: Mingming Han, Deepesh Pandey
American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology
-
Colon adenocarcinoma-derived cells possessing stem cell function can be modulated using renin-angiotensin system inhibitors
Authors: MJ Munro, L Peng, SK Wickremese, ST Tan
PLoS ONE, 2021-08-24;16(8):e0256280.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
ACE2 protein expression within isogenic cell lines is heterogeneous and associated with distinct transcriptomes
Authors: EJ Sherman, BT Emmer
Scientific Reports, 2021-08-05;11(1):15900.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Western Blot -
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs Antihypertensive Agents) Increase Replication of SARS-CoV-2 in Vero E6 Cells
Authors: Gabriel Augusto Pires de Souza, Ikram Omar Osman, Marion Le Bideau, Jean-Pierre Baudoin, Rita Jaafar, Christian Devaux et al.
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
-
Coronavirus-specific antibody production in middle-aged mice requires phospholipase A2G2D
Authors: Jian Zheng, David Meyerholz, Lok-Yin Roy Wong, Michael Gelb, Makoto Murakami, Stanley Perlman
Journal of Clinical Investigation
-
Expression of Components of the Renin-Angiotensin System by Cancer Stem Cells in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
Authors: S Siljee, B Milne, HD Brasch, N Bockett, J Patel, PF Davis, A Kennedy-Sm, T Itinteang, ST Tan
Biomolecules, 2021-04-07;11(4):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Tissue Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Role of Cigarette Smoke on Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 Protein Membrane Expression in Bronchial Epithelial Cells Using an Air-Liquid Interface Model
Authors: Massimo Caruso, Alfio Distefano, Rosalia Emma, Michelino Di Rosa, Giuseppe Carota, Sonja Rust et al.
Frontiers in Pharmacology
-
SARS‐CoV‐2 infection aggravates chronic comorbidities of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes in mice
Authors: Yuanwu Ma, Dan Lu, Linlin Bao, Yajin Qu, Jiangning Liu, Xiaolong Qi et al.
Animal Models and Experimental Medicine
-
Malignancy going viral: ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression in conjunctival neoplastic diseases
Authors: Rafael S. Grajewski, Alexander C. Rokohl, Martina Becker, Friedrich Paulsen, Ludwig M. Heindl
Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger
-
Cancer Stem Cells in Metastatic Head and Neck Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Express Components of the Renin-Angiotensin System
Authors: S Siljee, O Buchanan, HD Brasch, N Bockett, J Patel, E Paterson, GL Purdie, PF Davis, T Itinteang, ST Tan
Cells, 2021-01-27;10(2):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
Generation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Pseudotyped Virus for Viral Entry and Neutralization Assays: A 1-Week Protocol
Authors: Jose Manuel Condor Capcha, Guerline Lambert, Derek M. Dykxhoorn, Alessandro G. Salerno, Joshua M. Hare, Michael A. Whitt et al.
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine
-
A missing link between SARS‐CoV‐2 and the eye?: ACE2 expression on the ocular surface
Authors: Rafael S. Grajewski, Alexander C. Rokohl, Martina Becker, Felix Dewald, Clara Lehmann, Gerd Fätkenheuer et al.
Journal of Medical Virology
-
Comparison of Four SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assays
Authors: L Riepler, A Rössler, A Falch, A Volland, W Borena, D von Laer, J Kimpel
Vaccines, 2020-12-28;9(1):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
-
Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication by blocking membrane fusion
Authors: Ruochen Zang, James Brett Case, Eylan Yutuc, Xiucui Ma, Sheng Shen, Maria Florencia Gomez Castro et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
-
Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Factors in the Pancreas of Normal Organ Donors and Individuals with COVID-19
Authors: Kusmartseva I, Wu W, Syed F et al.
Cell Metabolism
-
SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Type 2 (ACE2) Is Expressed in Human Pancreatic beta -Cells and in the Human Pancreas Microvasculature
Authors: Daniela Fignani, Giada Licata, Noemi Brusco, Laura Nigi, Giuseppina E. Grieco, Lorella Marselli et al.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)
-
ACE2 localizes to the respiratory cilia and is not increased by ACE inhibitors or ARBs
Authors: IT Lee, T Nakayama, CT Wu, Y Goltsev, S Jiang, PA Gall, CK Liao, LC Shih, CM Schürch, DR McIlwain, P Chu, NA Borchard, D Zarabanda, SS Dholakia, A Yang, D Kim, H Chen, T Kanie, CD Lin, MH Tsai, KM Phillips, R Kim, JB Overdevest, MA Tyler, CH Yan, CF Lin, YT Lin, DT Bau, GJ Tsay, ZM Patel, YA Tsou, A Tzankov, MS Matter, CJ Tai, TH Yeh, PH Hwang, GP Nolan, JV Nayak, PK Jackson
Nat Commun, 2020-10-28;11(1):5453.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Human Lung Stem Cell-Based Alveolospheres Provide Insights into SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Interferon Responses and Pneumocyte Dysfunction
Authors: H Katsura, V Sontake, A Tata, Y Kobayashi, CE Edwards, BE Heaton, A Konkimalla, T Asakura, Y Mikami, EJ Fritch, PJ Lee, NS Heaton, RC Boucher, SH Randell, RS Baric, PR Tata
Cell Stem Cell, 2020-10-21;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Expression of the COVID‐19 receptor ACE2 in the human conjunctiva
Authors: Clemens Lange, Julian Wolf, Claudia Auw‐Haedrich, Anja Schlecht, Stefaniya Boneva, Thabo Lapp et al.
Journal of Medical Virology
-
Heterogeneous expression of the SARS-Coronavirus-2 receptor ACE2 in the human respiratory tract
Authors: ME Ortiz, A Thurman, AA Pezzulo, MR Leidinger, JA Klesney-Ta, PH Karp, P Tan, C Wohlford-L, PB McCray, DK Meyerholz
EBioMedicine, 2020-09-21;60(0):102976.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Gene expression and in situ protein profiling of candidate SARS-CoV-2 receptors in human airway epithelial cells and lung tissue
Authors: Jennifer A. Aguiar, Benjamin J-M. Tremblay, Michael J. Mansfield, Owen Woody, Briallen Lobb, Arinjay Banerjee et al.
European Respiratory Journal
-
ACE2 Protein Landscape in the Head and Neck Region: The Conundrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Authors: G Descamps, L Verset, A Trelcat, C Hopkins, JR Lechien, F Journe, S Saussez
Biology (Basel), 2020-08-18;9(8):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Heterogeneous expression of the SARS-Coronavirus-2 receptor ACE2 in the human respiratory tract
Authors: ME Ortiz Beza, A Thurman, AA Pezzulo, MR Leidinger, JA Klesney-Ta, PH Karp, P Tan, C Wohlford-L, PB McCray, DK Meyerholz
bioRxiv, 2020-08-13;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Generation of a Broadly Useful Model for COVID-19 Pathogenesis, Vaccination, and Treatment
Authors: Jing Sun, Zhen Zhuang, Jian Zheng, Kun Li, Roy Lok-Yin Wong, Donglan Liu et al.
Cell
-
The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues
Authors: Feria Hikmet, Loren Méar, Åsa Edvinsson, Patrick Micke, Mathias Uhlén, Cecilia Lindskog
Molecular Systems Biology
-
Robust ACE2 protein expression localizes to the motile cilia of the respiratory tract epithelia and is not increased by ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers
Authors: IT Lee, T Nakayama, CT Wu, Y Goltsev, S Jiang, PA Gall, CK Liao, LC Shih, CM Schurch, DR McIlwain, P Chu, NA Borchard, D Zarabanda, SS Dholakia, A Yang, D Kim, T Kanie, CD Lin, MH Tsai, KM Phillips, R Kim, JB Overdevest, MA Tyler, CH Yan, CF Lin, YT Lin, DT Bau, GJ Tsay, ZM Patel, YA Tsou, CJ Tai, TH Yeh, PH Hwang, GP Nolan, JV Nayak, PK Jackson
medRxiv, 2020-05-12;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a potential therapeutic target for EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
Authors: M Yamaguchi, S Hirai, T Sumi, Y Tanaka, M Tada, Y Nishii, T Hasegawa, H Uchida, G Yamada, A Watanabe, H Takahashi, Y Sakuma
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2017-04-20;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein.
Authors: Heurich A, Hofmann-Winkler H, Gierer S, Liepold T, Jahn O, Pohlmann S
J Virol, 2013-11-13;88(2):1293-307.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Functional Assay, Western Blot -
Selective and specific regulation of ectodomain shedding of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 by tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme.
Authors: Iwata M, Silva Enciso JE, Greenberg BH
Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 2009-09-16;297(5):C1318-29.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 confers endothelial protection and attenuates atherosclerosis.
Authors: Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Teoh H, Wang G, Shukla PC, Levitt KS, Oudit GY, Al-Omran M, Stewart DJ, Slutsky AS, Peterson MD, Backx PH, Penninger JM, Verma S
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 2008-07-25;295(4):H1377-84.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
JNK and PI3k/Akt signaling pathways are required for establishing persistent SARS-CoV infection in Vero E6 cells.
Authors: Mizutani T, Fukushi S, Saijo M, Kurane I, Morikawa S
Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2005-06-30;1741(1):4-10.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Susceptibility to SARS coronavirus S protein-driven infection correlates with expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 and infection can be blocked by soluble receptor.
Authors: Hofmann H, Geier M, Marzi A, Krumbiegel M, Peipp M, Fey GH, Gramberg T, Pohlmann S
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2004-07-09;319(4):1216-21.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Destabilizes Microvascular Homeostasis
Authors: Panigrahi S, Goswami T, Ferrari B et al.
Microbiology spectrum
-
Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Metastatic Malignant Melanoma Express Components of the Renin-Angiotensin System
Authors: Siljee S, Pilkington T, Brasch HD et al.
Cell Mol Neurobiol
-
Goblet Cell Hyperplasia Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection in COPD
Authors: JK Osan, SN Talukdar, F Feldmann, B Ann DeMont, K Jerome, KL Bailey, H Feldmann, M Mehedi
bioRxiv, 2020-11-12;0(0):.
-
Systematic Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Protein Distribution along Viral Entry Routes in Humans
Authors: Brautigam K, Reinhard S, Galvan JA et al.
Respiration; international review of thoracic diseases
FAQs
-
Is Catalog # MAB933 kappa or lambda light chain?
MAB933 is kappa light chain.
-
Does Human/Hamster ACE-2 Antibody, Catalog# MAB933, detect mouse ACE2?
We have not evaluated cross-reactivity of this antibody to mouse ACE-2. Human ACE-2 shares 83% amino acid sequence identity with mouse ACE-2. We have one citation on our webpage where researcher reports using MAB933 to detect mouse ACE-2.
Reviews for Human/Hamster ACE-2 Antibody
Average Rating: 4.5 (Based on 4 Reviews)
Have you used Human/Hamster ACE-2 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:






