Human DPPIV/CD26 Antibody Summary
Asp34-Pro766
Accession # Q53TN1
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPPIV/CD26 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysate of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). PVDF membrane was probed with 0.2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human DPPIV/CD26 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1180) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF109). A specific band was detected for DPPIV/CD26 at approximately 110 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPPIV/CD26 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysate of LoVo human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human DPPIV/CD26 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1180) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF017). A specific band was detected for DPPIV/CD26 at approximately 110 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
DPPIV/CD26 in Human PBMCs. DPPIV/CD26 was detected in immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using Goat Anti-Human DPPIV/CD26 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1180) at 1.7 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and plasma membranes. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View Larger
DPPIV/CD26 in Human Psoriatic Skin. DPPIV/CD26 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human psoriatic skin using Goat Anti-Human DPPIV/CD26 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1180) at 1 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to keratinocytes. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPPIV/CD26 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of LoVo human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for DPPIV/CD26 at approximately 168 kDa (as indicated) using 2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human DPPIV/CD26 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1180) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPPIV/CD26 by Western Blot Expression of different markers in the eight human colon cancer cell lines analyzed. (A) Western blot analysis of EpCAM, LGR5, CD26, E-cadherin and vimentin expression in total cell extracts from the eight cell lines (20 μg of protein in each line). Data shown are representative of three experiments. (B) E-cadherin and EpCAM expression analysis by immunofluorescence in HT-29 and Caco-2 cells. (C) CD44 and CD26 expression analysis by immunofluorescence in HT-29 and Caco-2 cells. (D) LGR5 expression analysis by immunofluorescence in DLD-1 and Caco-2 cells. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars: 50 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31285270), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPPIV/CD26 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Comparison of histone modifier sets between two hepatic cell cultures.(A) Differentiation scheme of hESC towards Hepatocyte-like cells (Hep-like). (B) Hep-like cells were generated from hESC and stained with antibodies specific for DPP4 and albumin. Nuclei were stained with the DNA dye H-33342 (blue). Scale bars: 100 µm. (C) RT-qPCR data from three independent experiments for hepatic (ALB, CYP3A, CYP7A1, DPP4, HNF4, MET) and neuronal (TH, DCX, TUBB3) markers. Relative gene expression was calculated using hESC as a calibrator and a set of three reference genes (HPRT, RPL13A, GAPDH). (D) Transcript levels of epigenetic modifiers were measured by RT-qPCR in human liver (huHep), Hep-like islets (Hep-like) and embryonic stem cells (hESC). Data for huHep and Hep-like are indicated as relative change compared to hESC (as reference cell). For comparative display, a scatter plot was constructed so that differentially expressed genes that show pos. association (between Hep-like and huHep) are found in red fields, and those that differed in the sense of regulation fall into blue fields. Values of >10 were set to 10. For quadrant count ratio analysis (QCR) only expression values >2 or <−2 were included. (E) The data measured in D were plotted as heat map, sorted according to rel. huHep expression levels. Transcripts that were >2-fold higher expressed in tissue than in hESC are marked in red, >2-fold lower expression is marked in blue. The color scale ranges from a fold regulation of −20 (dark blue) to +20 (dark red). Measures of variance and p-values are indicated in the supplemental material, genes not regulated significantly (vs. hESC) are displayed as “n.s.”. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102035), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPPIV/CD26 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Comparison of histone modifier sets between two hepatic cell cultures.(A) Differentiation scheme of hESC towards Hepatocyte-like cells (Hep-like). (B) Hep-like cells were generated from hESC and stained with antibodies specific for DPP4 and albumin. Nuclei were stained with the DNA dye H-33342 (blue). Scale bars: 100 µm. (C) RT-qPCR data from three independent experiments for hepatic (ALB, CYP3A, CYP7A1, DPP4, HNF4, MET) and neuronal (TH, DCX, TUBB3) markers. Relative gene expression was calculated using hESC as a calibrator and a set of three reference genes (HPRT, RPL13A, GAPDH). (D) Transcript levels of epigenetic modifiers were measured by RT-qPCR in human liver (huHep), Hep-like islets (Hep-like) and embryonic stem cells (hESC). Data for huHep and Hep-like are indicated as relative change compared to hESC (as reference cell). For comparative display, a scatter plot was constructed so that differentially expressed genes that show pos. association (between Hep-like and huHep) are found in red fields, and those that differed in the sense of regulation fall into blue fields. Values of >10 were set to 10. For quadrant count ratio analysis (QCR) only expression values >2 or <−2 were included. (E) The data measured in D were plotted as heat map, sorted according to rel. huHep expression levels. Transcripts that were >2-fold higher expressed in tissue than in hESC are marked in red, >2-fold lower expression is marked in blue. The color scale ranges from a fold regulation of −20 (dark blue) to +20 (dark red). Measures of variance and p-values are indicated in the supplemental material, genes not regulated significantly (vs. hESC) are displayed as “n.s.”. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102035), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
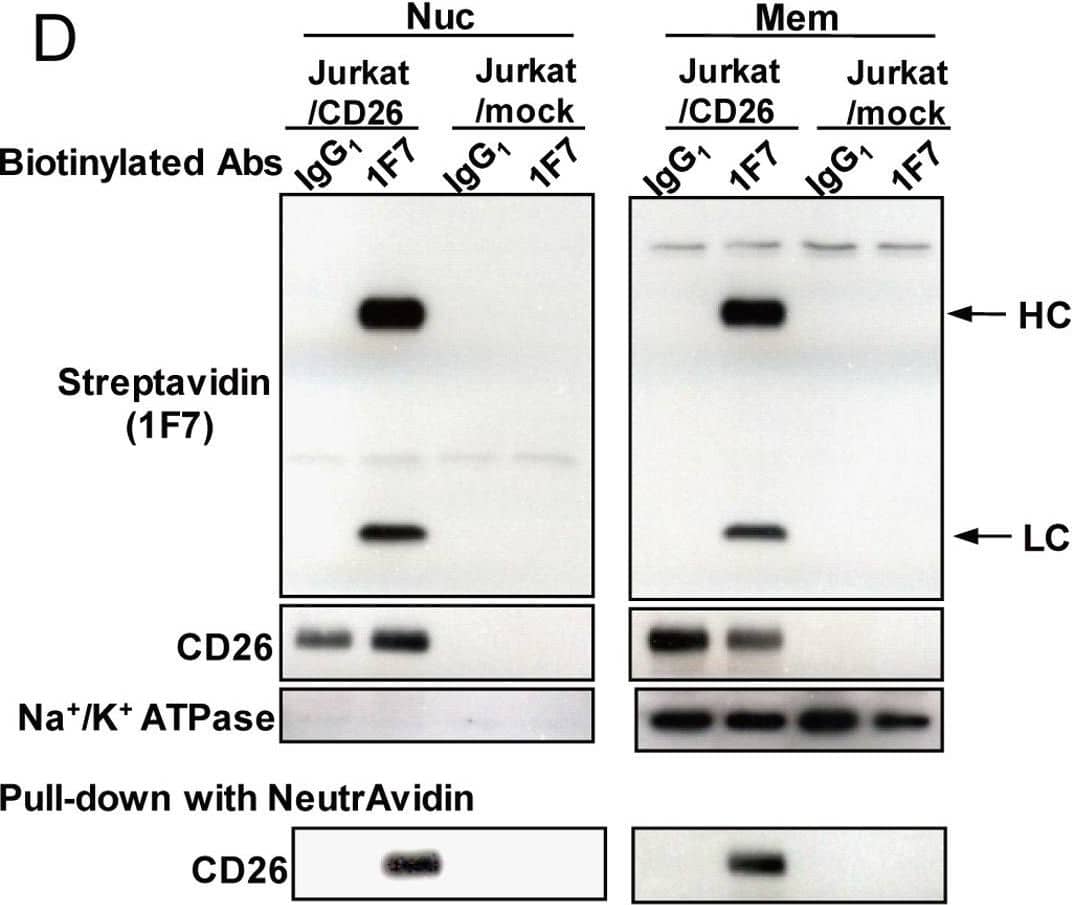
Detection of DPPIV/CD26 by Western Blot Nuclear Translocation of Antitumor CD26 mAbs in Cancer Cells. (D) Jurkat/mock or Jurkat/CD26 cells incubated with biotin-labeled control IgG1 or 1F7 for 1 hour. Nuclear (Nuc)&membrane (Mem) extracts of these cells pulled-down with Neutravidin,&then subjected to immunoblot analysis using streptavidin or antibodies to CD26 or Na+/K+ ATPase (membrane marker). HC, heavy chain; LC, light chain. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23638030), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: DPPIV/CD26
DPPIV/CD26 (EC 3.4.14.5) is a serine exopeptidase that releases Xaa-Pro dipeptides from the N-terminus of oligo- and polypeptides. It is a type II membrane protein consisting of a short cytoplasmic tail, a transmembrane domain, and a long extracellular domain. The extracellular domain contains glycosylation sites, a cysteine-rich region and the catalytic active site (Ser, Asp and His charge relay system). The amino acid sequence of the mouse DPPIV/CD26 extracellular domain is 84% and 91% identical to the human and rat counterparts, respectively. In the native state, DPPIV/CD26 is present as a noncovalently linked homodimer on the cell surface of a variety of cell types. The soluble form is also detectable in human serum and other body fluids, the levels of which may have clinical significance in patients with cancer, liver and kidney diseases, and depression.
DPPIV/CD26 plays an important role in many biological and pathological processes. It functions as T cell-activating molecule (THAM). It serves as a cofactor for entry of HIV in CD4+ cells. It binds adenosine deaminase, the deficiency of which causes severe combined immunodeficiency disease in humans. It cleaves chemokines such as stromal-cell-derived factor 1 alpha and macrophage-derived chemokine. It degrades peptide hormones such as glucagon. It truncates procalcitonin, a marker for systemic bacterial infections with elevated levels detected in patients with thermal injury, sepsis and severe infection, and in children with bacterial meningitis.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human DPPIV/CD26 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
56
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugate with Anti-CD26 Humanized Monoclonal Antibody and Transcription Factor IIH (TFIIH) Inhibitor, Triptolide, Inhibits Tumor Growth via Impairing mRNA Synthesis
Authors: Hayashi M, Madokoro H, Yamada K et al.
Cancers (Basel)
-
Surface expression marker profile in colon cancer cell lines and sphere-derived cells suggests complexity in CD26+ cancer stem cells subsets
Authors: Vazquez-Iglesias L, Barcia-Castro L, Rodriguez-Quiroga M et al.
Biol Open
-
The neonatal Fc receptor and DPP4 are human astrovirus receptors
Authors: Ingle, H;Molleston, JM;Hall, PD;Bui, D;Wang, L;Foster, L;Antia, A;Ding, S;Lee, S;Fremont, DH;Baldridge, MT;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Neutralization -
Apical bulkheads accumulate as adaptive response to impaired bile flow in liver disease
Authors: Mayer C, Nehring S, K�cken M et al.
EMBO reports
-
A bat MERS-like coronavirus circulates in pangolins and utilizes human DPP4 and host proteases for cell entry
Authors: Jing Chen, Xinglou Yang, Haorui Si, Qianchun Gong, Tengcheng Que, Jing Li et al.
Cell
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
A CRISPR screen in intestinal epithelial cells identifies novel factors for polarity and apical transport
Authors: KMC Klee, MW Hess, M Lohmüller, S Herzog, K Pfaller, T Müller, GF Vogel, LA Huber
Elife, 2023-01-20;12(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, ICC -
Mapping prohormone processing by proteases in human enteroendocrine cells using genetically engineered organoid models
Authors: J Beumer, J Bauzá-Mart, TS Veth, V Geurts, C Boot, H Gilliam-Vi, SS Poulsen, FK Knop, W Wu, H Clevers
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022-11-07;119(46):e2212057119.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Organoid
Applications: IHC -
Identification of potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 infection by combined pharmacological evaluation and cellular network prioritization
Authors: J.J. Patten, Patrick T. Keiser, Deisy Morselli-Gysi, Giulia Menichetti, Hiroyuki Mori, Callie J. Donahue et al.
iScience
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 expression is not associated with an activated fibroblast phenotype in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Authors: Måns Kadefors, Frida Berlin, Marie Wildt, Göran Dellgren, Sara Rolandsson Enes, Anders Aspberg et al.
Frontiers in Pharmacology
-
Seminal-Plasma-Mediated Effects on Sperm Performance in Humans
Authors: T Turunen, M Magris, M Malinen, J Kekäläinen
Cells, 2022-07-08;11(14):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Seminal Plasma
Applications: Western Blot -
Inter-individual Variation in Receptor Expression Influences MERS-CoV Infection and Immune Responses in Airway Epithelia
Authors: Kun Li, Christine Wohlford-Lenane, Jennifer A. Bartlett, Paul B. McCray
Frontiers in Public Health
-
Dysregulation and activities of ubiquitin specific peptidase 2b in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Authors: C Nadolny, X Zhang, Q Chen, SF Hashmi, W Ali, C Hemme, N Ahsan, Y Chen, R Deng
American journal of cancer research, 2021-10-15;11(10):4746-4767.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysate
Applications: Western Blot -
A CRISPR/Cas9 genetically engineered organoid biobank reveals essential host factors for coronaviruses
Authors: Joep Beumer, Maarten H. Geurts, Mart M. Lamers, Jens Puschhof, Jingshu Zhang, Jelte van der Vaart et al.
Nature Communications
-
Stability of human salivary extracellular vesicles containing dipeptidyl peptidase IV under simulated gastrointestinal tract conditions
Authors: Y Ogawa, Y Akimoto, M Ikemoto, Y Goto, A Ishikawa, S Ohta, Y Takase, H Kawakami, M Tsujimoto, R Yanoshita
Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2021-06-03;27(0):101034.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Functional inhibition of cancer stemness-related protein DPP4 rescues tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in renal cell carcinoma
Authors: S Kamada, T Namekawa, K Ikeda, T Suzuki, M Kagawa, H Takeshita, A Yano, K Okamoto, T Ichikawa, K Horie-Inou, S Kawakami, S Inoue
Oncogene, 2021-05-10;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC, Western Blot -
Advanced Microscopy for Liver and Gut Ultrastructural Pathology in Patients with MVID and PFIC Caused by MYO5B Mutations
Authors: Michael W. Hess, Iris M. Krainer, Przemyslaw A. Filipek, Barbara Witting, Karin Gutleben, Ilja Vietor et al.
Journal of Clinical Medicine
-
CD26 Identifies a Subpopulation of Fibroblasts that Produce the Majority of Collagen during Wound Healing in Human Skin
Authors: Christal A. Worthen, Yilei Cui, Jeffrey S. Orringer, Timothy M. Johnson, John J. Voorhees, Gary J. Fisher
Journal of Investigative Dermatology
-
Diagnostic significance of apical membranous and cytoplasmic dot-like CD26 expression in encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a useful marker for capsular invasion
Authors: S Takagi, M Hirokawa, K Nagashima, M Higuchi, K Kadota, R Ishikawa, M Sato, A Miyauchi, Y Miyake, R Haba
Endocr. J., 2020-09-02;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Chromatin and transcriptome changes in human myoblasts show spatio-temporal correlations and demonstrate DPP4 inhibition in differentiated myotubes
Authors: TJ Kolanowski, N Rozwadowsk, A Zimna, M Nowaczyk, M Siatkowski, W ?ab?d?, E Wiland, J Gapi?ski, S Jurga, M Kurpisz
Sci Rep, 2020-08-31;10(1):14336.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Trypsin Treatment Unlocks Barrier for Zoonotic Bat Coronavirus Infection.
Authors: Menachery V, Dinnon K, Yount B, McAnarney E, Gralinski L, Hale A, Graham R, Scobey T, Anthony S, Wang L, Graham B, Randell S, Lipkin W, Baric R
J Virol, 2020-02-14;94(5):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: cell culture
-
Teneligliptin prevents doxorubicin-induced inflammation and apoptosis in H9c2 cells
Authors: W Peng, D Rao, M Zhang, Y Shi, J Wu, G Nie, Q Xia
Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2019-12-24;0(0):108238.
Species: Rat
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Entry of Scotophilus Bat Coronavirus-512 and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in Human and Multiple Animal Cells
Authors: YN Chen, HC Hsu, SW Wang, HC Lien, HT Lu, SK Peng
Pathogens, 2019-11-22;8(4):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Insights into replicative senescence of human testicular peritubular cells
Authors: N Schmid, F Flenkentha, JB Stöckl, KG Dietrich, FM Köhn, JU Schwarzer, L Kunz, M Luckner, G Wanner, GJ Arnold, T Fröhlich, A Mayerhofer
Sci Rep, 2019-10-21;9(1):15052.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Development of novel monoclonal antibodies with specific binding affinity for denatured human CD26 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded and decalcified specimens
Authors: R Hatano, T Yamada, H Madokoro, H Otsuka, E Komiya, T Itoh, Y Narita, S Iwata, H Yamazaki, S Matsuoka, NH Dang, K Ohnuma, C Morimoto
PLoS ONE, 2019-06-13;14(6):e0218330.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Acute Respiratory Infection in Human Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4-Transgenic Mice Infected with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus
Authors: Naoko Iwata-Yoshikawa, Tadashi Okamura, Yukiko Shimizu, Osamu Kotani, Hironori Sato, Hanako Sekimukai et al.
Journal of Virology
-
A spike-modified Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infectious clone elicits mild respiratory disease in infected rhesus macaques
Authors: AS Cockrell, JC Johnson, IN Moore, DX Liu, KW Bock, MG Douglas, RL Graham, J Solomon, L Torzewski, C Bartos, R Hart, RS Baric, RF Johnson
Sci Rep, 2018-07-16;8(1):10727.
Species: Primate
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Experimental infection of dromedaries with Middle East respiratory syndrome-Coronavirus is accompanied by massive ciliary loss and depletion of the cell surface receptor dipeptidyl peptidase 4
Authors: AK Haverkamp, A Lehmbecker, I Spitzbarth, W Widagdo, BL Haagmans, J Segalés, J Vergara-Al, A Bensaid, JMA van den Br, ADME Osterhaus, W Baumgärtne
Sci Rep, 2018-06-27;8(1):9778.
Species: Camelid
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Discovery of novel bat coronaviruses in south China that use the same receptor as MERS coronavirus
Authors: CM Luo, N Wang, XL Yang, HZ Liu, W Zhang, B Li, B Hu, C Peng, QB Geng, GJ Zhu, F Li, ZL Shi
J. Virol., 2018-06-13;0(0):.
Species: Bat
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus and bat coronavirus HKU9 both can utilize GRP78 for attachment onto host cells
Authors: H Chu, CM Chan, X Zhang, Y Wang, S Yuan, J Zhou, RK Au-Yeung, KH Sze, D Yang, H Shuai, Y Hou, C Li, X Zhao, VK Poon, SP Leung, ML Yeung, J Yan, G Lu, DY Jin, GF Gao, JF Chan, KY Yuen
J. Biol. Chem., 2018-06-10;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Neutralization, Western Blot -
DPP4, the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Receptor, is Upregulated in Lungs of Smokers and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients
Authors: Leen J M Seys, W Widagdo, Fien M Verhamme, Alex Kleinjan, Wim Janssens, Guy F Joos et al.
Clinical Infectious Diseases
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Identification of sialic acid-binding function for the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike glycoprotein
Authors: W Li, RJG Hulswit, I Widjaja, VS Raj, R McBride, W Peng, W Widagdo, MA Tortorici, B van Dieren, Y Lang, JWM van Lent, JC Paulson, CAM de Haan, RJ de Groot, FJM van Kuppev, BL Haagmans, BJ Bosch
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2017-09-18;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Elevated CD26 Expression by Skin Fibroblasts Distinguishes a Profibrotic Phenotype Involved in Scar Formation Compared to Gingival Fibroblasts
Authors: W Mah, G Jiang, D Olver, C Gallant-Be, C Wiebe, DA Hart, L Koivisto, H Larjava, L Häkkinen
Am. J. Pathol., 2017-06-20;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
First-in-human phase 1 of YS110, a monoclonal antibody directed against CD26 in advanced CD26-expressing cancers
Authors: E Angevin, N Isambert, V Trillet-Le, B You, J Alexandre, G Zalcman, P Vielh, F Farace, F Valleix, T Podoll, Y Kuramochi, I Miyashita, O Hosono, NH Dang, K Ohnuma, T Yamada, Y Kaneko, C Morimoto
Br. J. Cancer, 2017-03-14;116(9):1126-1134.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
A humanized anti-CD26 monoclonal antibody inhibits cell growth of malignant mesothelioma via retarded G2/M cell cycle transition
Authors: Mutsumi Hayashi, Hiroko Madokoro, Koji Yamada, Hiroko Nishida, Chikao Morimoto, Michiie Sakamoto et al.
Cancer Cell International
-
TNF-alpha promotes breast cancer cell migration and enhances the concentration of membrane-associated proteases in lipid rafts
Authors: Dominika Wolczyk, Magdalena Zaremba-Czogalla, Anita Hryniewicz-Jankowska, Renata Tabola, Krzysztof Grabowski, Aleksander F. Sikorski et al.
Cell Oncol (Dordr)
-
Mapping the Specific Amino Acid Residues That Make Hamster DPP4 Functional as a Receptor for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus
Authors: Neeltje van Doremalen, Kerri L. Miazgowicz, Vincent J. Munster
Journal of Virology
-
Characterization of dedifferentiating human mature adipocytes from the visceral and subcutaneous fat compartments: fibroblast-activation protein alpha and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 as major components of matrix remodeling.
Authors: Lessard J, Pelletier M, Biertho L, Biron S, Marceau S, Hould F, Lebel S, Moustarah F, Lescelleur O, Marceau P, Tchernof A
PLoS ONE, 2015-03-27;10(3):e0122065.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Regulation of pulmonary graft-versus-host disease by IL-26+CD26+CD4 T lymphocytes.
Authors: Ohnuma K, Hatano R, Aune T, Otsuka H, Iwata S, Dang N, Yamada T, Morimoto C
J Immunol, 2015-03-18;194(8):3697-712.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Glycosylation of mouse DPP4 plays a role in inhibiting Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection.
Authors: Peck K, Cockrell A, Yount B, Scobey T, Baric R, Heise M
J Virol, 2015-02-04;89(8):4696-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: IHC -
High secretion of interferons by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells upon recognition of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
Authors: Scheuplein V, Seifried J, Malczyk A, Miller L, Hocker L, Vergara-Alert J, Dolnik O, Zielecki F, Becker B, Spreitzer I, Konig R, Becker S, Waibler Z, Muhlebach M
J Virol, 2015-01-21;89(7):3859-69.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Blocking -
Generation of a transgenic mouse model of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection and disease.
Authors: Agrawal A, Garron T, Tao X, Peng B, Wakamiya M, Chan T, Couch R, Tseng C
J Virol, 2015-01-14;89(7):3659-70.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
CD26/DPP4 cell-surface expression in bat cells correlates with bat cell susceptibility to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection and evolution of persistent infection.
Authors: Cai Y, Yu S, Postnikova E, Mazur S, Bernbaum J, Burk R, Zhang T, Radoshitzky S, Muller M, Jordan I, Bollinger L, Hensley L, Jahrling P, Kuhn J
PLoS ONE, 2014-11-19;9(11):e112060.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Lineage-specific regulation of epigenetic modifier genes in human liver and brain.
Authors: Weng, Matthias, Natarajan, Karthick, Scholz, Diana, Ivanova, Violeta, Sachinidis, Agapios, Hengstler, Jan G, Waldmann, Tanja, Leist, Marcel
PLoS ONE, 2014-07-23;9(7):e102035.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Regulation of somatostatin receptor 4-mediated cytostatic effects by CD26 in malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Authors: Yamamoto, J, Ohnuma, K, Hatano, R, Okamoto, T, Komiya, E, Yamazaki, H, Iwata, S, Dang, N H, Aoe, K, Kishimoto, T, Yamada, T, Morimoto, C
Br J Cancer, 2014-04-17;110(9):2232-45.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Fraction, Cell Lysates, Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot -
Prognostic significance of the combined expression of neutral endopeptidase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients after surgery resection
Authors: Jianyong Qiu, Jianyong Zhu, XiaoDong Guo, Zhiyan Li, Nianxin Xia, Yingxiang Yang et al.
OncoTargets and Therapy
-
In-vitro renal epithelial cell infection reveals a viral kidney tropism as a potential mechanism for acute renal failure during Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus infection.
Authors: Eckerle I, Muller M, Kallies S, Gotthardt D, Drosten C
Virol J, 2013-12-23;10(0):359.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Adenosine deaminase acts as a natural antagonist for dipeptidyl peptidase 4-mediated entry of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
Authors: Raj, V Stalin, Smits, Saskia L, Provacia, Lisette, van den Brand, Judith M, Wiersma, Lidewij, Ouwendijk, Werner J, Bestebroer, Theo M, Spronken, Monique, van Amerongen, Geert, Rottier, Peter J, Fouchier, Ron A M, Bosch, Berend J, Osterhaus, Albert D, Haagmans, Bart L
J Virol, 2013-11-20;88(3):1834-8.
Species: Ferret, Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
CD26 expression on T-anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) line Karpas 299 is associated with increased expression of versican and MT1-MMP and enhanced adhesion.
Authors: Havre, Pamela A, Dang, Long H, Ohnuma, Kei, Iwata, Satoshi, Morimoto, Chikao, Dang, Nam H
BMC Cancer, 2013-11-01;13(0):517.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Nuclear Localization of CD26 Induced by a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Inhibits Tumor Cell Growth by Modulating of POLR2A Transcription
Authors: Kohji Yamada, Mutsumi Hayashi, Hiroko Madokoro, Hiroko Nishida, Wenlin Du, Kei Ohnuma et al.
PLoS ONE
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry -
Differential Roles of Hath1, MUC2 and P27Kip1 in Relation with Gamma-Secretase Inhibition in Human Colonic Carcinomas: A Translational Study
Authors: Frédérique Souazé, Chantal Bou-Hanna, Christine Kandel, François Leclair, Julie Devallière, Béatrice Charreau et al.
PLoS ONE
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV is a potential molecular biomarker in diabetic kidney disease
Authors: Ai-li Sun, Jing-ti Deng, Guang-ju Guan, Shi-hong Chen, Yuan-tao Liu, Jing Cheng et al.
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research
-
Mechanisms of confluence-dependent expression of CD26 in colon cancer cell lines
Authors: Masako Abe, Pamela A Havre, Yasuyo Urasaki, Kei Ohnuma, Chikao Morimoto, Long H Dang et al.
BMC Cancer
-
Distinct gene expression-defined classes of gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
Authors: Yamaguchi U, Nakayama R, Honda K, Ichikawa H, Hasegawa T, Shitashige M, Ono M, Shoji A, Sakuma T, Kuwabara H, Shimada Y, Sasako M, Shimoda T, Kawai A, Hirohashi S, Yamada T
J. Clin. Oncol., 2008-09-01;26(25):4100-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Lymphatic-specific expression of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its dual role in lymphatic endothelial function.
Authors: Shin JW, Jurisic G, Detmar M
Exp. Cell Res., 2008-08-03;314(16):3048-56.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr, Western Blot -
Overexpression of CD26/DPPIV in mesothelioma tissue and mesothelioma cell lines.
Authors: Amatya VJ, Takeshima Y, Kushitani K et al.
Oncol Rep.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Are Expressed in the Microvasculature and Ducts of Human Pancreas but Are Not Enriched in beta Cells
Authors: Coate KC, Cha J, Shrestha S et al.
Int J Mol Sci
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human DPPIV/CD26 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 4 Reviews)
Have you used Human DPPIV/CD26 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:



