Human Clusterin Isoform 1 Antibody Summary
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Clusterin by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of human liver tissue and human serum. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human Clusterin Isoform 1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2937) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). Specific bands were detected for Clusterin Precusor at approximately 60-65 kDa and Clusterin a and beta chains at approximately 36 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Clusterin in Human Alzheimer's Disease Brain. Clusterin was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded of human Alzheimer's disease brain using Human Clusterin Isoform 1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2937) at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Clusterin/APOJ by Western Blot Extracellular clusterin interacts with alpha ‐synuclein preformed fibrils (pffs). (a) Medium from primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr, or with monomeric alpha ‐synuclein (m), were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin antibody. Ponceau‐S staining was used as a loading control. (b) Quantification of clusterin is normalized to GAPDH protein of cell lysates. Data are from eight independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test; **p =.0028. (c) alpha ‐Synuclein pffs isolated by centrifugation from total medium of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs, or monomeric alpha ‐synuclein (M), for 16 hr were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin and alpha ‐synuclein antibodies. Asterisk in the alpha ‐synuclein immunoblot indicates clusterin bands still present after Clusterin antibody stripping. (d) Clusterin immunoprecipitated from the medium of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr was subjected to immunoblotting using an alpha ‐synuclein antibody. (e) Quantification of clusterin— alpha ‐synuclein pffs interaction has been obtained by normalization of alpha ‐synuclein pffs bound to clusterin for alpha ‐synuclein pffs bound to protein‐G beads. Data are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using one‐sample t test; *p = .0493. (f) Z‐stack frames of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr and stained for alpha ‐synuclein (purple), clusterin (green), cadherin (red), and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 μm. (g) Maximum intensity Z‐projection confocal images of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr and stained for alpha ‐synuclein (purple), clusterin (red), Early Endosome Antigen 1 (EEA1) (green) and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 μm. Individual points of the graphs represent each single experiment [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com] Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33045109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Clusterin/APOJ by Western Blot Extracellular clusterin interacts with alpha ‐synuclein preformed fibrils (pffs). (a) Medium from primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr, or with monomeric alpha ‐synuclein (m), were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin antibody. Ponceau‐S staining was used as a loading control. (b) Quantification of clusterin is normalized to GAPDH protein of cell lysates. Data are from eight independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test; **p =.0028. (c) alpha ‐Synuclein pffs isolated by centrifugation from total medium of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs, or monomeric alpha ‐synuclein (M), for 16 hr were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin and alpha ‐synuclein antibodies. Asterisk in the alpha ‐synuclein immunoblot indicates clusterin bands still present after Clusterin antibody stripping. (d) Clusterin immunoprecipitated from the medium of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr was subjected to immunoblotting using an alpha ‐synuclein antibody. (e) Quantification of clusterin— alpha ‐synuclein pffs interaction has been obtained by normalization of alpha ‐synuclein pffs bound to clusterin for alpha ‐synuclein pffs bound to protein‐G beads. Data are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using one‐sample t test; *p = .0493. (f) Z‐stack frames of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr and stained for alpha ‐synuclein (purple), clusterin (green), cadherin (red), and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 μm. (g) Maximum intensity Z‐projection confocal images of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr and stained for alpha ‐synuclein (purple), clusterin (red), Early Endosome Antigen 1 (EEA1) (green) and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 μm. Individual points of the graphs represent each single experiment [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com] Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33045109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Clusterin/APOJ by Western Blot Extracellular clusterin interacts with alpha ‐synuclein preformed fibrils (pffs). (a) Medium from primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr, or with monomeric alpha ‐synuclein (m), were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin antibody. Ponceau‐S staining was used as a loading control. (b) Quantification of clusterin is normalized to GAPDH protein of cell lysates. Data are from eight independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test; **p =.0028. (c) alpha ‐Synuclein pffs isolated by centrifugation from total medium of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs, or monomeric alpha ‐synuclein (M), for 16 hr were subjected to immunoblotting using clusterin and alpha ‐synuclein antibodies. Asterisk in the alpha ‐synuclein immunoblot indicates clusterin bands still present after Clusterin antibody stripping. (d) Clusterin immunoprecipitated from the medium of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr was subjected to immunoblotting using an alpha ‐synuclein antibody. (e) Quantification of clusterin— alpha ‐synuclein pffs interaction has been obtained by normalization of alpha ‐synuclein pffs bound to clusterin for alpha ‐synuclein pffs bound to protein‐G beads. Data are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Data were analyzed using one‐sample t test; *p = .0493. (f) Z‐stack frames of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr and stained for alpha ‐synuclein (purple), clusterin (green), cadherin (red), and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 μm. (g) Maximum intensity Z‐projection confocal images of primary astrocytes treated with alpha ‐synuclein pffs for 16 hr and stained for alpha ‐synuclein (purple), clusterin (red), Early Endosome Antigen 1 (EEA1) (green) and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 μm. Individual points of the graphs represent each single experiment [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com] Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33045109), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
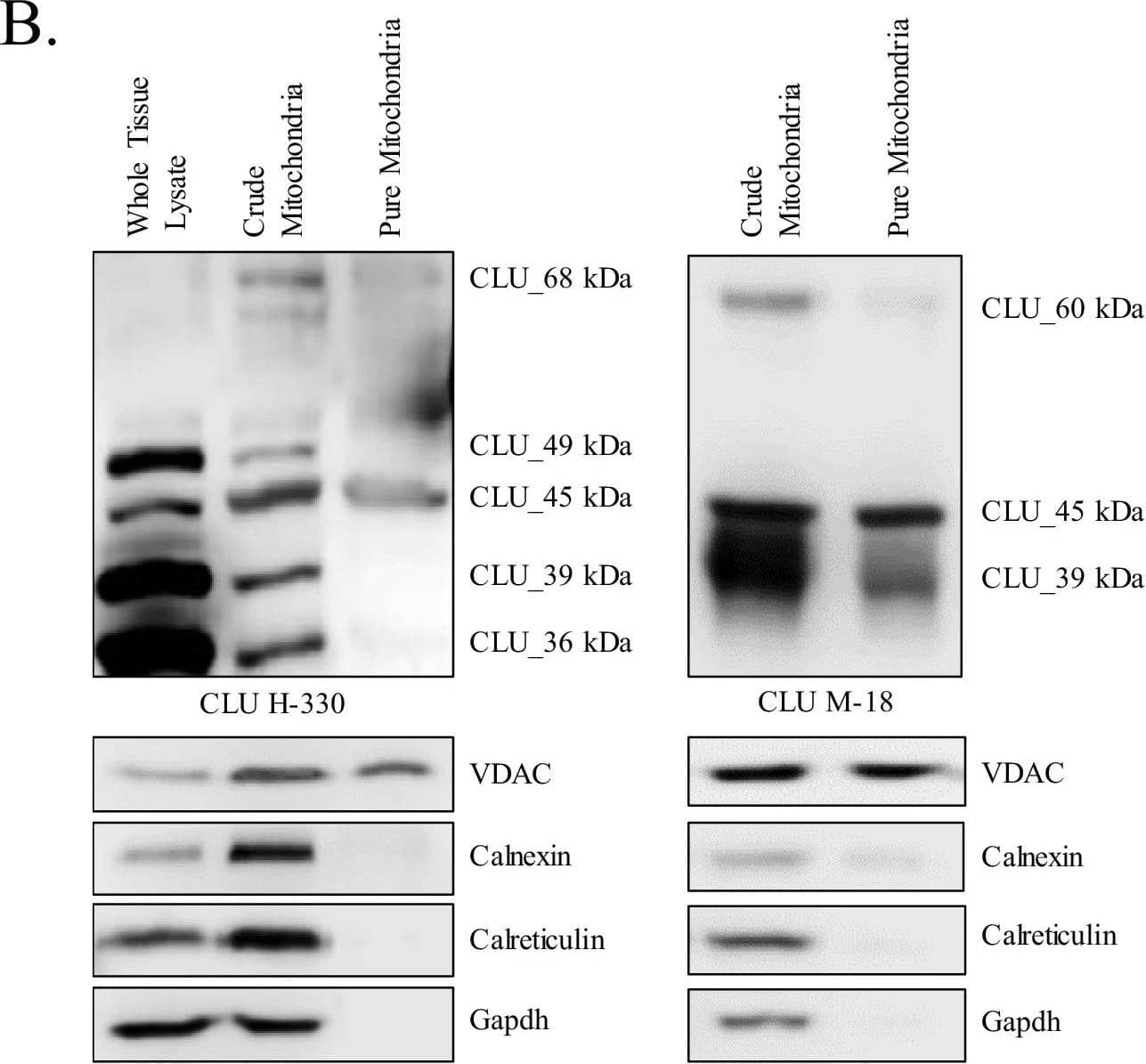 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Rat Clusterin/APOJ by Western Blot Identification of a mitochondrial CLU protein isoform.(A) DIV 9 Mitotracker-stained (green) primary neurons were probed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU H-330 (red) and visualized using 40X confocal microscopy. (B) Pure cortical mitochondria were isolated as indicated. Equal concentrations of whole tissue lysate, crude mitochondria, and pure mitochondria were analyzed via SDS-PAGE and probed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU H-330 (left panel) and anti-CLU M-18 (right panel) (n = 3 independent isolations). Biochemical characterization of isolated fractions was performed using a panel of organelle-specific antibodies: voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) (mitochondria), calnexin and calreticulin (ER), and Gapdh (cytosol). (C) Crude and pure mitochondria were isolated and subjected to endoglycosidase treatment using PNGase F and Endo H. Deglycosylated mitochondrial lysates were then analyzed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU M-18. Red font: deglycosylated protein isoforms; blue font: isoforms that were unaffected by glycosidase treatment; green asterisk: excess Endo H enzyme.Positive controls for deglycosylation studies.RNase B, a high mannose glycoprotein, has a single N-linked glycosylation site and was used as a positive control for endoglycosidases that cleave N-linked carbohydrates. Fetuin, a glycoprotein containing sialylated N-linked and O-linked glycans, was used as a positive control for endoglycosidases that cleave both N-linked and O-linked carbohydrates. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31738162), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
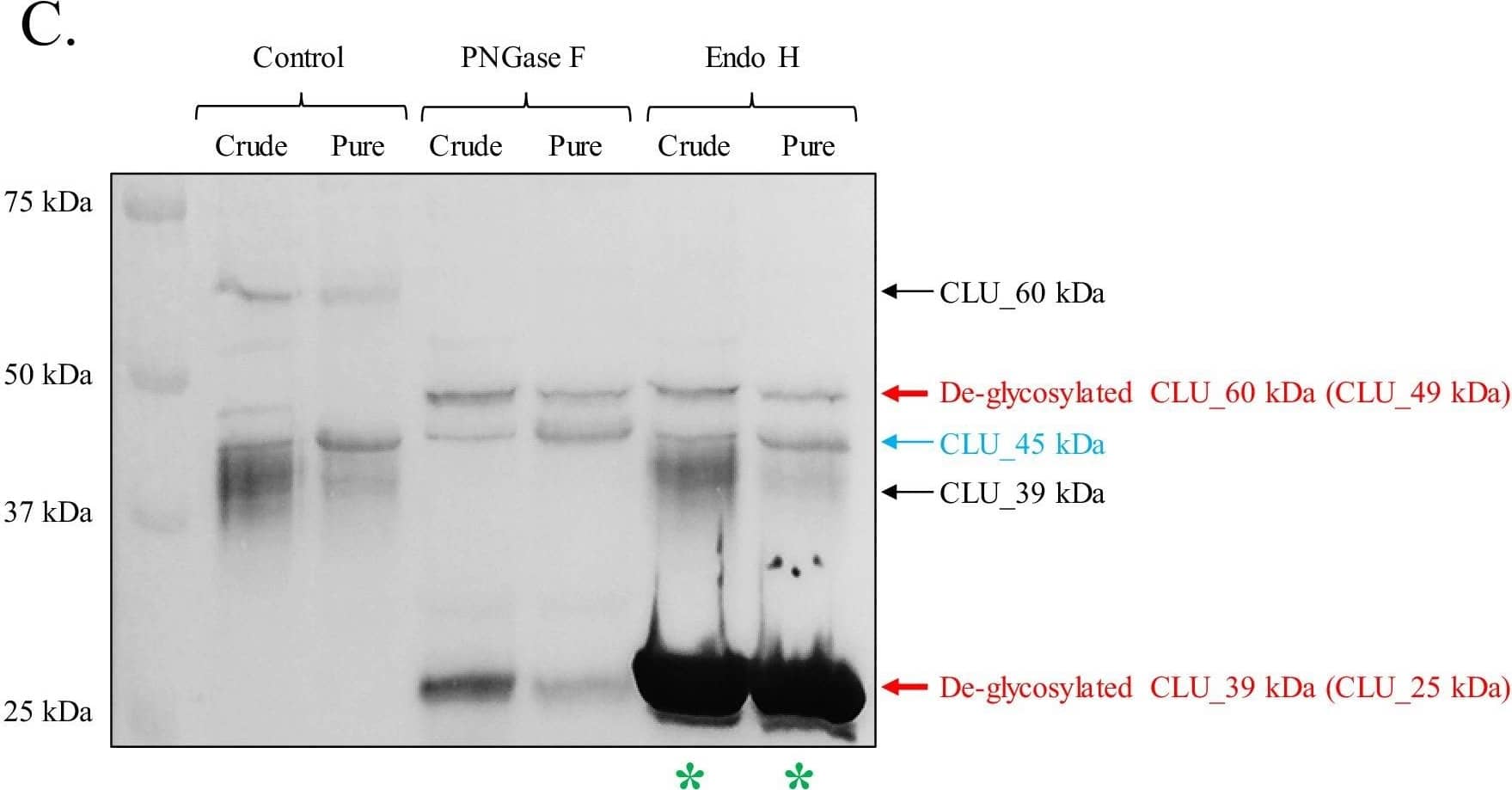 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Rat Clusterin/APOJ by Western Blot Identification of a mitochondrial CLU protein isoform.(A) DIV 9 Mitotracker-stained (green) primary neurons were probed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU H-330 (red) and visualized using 40X confocal microscopy. (B) Pure cortical mitochondria were isolated as indicated. Equal concentrations of whole tissue lysate, crude mitochondria, and pure mitochondria were analyzed via SDS-PAGE and probed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU H-330 (left panel) and anti-CLU M-18 (right panel) (n = 3 independent isolations). Biochemical characterization of isolated fractions was performed using a panel of organelle-specific antibodies: voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) (mitochondria), calnexin and calreticulin (ER), and Gapdh (cytosol). (C) Crude and pure mitochondria were isolated and subjected to endoglycosidase treatment using PNGase F and Endo H. Deglycosylated mitochondrial lysates were then analyzed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU M-18. Red font: deglycosylated protein isoforms; blue font: isoforms that were unaffected by glycosidase treatment; green asterisk: excess Endo H enzyme.Positive controls for deglycosylation studies.RNase B, a high mannose glycoprotein, has a single N-linked glycosylation site and was used as a positive control for endoglycosidases that cleave N-linked carbohydrates. Fetuin, a glycoprotein containing sialylated N-linked and O-linked glycans, was used as a positive control for endoglycosidases that cleave both N-linked and O-linked carbohydrates. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31738162), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 degreesC as supplied. 1 month, 2 to 8 degreesC under sterile conditions after reconstitution. 6 months, -20 to -70 degreesC under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Clusterin
Clusterin, also known as Apolipoprotein J, Sulfated Glycoprotein 2 (SGP-2), TRPM-2, and SP-40,40, is a secreted multi-functional protein that was named for its ability to induce cellular clustering. It binds a wide range of molecules and may function as a chaperone of misfolded extracellular proteins. It also participates in the control of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis (1, 2). Clusterin is predominantly expressed in adult testis, ovary, adrenal gland, liver, heart, and brain and in many epithelial tissues during embryonic development (3). Human Clusterin is synthesized as a precursor that contains two coiled coil domains, three nuclear localization signals (NLS), and one heparin binding domain (4-6). Intracellular cleavages of the precursor remove the signal peptide and generate comparably sized alpha and beta chains which are secreted as an 80 kDa N-glycosylated disulfide-linked heterodimer (7, 8). Mature human Clusterin shares 77% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat Clusterin. High μg/mL concentrations of Clusterin circulate predominantly as a component of high density lipoprotein particles, and these are internalized and degraded through interactions with LRP-2/Megalin (9, 10). In human, an alternately spliced 50 kDa isoform of Clusterin (nCLU) lacks the signal peptide and remains intracellular (5, 11). This molecule is neither glycosylated nor cleaved into alpha and beta chains (11). In the cytoplasm, nCLU destabilizes the actin cytoskeleton and inhibits NF kappa B activation (12, 13). Cellular exposure to ionizing radiation promotes the translocation of nCLU to the nucleus where it interacts with Ku70 and promotes apoptosis (5, 11). This function contrasts with the cytoprotective effect of secreted Clusterin (14). During colon cancer tumor progression there is a downregulation of the intracellular form and an upregulation of the glycosylated secreted form (11).
- Carver, J.A. et al. (2003) IUBMB Life 55:661.
- Shannan, B. et al. (2006) Cell Death Differ. 13:12.
- French, L.E. et al. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 122:1119.
- Kirszbaum, L. et al. (1989) EMBO J. 8:711.
- Leskov, K.S. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:11590.
- Pankhurst, G.J. et al. (1998) Biochemistry 37:4823.
- Burkey, B.F. et al. (1991) J. Lipid. Res. 32:1039.
- de Silva, H.V. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265:14292.
-
Jenne, D.E. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:11030.
-
Kounnas, M.Z. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:13070.
-
Pucci, S. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:2298.
-
Moretti, R.M. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:10325.
-
Santilli, G. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:38214.
-
Trougakos, I.P. et al. (2004) Cancer Res. 64:1834.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Clusterin Isoform 1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
4
Citations: Showing 1 - 4
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Brain clusterin protein isoforms and mitochondrial localization
Authors: Sarah K Herring, Hee-Jung Moon, Punam Rawal, Anindit Chhibber, Liqin Zhao
eLife
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Quantitative glycoproteomics reveals new classes of STT3A- and STT3B-dependent N-glycosylation sites
Authors: Natalia A. Cherepanova, Sergey V. Venev, John D. Leszyk, Scott A. Shaffer, Reid Gilmore
Journal of Cell Biology
-
Semen clusterin is a novel DC-SIGN ligand.
Authors: Sabatte J, Faigle W, Ceballos A, Morelle W, RodrÃgues CR, Lenicov FR, Thepaut M, Fieschi F, Malchiodi E, Fernandez M, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Lortat-Jacob H, Michalski JC, Geffner J, Amigorena S
J. Immunol., 2011-10-17;187(10):5299-309.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Semen, Seminal Plasma, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot -
Extracellular clusterin limits the uptake of alpha-synuclein fibrils by murine and human astrocytes
Authors: Filippini A, Mutti V, Faustini G et al.
Glia
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Clusterin Isoform 1 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human Clusterin Isoform 1 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human Clusterin Isoform 1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
