Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 Antibody Summary
Asn2-Ser604
Accession # U45878
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
cIAP-2/HIAP-1 in Human Colon Tissue. cIAP-2/HIAP-1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon tissue using Goat Anti-Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF8171) at 1 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to colon glands. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
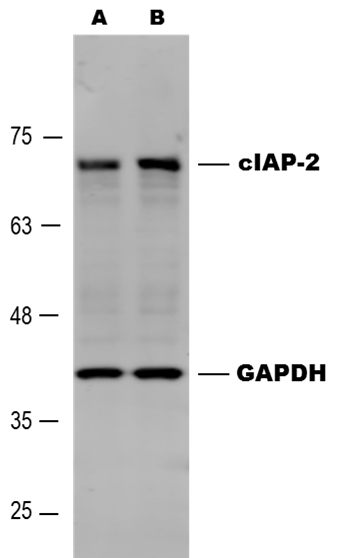
Detection of Human cIAP‑2/HIAP‑1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of Raji human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line and Daudi human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF8171) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). A specific band was detected for cIAP-2/HIAP-1 at approximately 68 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 5.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human cIAP‑2/HIAP‑1 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of Raji human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line and Daudi human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for cIAP-2/HIAP-1 at approximately 70 kDa (as indicated) using 5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF8171) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot IAP expression in glioblastoma cell lines. Expression levels of cIAP1, cIAP2, XIAP and ML-IAP were analyzed by western blotting and quantified in U87MG and GL261 adherent GBM cell lines, and in GBM6 and GBM9 spheres. Expression level of beta -actin served as loading control. The four GBM cell lines expressed heterogeneously cIAP1, cIAP2, XIAP and ML-IAP. A representative experiment of four experiments is shown. Quantification was performed using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) and data presented were normalized to beta -actin expression Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27490930), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Prognostic value of cIAP1, cIAP2, XIAP and ML-IAP protein expression in human glioblastomas (cohorts 1 and 2). (a) cIAP1-, cIAP2-, XIAP- and ML-IAP-positive stainings in GBM. IAPs were heterogeneously expressed by tumor cells in GBM samples (Table 1). Stainings were diffused with a stronger punctuated positivity into the cytoplasm. Black arrows highlight cIAP2-positive nuclei. Scale bars, 50 μm. (b) Correlation of ML-IAP protein expression with PFS and OS in cohort 1. The cutoff was 35% and was determined by performing a ROC curve. ML-IAP expression of ⩾35% was correlated with a poor prognosis. (c) Correlation of ML-IAP protein expression with PFS and OS in cohort 2. The cutoff was the same as that for cohort 1 analysis (35%). ML-IAP expression of ⩾35% was correlated with a poor prognosis Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27490930), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot Apoptosis and IAP expression upon SMAC mimetic GDC-0152 treatment in glioblastoma cell lines. (a) Apoptosis (SubG0/G1) of DMSO control and GDC-0152-treated cells was determined by flow cytometry of propidium iodide-stained nuclei and percentage of apoptosis is shown. U87MG and GL261 cell lines were treated for 72 h and GBM6 and GBM9 cell lines were treated for 8 days at the indicated concentrations. At these respective time points, percentage of U87MG cells dead by apoptosis, percentage of GL261 cells, percentage of GBM6 cells and percentage of GBM9 cells. Data are expressed as mean+S.E.M. Three independent experiments were performed for the GL261 cell lines and five for the U87MG, GBM6 and GBM9 cell lines. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.005. (b) Expression levels of cIAP1, cIAP2, XIAP and ML-IAP were analyzed by western blotting. Cell lines were treated with 1 μM of GDC-0152. U87MG and GL261 were treated for 72 h and GBM6 and GBM9 cell lines for 8 days. In all GBM cell lines GDC-0152 decreased IAP expression. Expression level of beta -actin served as loading control. A representative experiment of three experiments is shown Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27490930), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
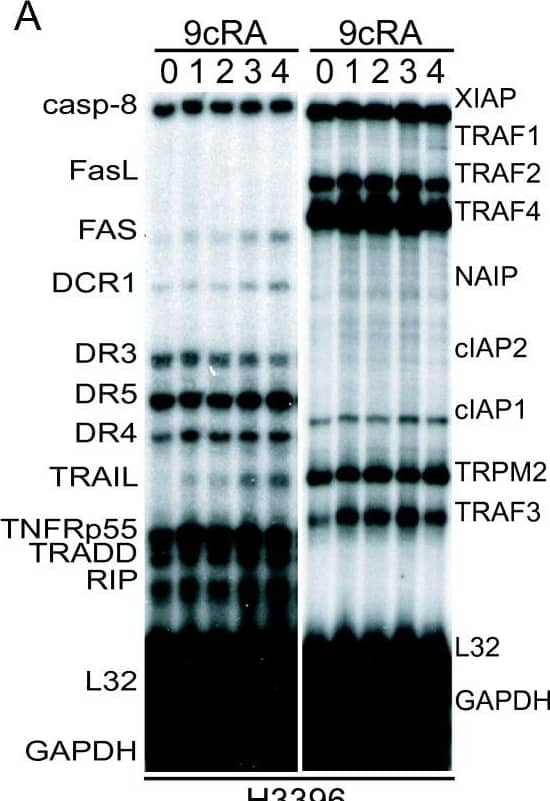
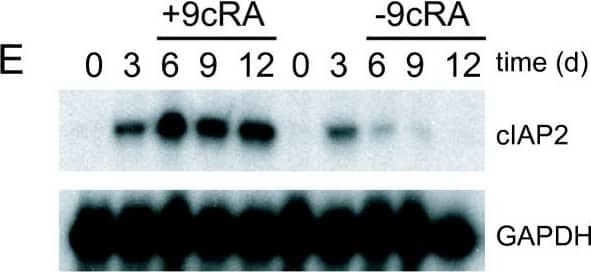
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot 9-cis-RA induces the expression of cIAP2 in breast cancer cells in a cell context dependent manner. (A, B, C) Multiplex RNase protections assays (RPAs) to monitor the effect of 9-cis-RA on the expression of death receptor, death ligands, IAP and TRAF family members in four different breast cancer cell lines. Breast cancer cells were treated for the indicated time with 9-cis-RA at a concentration of 10-6 M. (D) Western blot of whole cell extracts of 9-cis-RA-treated T47D cells and H3396 cells for 0, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours with anti-cIAP2. The nonspecific signal (n. sp.) confirms equal loading. As a positive control, breast cancer cells were treated with 50 μg/ml of hTNF alpha for 24 and 48 hours. (E) Reversibility of 9-cis-RA-induced cIAP2 gene expression. T47D cells were treated either in the absence or presence of 1 μM 9- cis-RA and after 3 days, total RNA was extracted. In parallel flasks, the medium was removed, and cells were washed and treated with either fresh control medium or medium with 10-6 M of 9-cis-RA and grown for additional 3, 6 and 9 days. Media and ligands were renewed every 3 days. RNA was isolated and analyzed by RPA as described in (A). Equal loading was confirmed by GAPDH RNA level. The images shown are from one representative experiment performed twice with similar results. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (http://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-9-15), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
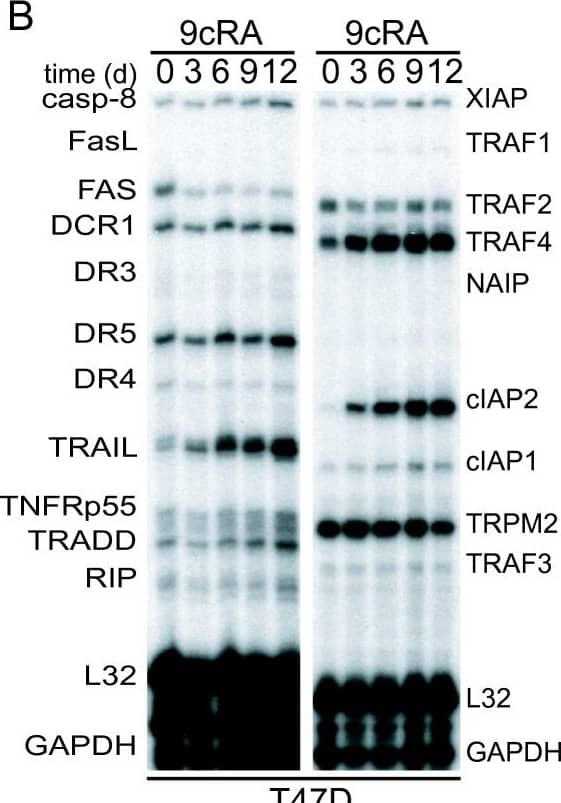
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot 9-cis-RA induces the expression of cIAP2 in breast cancer cells in a cell context dependent manner. (A, B, C) Multiplex RNase protections assays (RPAs) to monitor the effect of 9-cis-RA on the expression of death receptor, death ligands, IAP and TRAF family members in four different breast cancer cell lines. Breast cancer cells were treated for the indicated time with 9-cis-RA at a concentration of 10-6 M. (D) Western blot of whole cell extracts of 9-cis-RA-treated T47D cells and H3396 cells for 0, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours with anti-cIAP2. The nonspecific signal (n. sp.) confirms equal loading. As a positive control, breast cancer cells were treated with 50 μg/ml of hTNF alpha for 24 and 48 hours. (E) Reversibility of 9-cis-RA-induced cIAP2 gene expression. T47D cells were treated either in the absence or presence of 1 μM 9- cis-RA and after 3 days, total RNA was extracted. In parallel flasks, the medium was removed, and cells were washed and treated with either fresh control medium or medium with 10-6 M of 9-cis-RA and grown for additional 3, 6 and 9 days. Media and ligands were renewed every 3 days. RNA was isolated and analyzed by RPA as described in (A). Equal loading was confirmed by GAPDH RNA level. The images shown are from one representative experiment performed twice with similar results. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (http://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-9-15), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
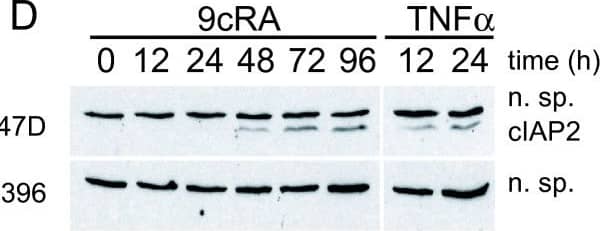
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot 9-cis-RA induces the expression of cIAP2 in breast cancer cells in a cell context dependent manner. (A, B, C) Multiplex RNase protections assays (RPAs) to monitor the effect of 9-cis-RA on the expression of death receptor, death ligands, IAP and TRAF family members in four different breast cancer cell lines. Breast cancer cells were treated for the indicated time with 9-cis-RA at a concentration of 10-6 M. (D) Western blot of whole cell extracts of 9-cis-RA-treated T47D cells and H3396 cells for 0, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours with anti-cIAP2. The nonspecific signal (n. sp.) confirms equal loading. As a positive control, breast cancer cells were treated with 50 μg/ml of hTNF alpha for 24 and 48 hours. (E) Reversibility of 9-cis-RA-induced cIAP2 gene expression. T47D cells were treated either in the absence or presence of 1 μM 9- cis-RA and after 3 days, total RNA was extracted. In parallel flasks, the medium was removed, and cells were washed and treated with either fresh control medium or medium with 10-6 M of 9-cis-RA and grown for additional 3, 6 and 9 days. Media and ligands were renewed every 3 days. RNA was isolated and analyzed by RPA as described in (A). Equal loading was confirmed by GAPDH RNA level. The images shown are from one representative experiment performed twice with similar results. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (http://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-9-15), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
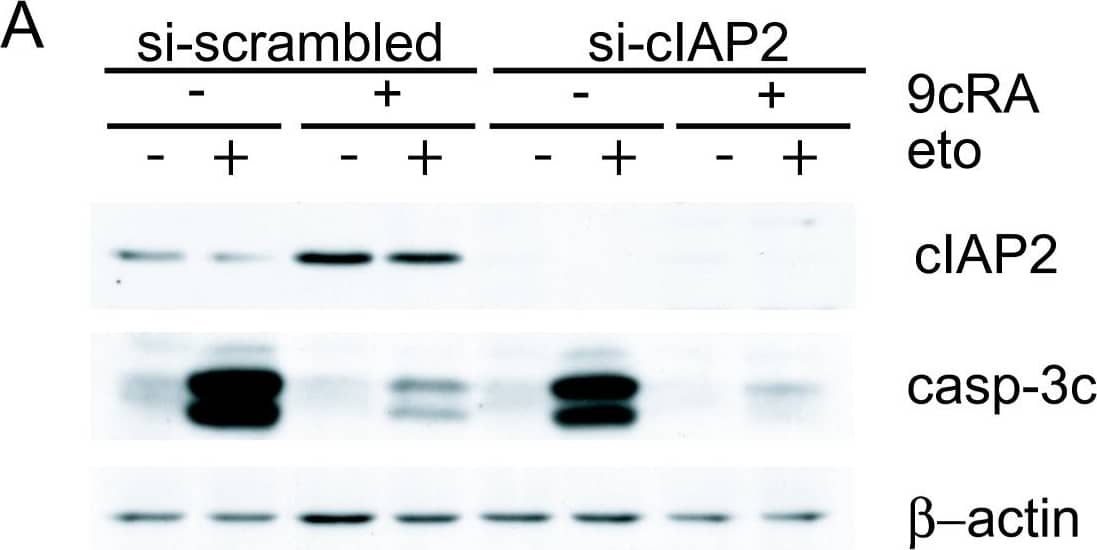
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot Suppression of cIAP2 expression is not sufficient to abrogate 9-cis-RA inhibition of etoposide-induced apoptosis in T47D cells. (A) T47D cells were transfected with either scrambled-siRNA or cIAP2-siRNA and pretreated with or without 9-cis-RA for 30 h, followed by treatment with etoposide 100 μM for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blot for the expression of cleaved caspase-3, cIAP2 and beta -actin using specific antibodies. The images shown are from one representative experiment performed three times with similar results. (B) T47D cells were transfected with either scrambled-siRNA (white bars) or cIAP2-siRNA (black bars). After 24 h, lipid-siRNA complexes were removed from media and cells were pretreated with or without 1 μM 9-cis-RA for 30 h, followed by treatment with etoposide 100 μM for 72 h. The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by FACS analysis after staining with propidium iodide. The values represent the mean ± SD of three experiments performed in duplicate. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences against the corresponding untreated cells. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (http://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-9-15), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot 9-cis-RA induces the expression of cIAP2 in breast cancer cells in a cell context dependent manner. (A, B, C) Multiplex RNase protections assays (RPAs) to monitor the effect of 9-cis-RA on the expression of death receptor, death ligands, IAP and TRAF family members in four different breast cancer cell lines. Breast cancer cells were treated for the indicated time with 9-cis-RA at a concentration of 10-6 M. (D) Western blot of whole cell extracts of 9-cis-RA-treated T47D cells and H3396 cells for 0, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours with anti-cIAP2. The nonspecific signal (n. sp.) confirms equal loading. As a positive control, breast cancer cells were treated with 50 μg/ml of hTNF alpha for 24 and 48 hours. (E) Reversibility of 9-cis-RA-induced cIAP2 gene expression. T47D cells were treated either in the absence or presence of 1 μM 9- cis-RA and after 3 days, total RNA was extracted. In parallel flasks, the medium was removed, and cells were washed and treated with either fresh control medium or medium with 10-6 M of 9-cis-RA and grown for additional 3, 6 and 9 days. Media and ligands were renewed every 3 days. RNA was isolated and analyzed by RPA as described in (A). Equal loading was confirmed by GAPDH RNA level. The images shown are from one representative experiment performed twice with similar results. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (http://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-9-15), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
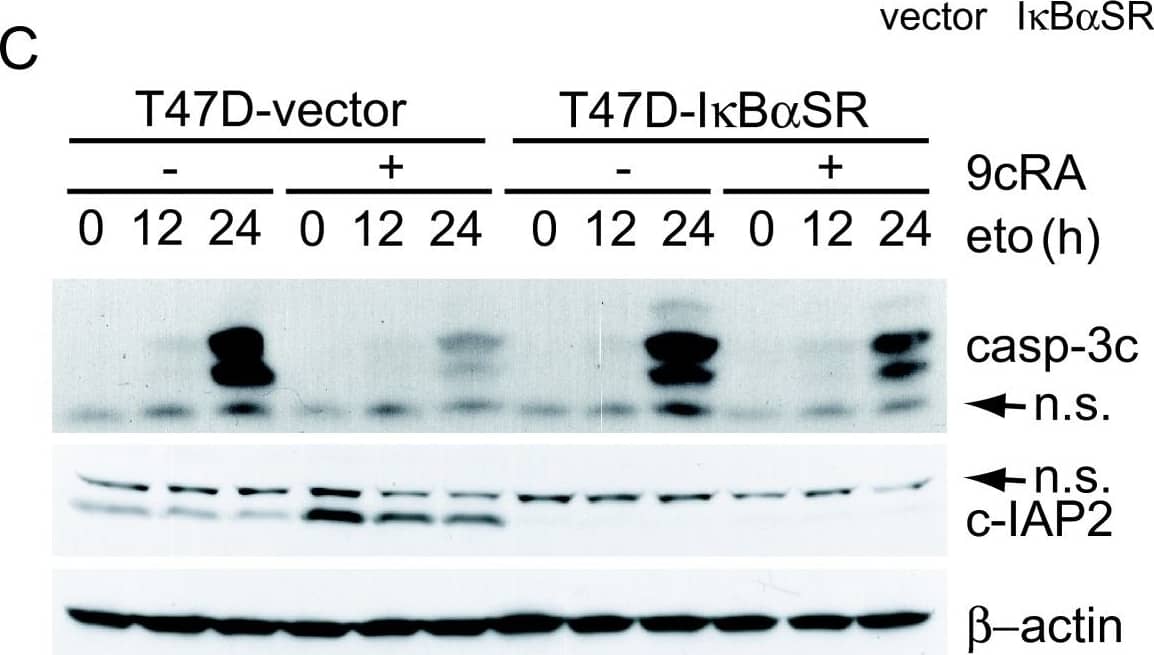
Detection of Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 by Western Blot Over-expression of the super-repressor of NF-kappa B activation, I kappa B alpha -SR(S32A/S36A), leads to significant abrogation of retinoic acid-mediated inhibition of etoposide-induced apoptosis. (A) T47D-vector and T47D-I kappa B alpha SR cells were untreated or incubated for the indicated time with hTNF alpha (50 ng/ml). Extracts were analyzed by western blotting with an I kappa B alpha antibody. Equal loading was confirmed with an anti-beta -actin antibody. The images shown are from one representative experiment performed three times with similar results. (B) T47D-vector or T47D-I kappa B alpha SR cells were untreated or treated with 9-cis-RA for 48 h and expression of cIAP2 and beta -actin were analysed by Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Reaction and real time PCR. The values represent the mean ± SD of three different experiments performed in duplicate. (C) T47D-vector or T47D-I kappa B alpha SR cells were pretreated with or without 9-cis-RA for 30 h, followed by treatment with etoposide 100 μM as previously indicated. At the indicated times, cell lysates were analyzed by western blot for the expression of cleaved caspase-3, cIAP2 and beta -actin using specific antibodies. The images shown are from one representative experiment performed three times with similar results. (D) T47D-vector or T47D-I kappa B alpha SR cells were pretreated with or without 9-cis-RA for 30 h, followed by treatment with etoposide 100 μM for 72 h. The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by FACS analysis after staining with propidium iodide. The values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Asterisks denote the existence of statistically significant differences between the indicated groups; N.S.: not significant (Student's t-test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (http://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-4598-9-15), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: cIAP-2/HIAP-1
cIAP-2 (also known as MIHC and HIAP-1) is a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family of proteins that inhibit the proteolytic activity of mature caspases. cIAP-2 has 3 BIR (baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis) domains, a RING finger domain, and a caspase recruitment domain (CARD). cIAP-2 inhibits caspases through the direct interaction of its BIR domain with the active caspase. Caspase activity may be restored through interactions with the Reaper like motif on mitochondrial proteins such as SMAC/Diablo or HtrA2/Omi. cIAP-2 is reported to be cleaved by HtrA2/Omi.
- Roy, N. et al. (1997) EMBO J. 23:6914.
- Deveraux, Q. et al. (1997) Nature 388:300.
- Deveraux, Q. and J. Reed (1999) Genes & Develop. 13:239.
- Srinivasula, S.M. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:31469.
- Yang, Q-H. et al. (2003) Genes Dev. 17:1487.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
17
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression in glioblastomas and their in vitro and in vivo targeting by SMAC mimetic GDC-0152
Authors: Tchoghandjian A, Souberan A, Tabouret E et al.
Cell Death Dis
-
Death agonist antibody against TRAILR2/DR5/TNFRSF10B enhances birinapant anti-tumor activity in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
Authors: Y An, J Jeon, L Sun, A Derakhshan, J Chen, S Carlson, H Cheng, C Silvin, X Yang, C Van Waes, Z Chen
Scientific Reports, 2021-03-18;11(1):6392.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Dual Antagonist of cIAP/XIAP ASTX660 Sensitizes HPV(−) and HPV(+) Head and Neck Cancers To TNF alpha, TRAIL, and Radiation Therapy
Authors: Roy Xiao, Yi An, Wenda Ye, Adeeb Derakhshan, Hui Cheng, Xinping Yang et al.
Clinical Cancer Research
-
Absence of Cytosolic 2-Cys Prx Subtypes I and II Exacerbates TNF-?-Induced Apoptosis via Different Routes
Authors: S Lee, JY Lee, EW Lee, S Park, DH Kang, C Min, DJ Lee, D Kang, J Song, J Kwon, SW Kang
Cell Rep, 2019-02-19;26(8):2194-2211.e6.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
ASTX660, a novel non-peptidomimetic antagonist of cIAP1/2 and XIAP, potently induces TNF-? dependent apoptosis in cancer cell lines and inhibits tumor growth
Authors: GA Ward, EJ Lewis, JS Ahn, CN Johnson, JF Lyons, V Martins, JM Munck, SJ Rich, T Smyth, NT Thompson, PA Williams, NE Wilsher, NG Wallis, G Chessari
Mol. Cancer Ther., 2018-04-25;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Human Parvovirus Infection of Human Airway Epithelia Induces Pyroptotic Cell Death by Inhibiting Apoptosis
Authors: Xuefeng Deng, Wei Zou, Min Xiong, Zekun Wang, John F. Engelhardt, Shui Qing Ye et al.
Journal of Virology
-
Anticancer efficacy of the hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide is enhanced in combination with proapoptotic receptor agonists against osteosarcoma
Authors: V Liapis, A Zysk, M DeNichilo, I Zinonos, S Hay, V Panagopoul, A Shoubridge, C Difelice, V Ponomarev, W Ingman, GJ Atkins, DM Findlay, ACW Zannettino, A Evdokiou
Cancer Med, 2017-08-10;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Pro-Apoptotic Activity of New Honokiol/Triphenylmethane Analogues in B-Cell Lymphoid Malignancies
Molecules, 2016-07-30;21(8):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Transcriptional repression by the HDAC4–RelB–p52 complex regulates multiple myeloma survival and growth
Authors: Subrahmanya D. Vallabhapurapu, Sunil K. Noothi, Derek A. Pullum, Charles H. Lawrie, Rachel Pallapati, Veena Potluri et al.
Nature Communications
-
USP11-dependent selective cIAP2 deubiquitylation and stabilization determine sensitivity to Smac mimetics.
Authors: Lee E, Seong D, Seo J, Jeong M, Lee H, Song J
Cell Death Differ, 2015-01-23;22(9):1463-76.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Doxorubicin overcomes resistance to drozitumab by antagonizing Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins (IAPs).
Authors: Zinonos I, Labrinidis A, Liapis V, Hay S, Panagopoulos V, Denichilo M, Ponomarev V, Ingman W, Atkins G, Findlay D, Zannettino A, Evdokiou A
Anticancer Res, 2014-12-01;34(12):7007-20.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
HAX1 regulates E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of cIAPs by promoting their dimerization
Authors: Jin Sun Choi, Byoung Chul Park, Seung Wook Chi, Kwang-Hee Bae, Sunhong Kim, Sayeon Cho et al.
Oncotarget
-
The novel SMAC mimetic birinapant exhibits potent activity against human melanoma cells.
Authors: Krepler C, Chunduru S, Halloran M, He X, Xiao M, Vultur A, Villanueva J, Mitsuuchi Y, Neiman E, Benetatos C, Nathanson K, Amaravadi R, Pehamberger H, McKinlay M, Herlyn M
Clin Cancer Res, 2013-02-12;19(7):1784-94.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Dacarbazine and the agonistic TRAIL receptor-2 antibody lexatumumab induce synergistic anticancer effects in melanoma.
Authors: Engesaeter B, Engebraaten O, Florenes V, Maelandsmo G
PLoS ONE, 2012-09-20;7(9):e45492.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Retinoic acid protects human breast cancer cells against etoposide-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB-dependent but cIAP2-independent mechanisms
Authors: Ana M Jiménez-Lara, Ana Aranda, Hinrich Gronemeyer
Molecular Cancer
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
cIAP1 Localizes to the nuclear compartment and modulates the cell cycle.
Authors: Samuel T, Okada K, Hyer M, Welsh K, Zapata JM, Reed JC
Cancer Res., 2005-01-01;65(1):210-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Western Blot -
Survivin interacts with Smac/DIABLO in ovarian carcinoma cells but is redundant in Smac-mediated apoptosis.
Authors: McNeish IA, Lopes R, Bell SJ, McKay TR, Fernandez M, Lockley M, Wheatley SP, Lemoine NR
Exp. Cell Res., 2005-01-01;302(1):69-82.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human cIAP-2/HIAP-1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: