HCoV-NL63 Human Coronavirus Spike RBD Antibody
HCoV-NL63 Human Coronavirus Spike RBD Antibody Summary
Ala475-Asp634
Accession # YP_003767.1
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
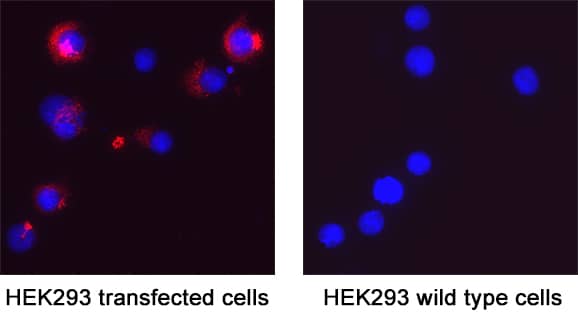 View Larger
View Larger
Spike RBD in HEK293 Human Cell Line Transfected with HCoV-NL63. Spike RBD was detected in immersion fixed HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with HCoV-NL63 (positive staining) and HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line (non-transfected, negative staining) using Rabbit Anti-HCoV-NL63 Human Coronavirus Spike RBD Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB11023) at 3 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL004) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. Staining was performed using our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Spike RBD
HCoV-NL63, a virus first isolated from a child suffering from respiratory disease in 2003, belongs to a family of viruses known as coronaviruses that are commonly comprised of a large plus-strand RNA genome and four structural proteins: Spike protein (S), Envelope protein (E), Membrane protein (M), and Nucleocapsid protein (N) (1, 2). Other well-known human coronaviruses include three viruses that cause relatively mild respiratory disease: HCoV-229E, HCoV-HKU1 and HCov-OC43, plus three viruses that cause the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV), the Middle East Respirator Syndrome (MERS-CoV), and the global pandemic Covid-19 (SARS-CoV2). HCov-NL63 Spike Protein (S Protein) is a glycoprotein that mediates membrane fusion and viral entry. As with most coronaviruses, proteolytic cleavage of the S protein generates two distinct peptides, S1 and S2 subunits. The S1 subunit is focused on attachment of the protein to the host receptor while the S2 subunit is involved with cell fusion. Although HCoV-NL63 S protein shares high homology (56%) with HCoV-229E, it does not employ CD13 (aminopeptidase N) as the receptor like HCoV-229E. Instead, HCoV-NL63 engages Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE-2), the same receptor as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV2, for cellular entry and replication (3). The receptor binding domain (RBD) of HCoV-NL63 is located at C-terminal region of S1 subunit (4, 5). Although NL63-CoV and SARS-CoV do not share structural homology in RBD region, they bind an overlapping region of ACE-2 (6, 7).
- Van der Hoek, L. et al. (2004) Nat. Med. 10:368.
- Fouchier, R.M. et al. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101:6212.
- Hofmann, H. et al. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102:7988.
- Hofmann, H. et al. (2006) J. Virol. 80:8639.
- Lin, H. et al. (2008) J. Gen. Virol. 89:1015.
- Li, W. et al. (2007) Virology 367:367.
- Wu, K. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106:19970.
Product Datasheets
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for HCoV-NL63 Human Coronavirus Spike RBD Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review HCoV-NL63 Human Coronavirus Spike RBD Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used HCoV-NL63 Human Coronavirus Spike RBD Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
