GDP-Cy3-Fucose Summary
Key Benefits
Learn more about Fluorescent Glycan Labeling and Detection

|
Formula |
C51H79N11O25P2S3 |
|
Molecular Weight |
1404.37 |
|
Formulation |
Lyophilized with Tris, pH 8.0 |
|
Stability & Storage |
Store the unopened product at < -20 °C. Good for 12 months from date of receipt. |
Applications
- Fluorescent labeling with Cy3 of free glycans as well as glycoproteins and glycolipids.
- Fluorescent detection of specific glycan epitopes on glycoproteins as well as cell surface.
- Quantitation of fucosylation level of specific glycans.
- Together with CMP-Cy5-Sialic Acid, allows dual labeling and detection of sialoglycans.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Excitation at 550 nm and emission at 570 nm, exhibits green fluorescent light under microscope.
- The fluorescent dye is conjugated to the C6 position of the fucose.
- Can be directly introduced into glycoproteins and glycolipids via various fucosyltransferases.
- Can be introduced to live cells for glycan imaging.
- Have minimum side-effect on target molecules.
- Very convenient and user-friendly.
For Details:
Wu et al., (2019) Glycobiology 29: 750-754.
Wu et al., (2020) Glycobiology 30:454-462.
Wu, ZL. et al., (2020) Glycobiology 30:970.
Related Reagents
Click Chemistry
- CMP-Cy3-Sialic Acid (ES402)
- GDP-Cy5-Fucose (ES301)
- CMP-Cy5-Siaic Acid (ES302)
- GDP-Azido-Fucose (ES101)
- CMP-Azido-Sialic Acid (ES102)
- UDP-Azido-GalNAc (ES103)
- UDP-Azido-GlcNAc (ES104)
- CMP-C9-Biotin-Sialic Acid (ES201)
Enzymes and detection reagents
Data Examples
|
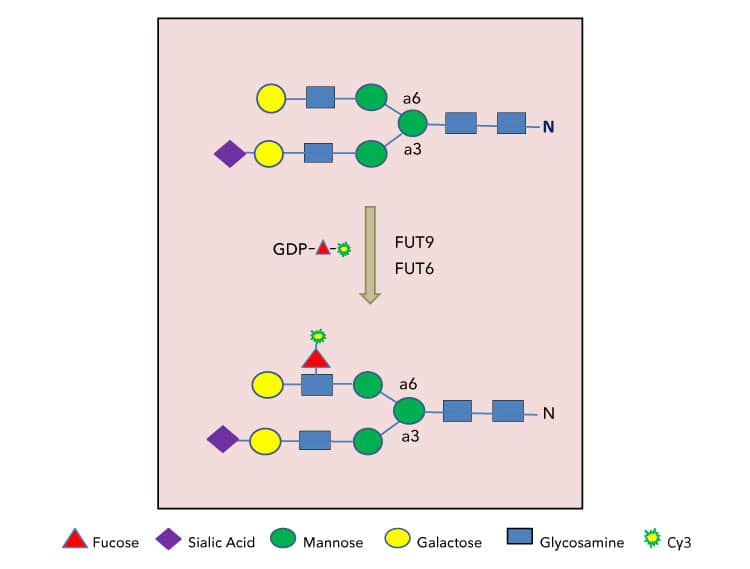
Strategies for substrate glycan labeling with GDP-Cy3-Fucose. Only terminal lactosamine structure on N-glycans are depicted here for FUT6 or FUT9 labeling. Substrate glycans for other fucosyltransferases can be labeled under the same principle. |
|
Labeling bovine fetuin (Fet) using GDP-Cy3-Fucose. Bovine fetuin was purified from crude fetuin by gel filtration. Samples of fetuin were labeled with Recombinant Human Fucosyltransferase 9/FUT9 Protein (Catalog # 9347-GT). In control lanes, no fetuin was present, revealing the self-labeling of FUT9 itself. Each lane contained 1 μg of fetuin except the controls. Samples were not labeled in the absence of neuraminidase but labeled strongly on asialo-fetuin (aFet) (generated by addition of Recombinant C. perfringens Neuraminidase Protein (Catalog # 5080-NM), Samples were separated on 4-20% gradient SDS-PAGE and imaged with TCE staining (top panel) and a fluorescent imager (lower panel). The bands of fetuin corresponding to the neuraminidase treated samples appear to be darker than those of without neuraminidase treatment because of the incorporation of Cy3. |
|
Cellular glycan imaging with GDP-Cy3-Fucose. HeLa cells were stained by incorporation GDP-Cy3-Fucose (Catalog # ES401) by Recombinant Human Fucosyltransferase 9/FUT9 Protein (Catalog # 9347-GT) (green). Hela cells on a 96 well plate were briefly treated with Recombinant C. perfringens Neuraminidase Protein (Catalog # 5080-NM) to remove preexisting sialic acids. The treated cells were then labeled by FUT9 in the presence of GDP-Cy3-Fucose for 30 minutes. After the labeling, the solution was quickly removed by aspiration and washing two times with PBS. Afterwards, the cells were fixed and stained with DAPI (red) in the presence of 0.5% Triton X 100 to reveal the cell nuclei. These images show that N-glycans on HeLa cells display differential expression. For details on cell imaging with fluorophore-conjugated sugars, please refer to Wu. L. et al., (2020) Glycobiology 30:454-462. |
Table 1. Guideline for using CMP-Cy5-Sialic Acid for sialoglycan labeling and detection
| Sialyltransferase | Catalog # | Substrate | GDP-Cy3-Fucose Tolerance |
| FUT1 | Terminal Gal in H antigen | Not determined | |
| FUT2 | 7770-GT | Terminal Gal in H antigen | yes |
| FUT3 | 4950-GT | GlcNAc in type 1 glycan chain | yes |
| FUT4 | GlcNAc in terminal lactosamine | yes | |
| FUT5 | 4949-GT | GlcNAc in terminal lactosamine | yes |
| FUT6 | GlcNAc in terminal lactosamine | yes | |
| FUT7 | 6409-GT | GlcNAc in sialylated lactosamine | yes |
| FUT8 | 5768-GT | Core GlcNAc in N-glycans | yes |
| FUT9 | 9347-GT | GlcNAc in non-sialylated lactosamine | yes |
| FUT10 | Unknown | unknown | |
| FUT11 | 5964-GT | Unknown | unknown |
| POFUT1 | 7409-GT | Notch receptor | Not determined |
Specifications
Product Datasheets
Assay Procedure
Sample Protocol for Direct Fluorescent Glycan Labeling with GDP-Cy3-Fucose
Protocols are guidelines. Parameters need to be optimized by end users.
Materials
- Assay Buffer: 25 mM Tris, 10 mM MnCl2, pH 7.5
- Sample protein
- Fucosyltransferases such as rhFUT9 (Catalog # 9347-GT)
- GDP-Cy3-Fucose (Catalog # ES401)
- Protein sample loading dye
- SDS-PAGE and Western Blot reagents or equivalent
- Fluorescent imager in a green fluorescent channel
Assay Procedure
- Prepare a reaction mixture by combining 0.1 to 5 µg of a sample protein, 0.2 nmol GDP-Cy3-Fucose, 0.5 µg of a Fucosyltransferase such as FUT9, add Assay Buffer to the final volume to 30 µL.
- Prepare a negative control by repeating above but omitting the fucosyltransferases.
- Incubate all the reactions and controls at 37 °C for 60 minutes.
- Stop the reactions and controls by adding appropriate volume of protein sample loading dye to each reaction.
- Separate the reactions and controls by SDS-PAGE.
- Image the gel with a fluorescent imager in a green fluorescent channel.
- Image the gel with trichloroethanol (TCE) imaging (if TCE is incorporated into the gel) or any other regular protein gel imaging method such as Coomassie® blue staining or silver staining.
Final Assay Conditions Per Reaction
- Sample protein: 0.1 to 5 µg
- GDP-Cy3-Fucose: 0.2 nmol
- Fucosyltransferase: 0.5 µg
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Small Molecule FAQsReviews for GDP-Cy3-Fucose
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review GDP-Cy3-Fucose and earn rewards!
Have you used GDP-Cy3-Fucose?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image